Understand that the first chordates, from which vertebrates later evolved, arose in the Cambrian Explosion, ~ 500 MYA.
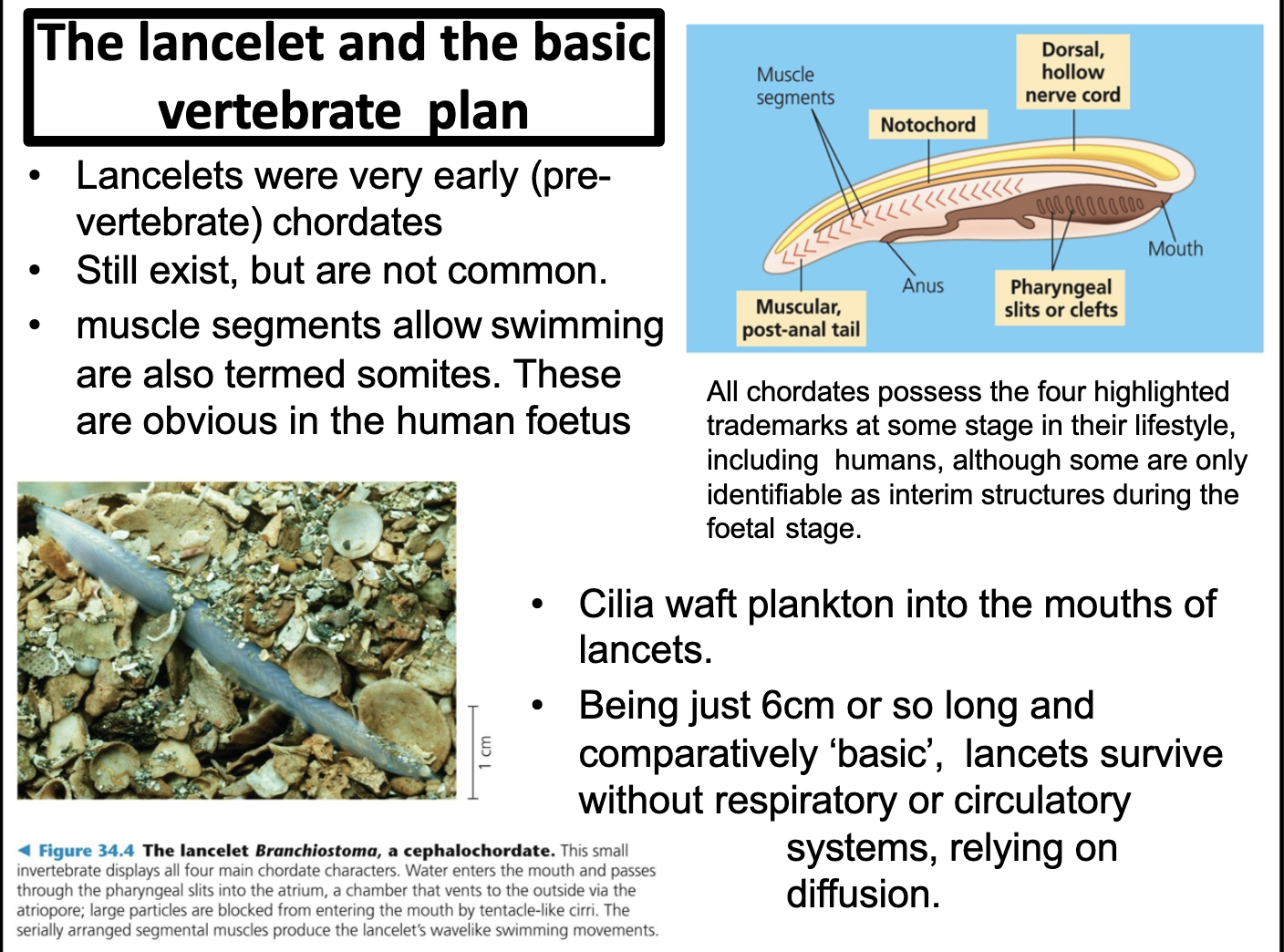
1) lancelet -> with notochord, tail, pharyngeal slits and hollow nerve cord
2) hag fish -> having head (ear, eyes, nasal opening and brain) BUT now jaws and vertebrate
3) lampreys -> earliest vertebrate, it has no jaws
With jaws -> sharks and rays
4) tiktaalik -> fish and amphibian intermediate
-> amphibian
-> reptile
-> mammals
Be able to describe, and distinguish between, the body structures of the fish like pre-vertebrates, the lancets, hagfish and lampreys, with an emphasis on the how the basic vertebrate body plan was developed.
1) Lancelet
-Has notochord
-dorsal hollow nerve cord
-tail
-pharyngeal slit ( becomes tp
2) Hag fish
-Has brain (eyes, ears, and nasal opening)
-protected by a skull of cartilage
-tooth like formation but no jaws
3) Lampreys
-1,2 have no vertebrate BUT THIS HAS ! (earliest vertebrate, but it hasn't mineralised yet)
-exoparasites
-no jaws
-rasping tongue to gain nutrients
Understand that the earliest vertebrate skeletons were composed of cartilage, as seen today in sharks, that all foetal skeletons retain this feature, but that cartilage is largely replaced by bone in other adult vertebrates.
Understand the significance of the fossil Tiktaalik to the evolution of terrestrial vertebrates.
Tiktaalik has both fish and tetrapods' characteristics. The characteristic of fish that they have are gills, scales, fins and lungs. They have neck and ribs, fin skeleton, eyes on top of the skull, and one single proximal limb bone, and two distal bones, which is a characteristic of tetrapods. As their limb bone could give rise to limbs, which for the next organism to move on the ground, terrestrial vertebrates could evolute from there.
Be able to define those characteristics common to all mammals, to list the 3 major groups of mammals, and to make sense of the statement “that current mammals, including humans would not be here today but for the impact of an asteroid”.
Mammals characteristic 1) produce milk 2) have hair 3) warm blooded
Humman, mammals evoluted from the chordate 500MYA , after the Cambrian explosion occured.
Chordate refers to the animals with notochord, which is a precursor of the vertebrate. The first animal having this feature is lancelet. It has tail, pharygngeal slits, notohord, and dorsal hollow nerve cord.
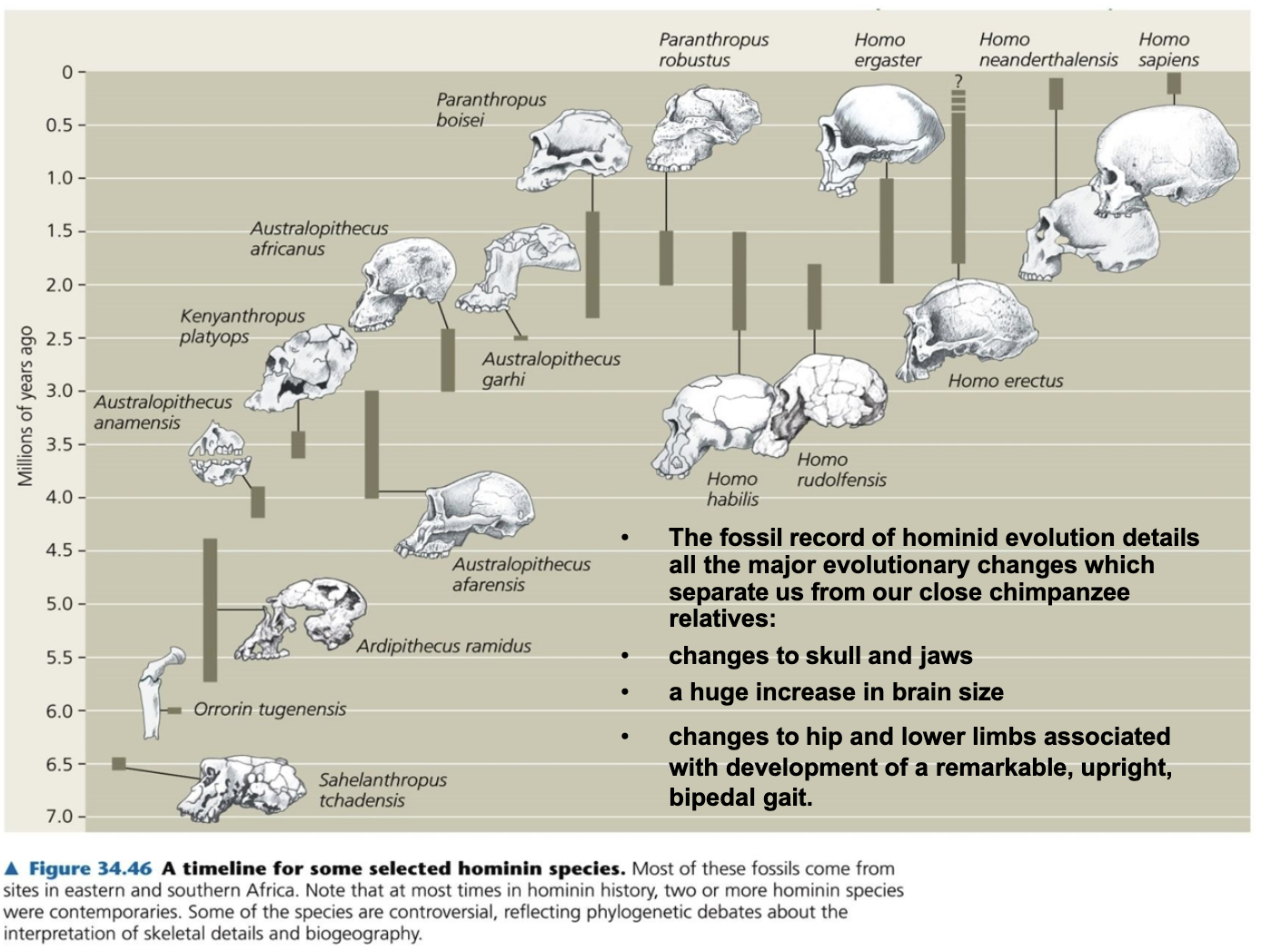
Be able to list time lines for when the first primates evolved, when the first apes evolved and when hominids diverged from the chimpanzee family.
First primates arose about 50 MYA. Old World and New World monkey evolved seperately for the last 35 MYA. Apes arouse about 22MYA .
6-8MYA, Hominid (Human) seperated from the closet relatives, which is chimpanzees
To be able to briefly discuss hominid evolution, and the success or otherwise of other hominid species and whether modern humans co- existed with other Homo species.
-Primates arouse in 50MYA
-Old world monkey and New world monkey diverged 35 MYA
-22MYA apes arouse
-Hominid diverged from the ancester which we share with chimpanzee 6-8MYA
-Homosapiens is the only still existing hominids
-The last Neanderthals (30,000YA) and H.fluresiensis (10,000YA) were the most recent huminids that existed.
H. fluresiensis possibly co-existed with humans until ~10,000 YA
-Early hominids migrated out of Africa at least 200,000 YA
-Modern hymans did the same in a number of migrations, perhaps 80,000 YA
-Eventually occupied most all the landmasses of the earth
-Migration via then existing land bridges allowed humans to reach North america about 30,000 YA
-In humans the degree of sexual dimorphism is reduced
-Indicates that parenting became more of a shared task
-In contrast to chimpanzees, human babies are less developed, requiring more care and for a far longer period
-Human babies are born with large brains and an ability to think consciously
Changes between chaimpanzees and humans were
-Skull and jaw conformational change
-Brain size
-changes to lower limb and hip (to develop upright trait)
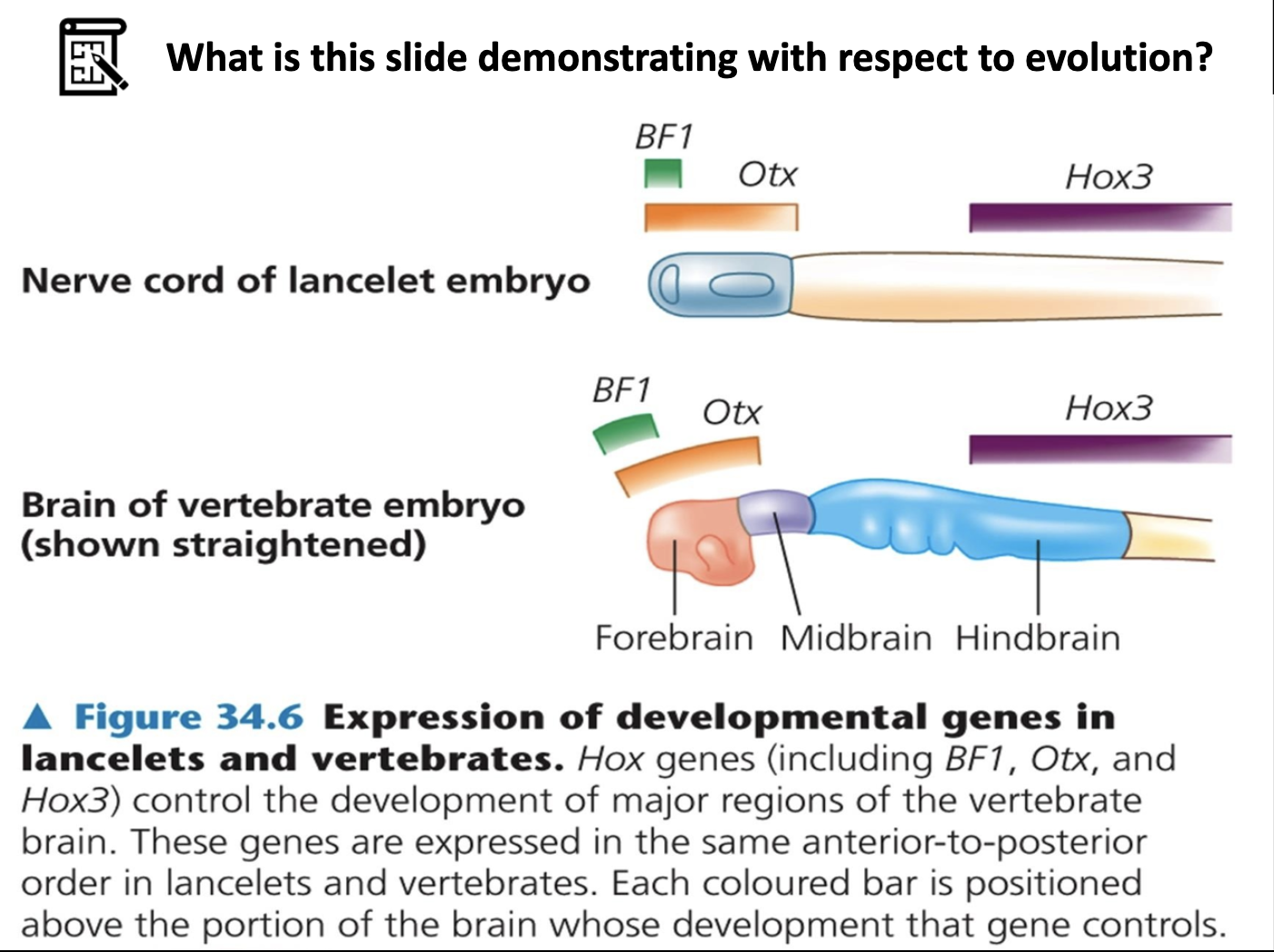
Understand how the process known as heterochrony explains differences in skull development from child to adult between chimpanzees and humans, and how this reflects changes in gene expression, not necessarily gene mutation.
It explains that gene it self hasn't changed that much from chimpanzee's ancestor to human but the timing of gene expression, cession or inhibition of expression affects to the physical appearance between chimpanzees and human. Paedomorphosis shows that the of appearance of adult human skull is similar to the foetal of ancestor, which is baby chimpanzee.
To describe those vertebrate precursor structures visible in the human foetus that are not present in adult humans.
There are vestigial evidences that appear in foetus phases that resembles to our ancestor. One is tail and the other one is pharyngeal pouches
Be able to briefly present the evidence that an increase in numbers of an amylase gene is associated with dietary intake of carbohydrates.
People who had lived in agricultural society and sourced starch rich food for their diet had more AMY1 enzymes than people from hunter-gatherers society. As they had to hydrolyse more starch, they needed more amylase which is an enzyme responsible for digestion for starchy food.
It indicates that diet affects to the human gene expression to the AMY enzyme
Be able to discuss the statement: ‘Evolution cannot furnish perfect organisms”.
Evolution doesn't make the perfect organism
Evoution predominantly occured by natural selection, and it is affected by environmental changes.
Depending on the changes, it selects, favors the between the EXISTING individuals from the population. It doesn't create the best suit individual.
Be able to discuss the statement: “Evolution is not goal orientated”.

PPT


EARLY VERTEBRATE EVOLUTION

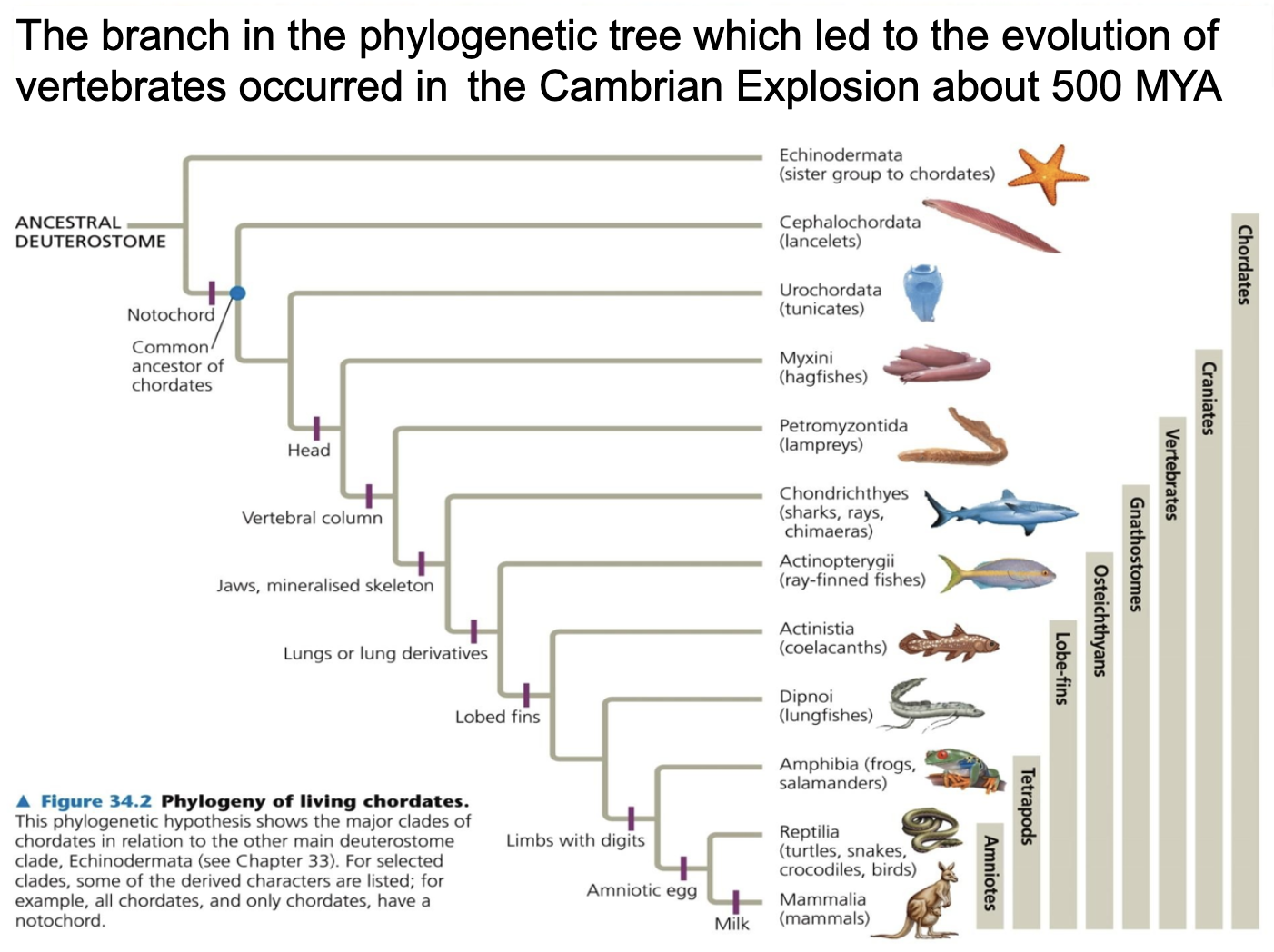





Echinodermata (sister group to chordates)
Cephalochordata (lancelets)
Urochordata (tunicates)
-> HEADS
Myxini (hagfishes)
-> VERTEBRAL COLUMN
Petromyzontida (lampreys)
-> JAWS, MINERALISED SKELETON
Chondrichthyes (sharks, rays, chimaeras)
-> LUNGS OR LUNGS DERIVATIVES
Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes)
-> LOBED FINS
Actinistia (coelacanths)
Dipnoi (lungfishes)
MOVING ON TO LANDS
Amphibia (frogs, slamanders)
-> LIMBS WITH DIGITS
Reptilia (turtles, snakes, crocodiles, birds)
-> AMNIOTIC EGG
Mammalia (Mammals) MILK
MOVING ONTO LAND


DINOSAURS

MAMMALS


PRIMATES AND EARLY HOMINIDS

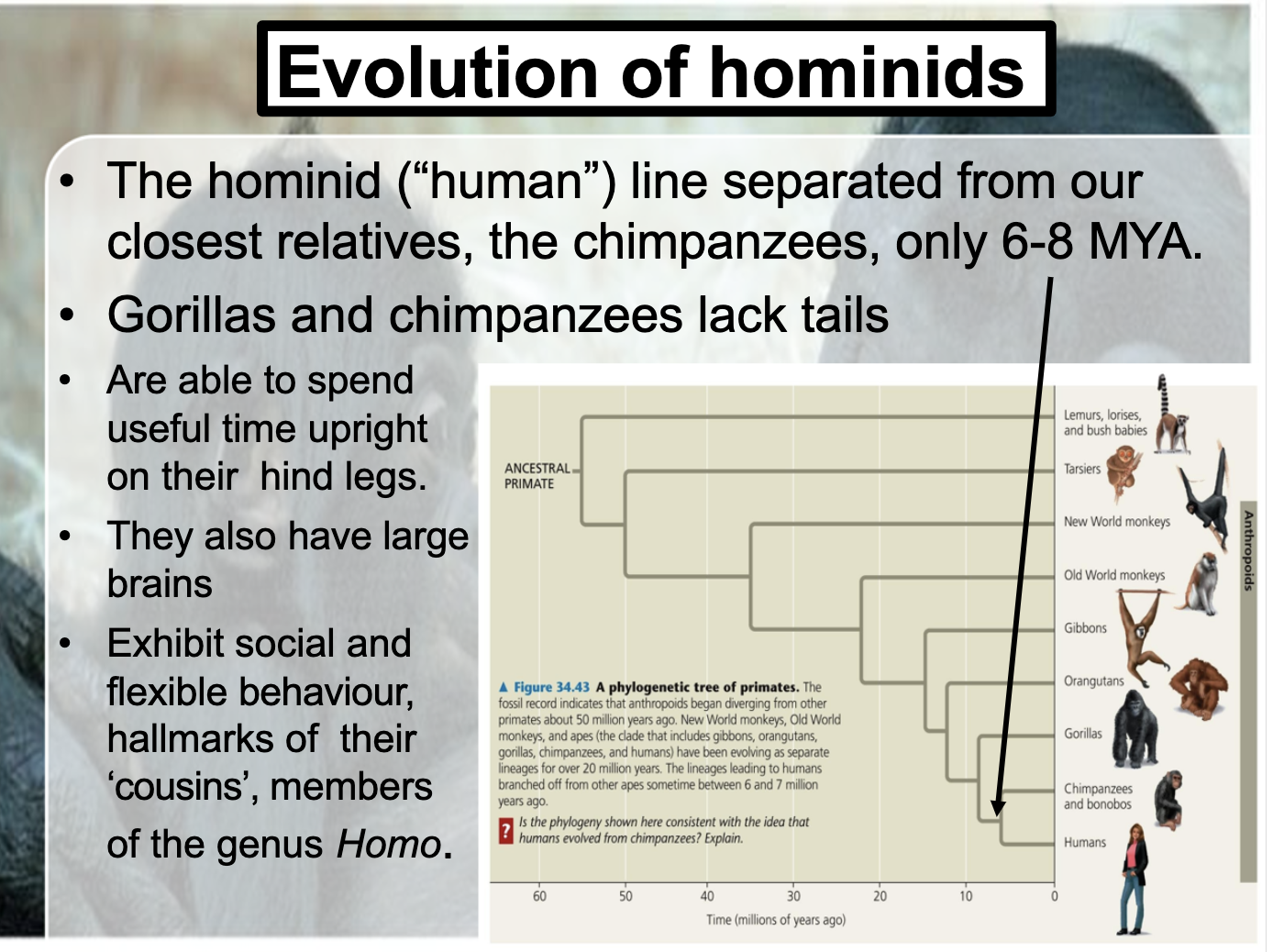
This long thumb and its ability to easily touch the other fingers allow humans to firmly grasp and manipulate objects of many different shapes.




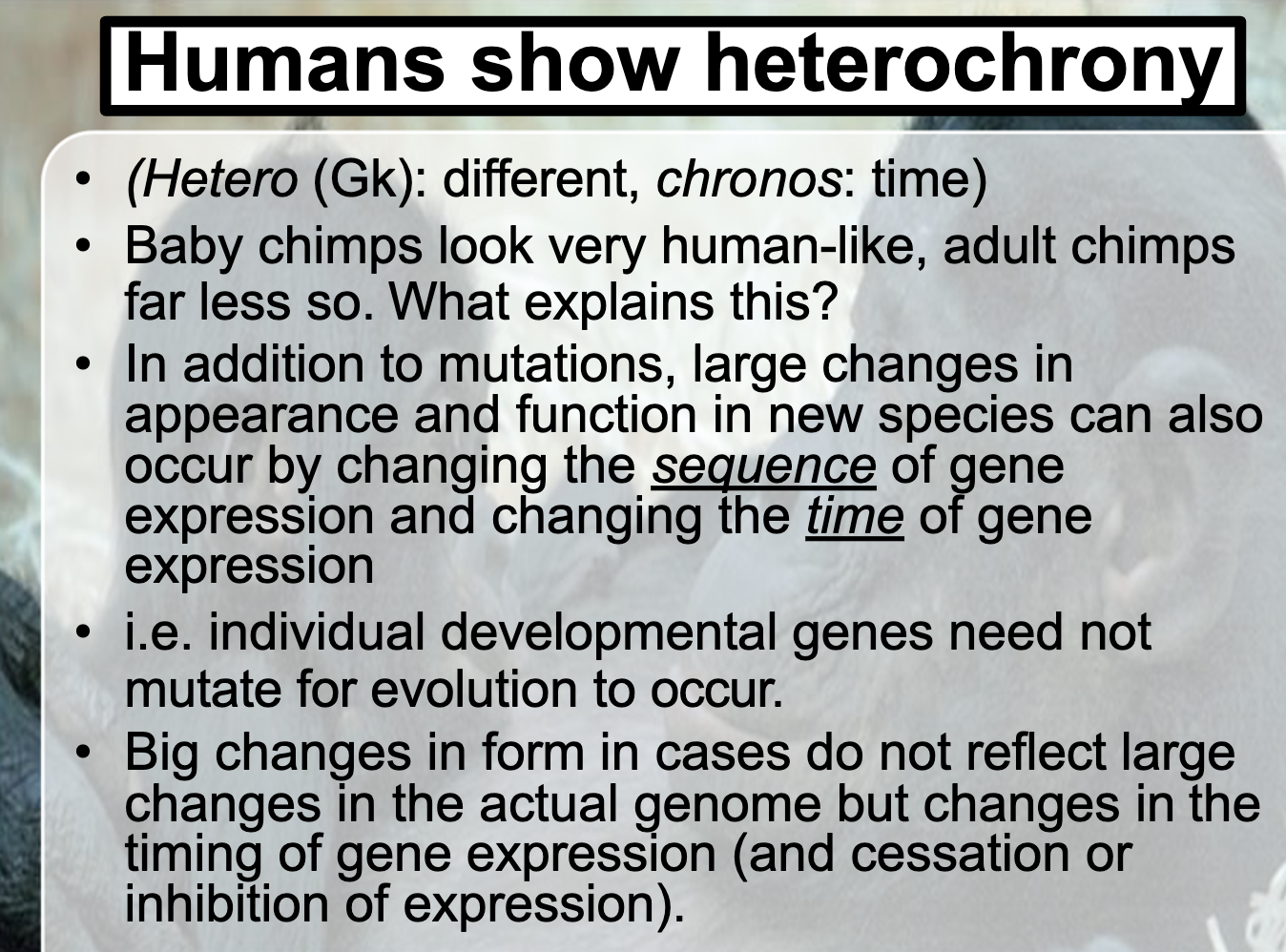

Paedomorphosis refers to the phenomenon that the adult form of desendent resemble to the juvenile appearance of the ancestor.
Heterochrony explains this, as gene it self hasn't changed that much, by changing the sequence of the gene expression and timing of the gene expression, it achieved this.
Not much of a gene mutation (change in genome) is involved here. More important thing here is timing and sequence of gene expression
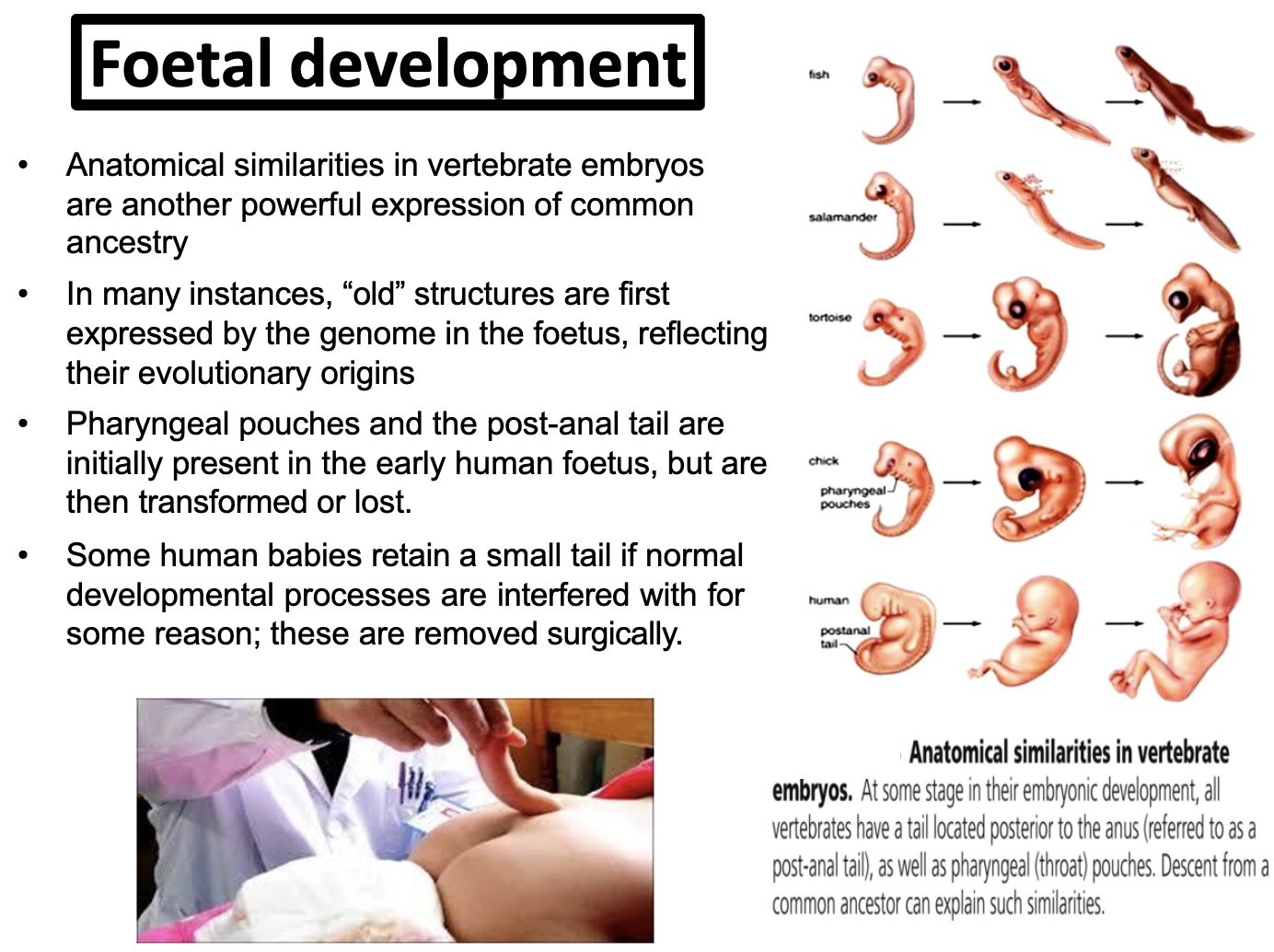

EXAMPLE OF HUMAN EVOLUTION







Self Paced Quiz


-Primates arouse in 50MYA
-Old world monkey and New world monkey diverged into for 35 MYA
-20MYA, apes emerged.
-About 6-8 MYA, huminid branced from the ancestor which we share with chimpansees.
-Before the Homo sapiens (which is the only form still exists), we had 20 different hominids.
-The last one according to the record was Neanderthals in Europe (40,000YA) and Homo floresiensis (10,000YA)


Vestigial structure is the feature still remain in the individual which was significant for their ancestors but not them
-Some snakes retain vestiges of the pelvic and leg bones of their walking reptilian ancestors
-Blind cave fish have eye remnants buried under their scale
-Rarely, humans are born with a tail
-Humans have the genes for tail formation. Not normally expressend in humans.


During the foetal stage, we can see the tail and pharyngeal pouches.
Both two features were all shown in vertebrate evolution (chordate).
The tail was found since the lancelet, and the pharyngeal pouches becomes in gills in fish and ear bones to humans and other mammals)

4. DNA sequences in many human genes are very similar to the sequences of correspronding genes in chimpanzees. The most likely explanation of this result is that humans and chimpanzees share a relatively recent common ancestor


5.
1) Natural selection doesn’t CREATE perfectly fit organism, It just SELECT/ FAVOR the individual who is more fitted to the environment within the variation existing in the population group.
2) Natural selection is not always the best option- As it changes/ alters some features of pre-existing organisms, it can be developed but not can fully fix all the demands.
3) Natural selection is highly dependent on the environmental changes and it is not always the same. As environment changes randomly the fittest individual favoured by the natural is not always the fittest. Also, there is always compromise. For an example, as human become erectable (stand upright for their entire life, emptying nasal sinus and child birth became much harder)


6.
Tiktaalik is an animal with both fish and tetrapods characteristic.
For a fish characteristic, it has gills, fins, scales and lungs
For a tetrapods characteristic, it has head, neck and ribs/ fin skeleton/ flat skull eyes attached on the top, and single proximal and double distal bones.
It arouse the emergence of amphibians which has watery origins (breed in the water and having tadpole phase and gills but also has the characteristic of tetrapods) but the first vertebrates to come out onto land walking on the land
It is approxiamtely ~375 million years old.


7.
Since the Cambrian Explosion in 500MYA, chordorate (which refers to an animals having notochord) underwent to the evolution to the mammals which also include human.
1) First by having notochord (which is a precursor of the vertebrate), => lancelet
2) then having head (brain, eyes and ears) => hag fish
3)vertebrae (vertebral column), => lampreys
4)jaws and mineralised skeleton, => sharks, rays (but some still has cartilaginous skeleton)
5)lobed fins, => (tiktaalik is the aniaml having fish components (gills, scales, lungs, fins) and tetrapods component (single proximal, two distal bones, head and neck and ribs, fin skeleton, flat skull eyes on top) and it leads to amphibian emergence (which breeds in water, having tadpole phase but having tetrapods appearance)
6) limbs and four digits,
7) and enable to breed amniotic eggs,
8) and producing milk => mammals
-> Chordate had unerwent the evolution and differentiated into different organisms.


8.
Paedomorphosis explains the appearance of a foetal phase/ juvenile of the ancestor passes down, and it shown in the adult phase of the descendent.
Amohibian axolotl is an example of this, even if it has fully grown up, it contains larval (tadpole) characteristic including tails and gills


9.
People who had lived in agricultural society had high-starch diet, which made them to break dowm more carbohydrates by amylase. AMY1 the amylase gene is more expressed (copied) in their gene based on their diet. On the other hand, people who came from hunter-gatherers society, they had less AMY 1 copies than people who had high starcy diet. AMY1 is a gene for producing Salivary amylase, and it is enzyme for breaking down carbohydrates. As people diet changed to more starcy diet, more copies of AMY1 is produced and it imporved the digestion of starcy foods and buffer the fitness-reducing effects of intestinal disease
'Griffith college Tri1 2023 > 1005 QBT (GnD)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [WEEK11] Evolution of Populations and Speciation (0) | 2023.05.23 |
|---|---|
| [WEEK10] How did life start on Earth? (0) | 2023.05.13 |
| [WEEK10] Charles Darwin and the theory of evolution (0) | 2023.05.13 |
| [WEEK8] Part 3 Developmental Genetics (0) | 2023.04.30 |
| [WEEK6] Part 1 Gene Expression (0) | 2023.04.12 |



