Learning objectives
Know the basic stages of embryonic development in animals, 3 germ layers & their fates.
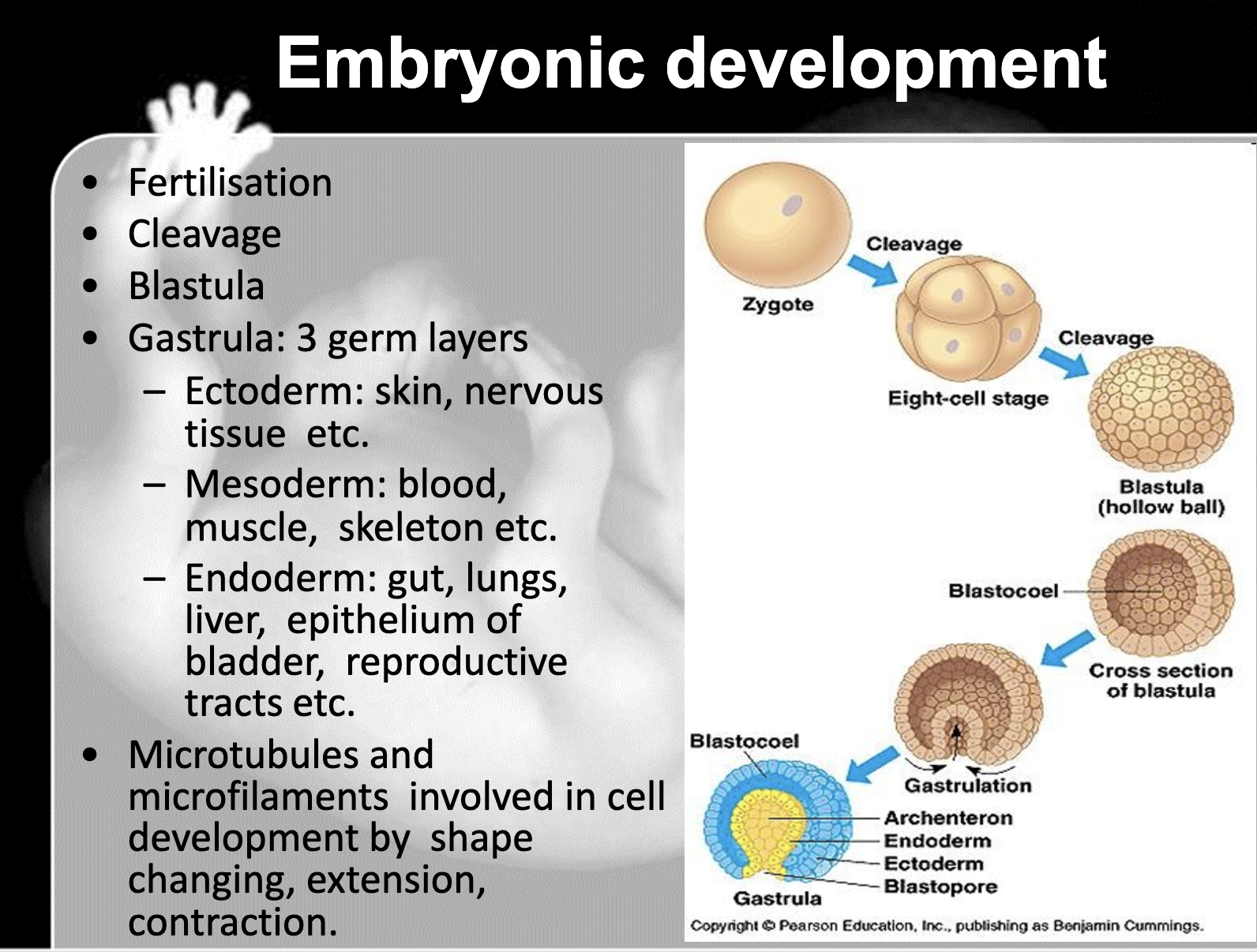
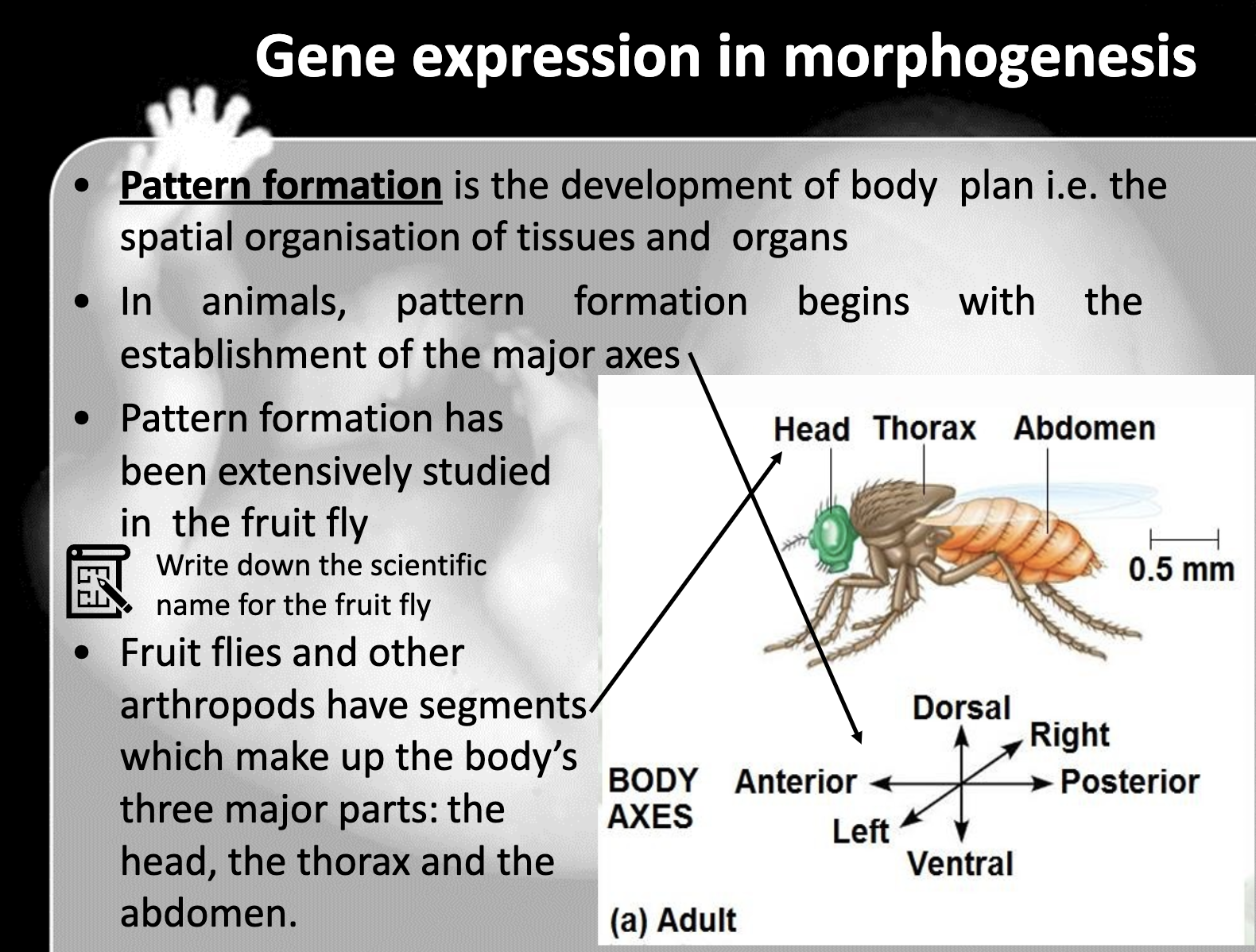
Embryonic development in animals
-fertilisation -> cleavage (mitotic cell division) -> blastula (hollow egg) -> gastrula
gastrulation is supported by microtubules and microfilaments to change shape and extension, contractions
3 germ layers include endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm
Ectoderm -> skin and nervous system
Mesoderm -> development of several cell types such as bone, muscle, and connective tissue
Endoderm -> linings of digestive and respiratory system, and form organs such as the liver and pancreas
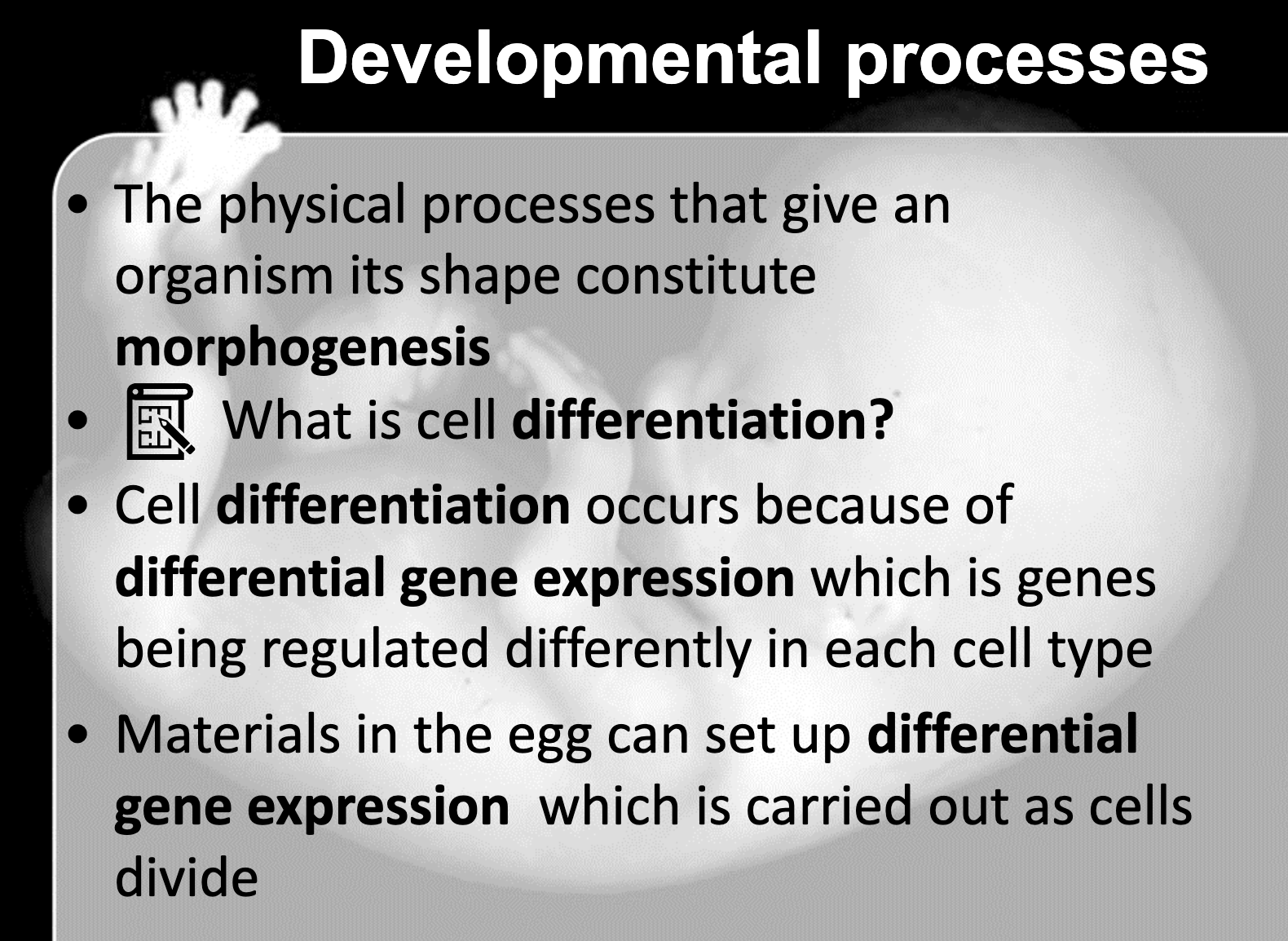
Define morphogenesis and morphogen.
-Morphogenesis is the process of the cell deveolping the physical formation to become an organism
Morphogen is the gradient of the substance which determine the feature and axes,,
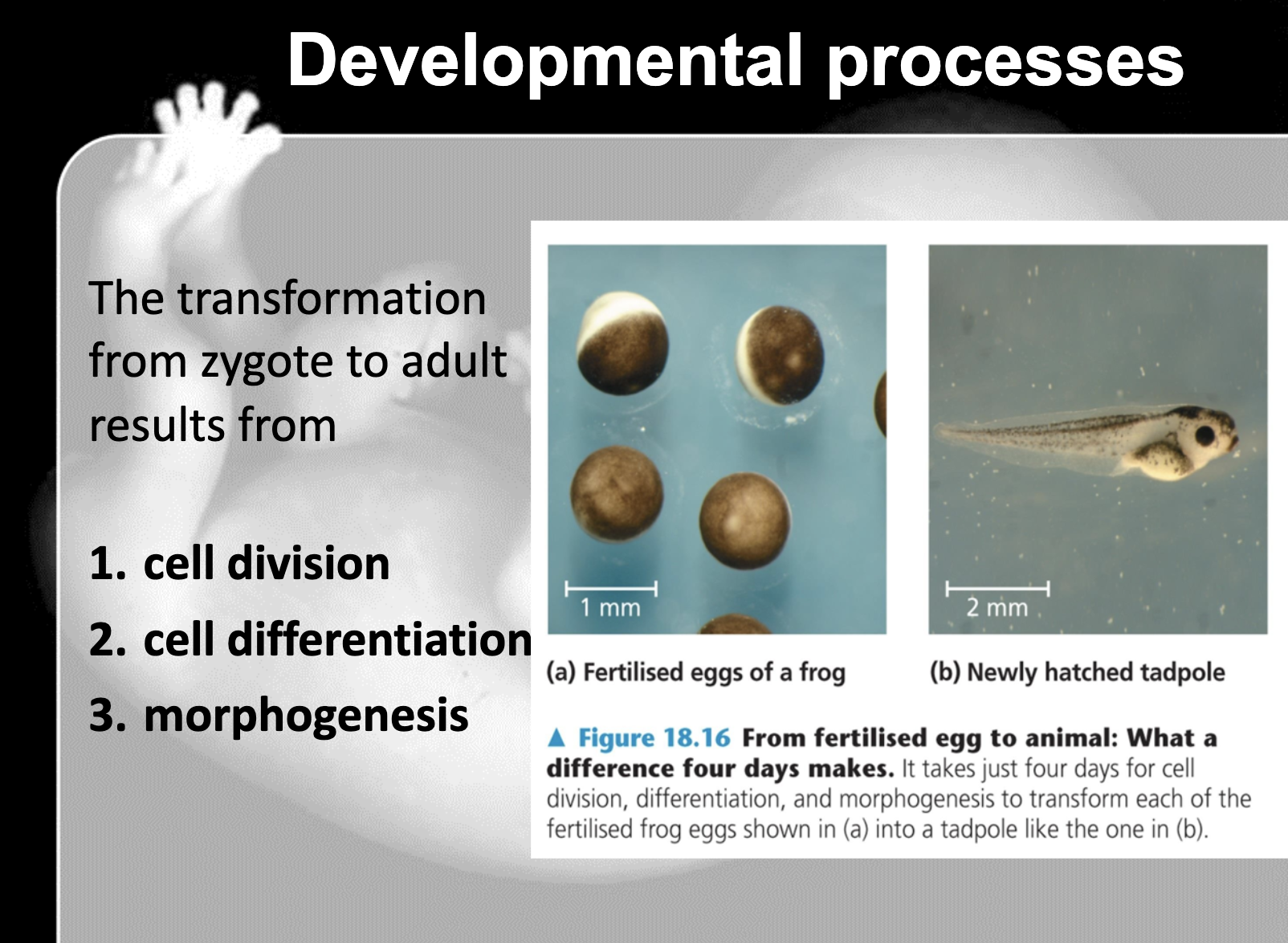
Describe the 3 interrelated processes that transform a zygote to a mature organism.
-Embryonic development includes cell division, cell differentiation and morphogenesis
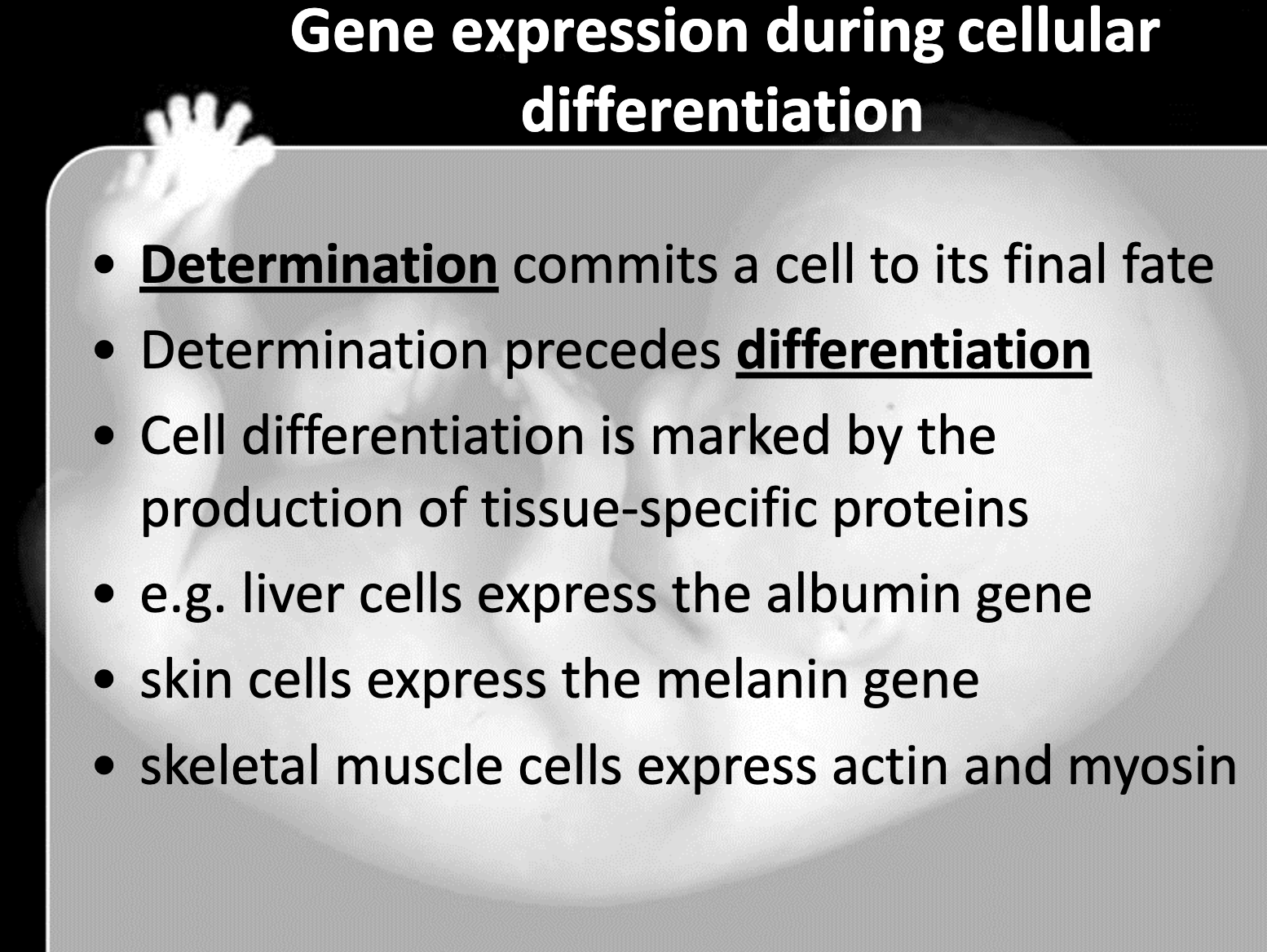
Define determination and differentiation.
-Determination perceds differentiation
It all indicate the cell differentiation of which the cell becomes more specific cell
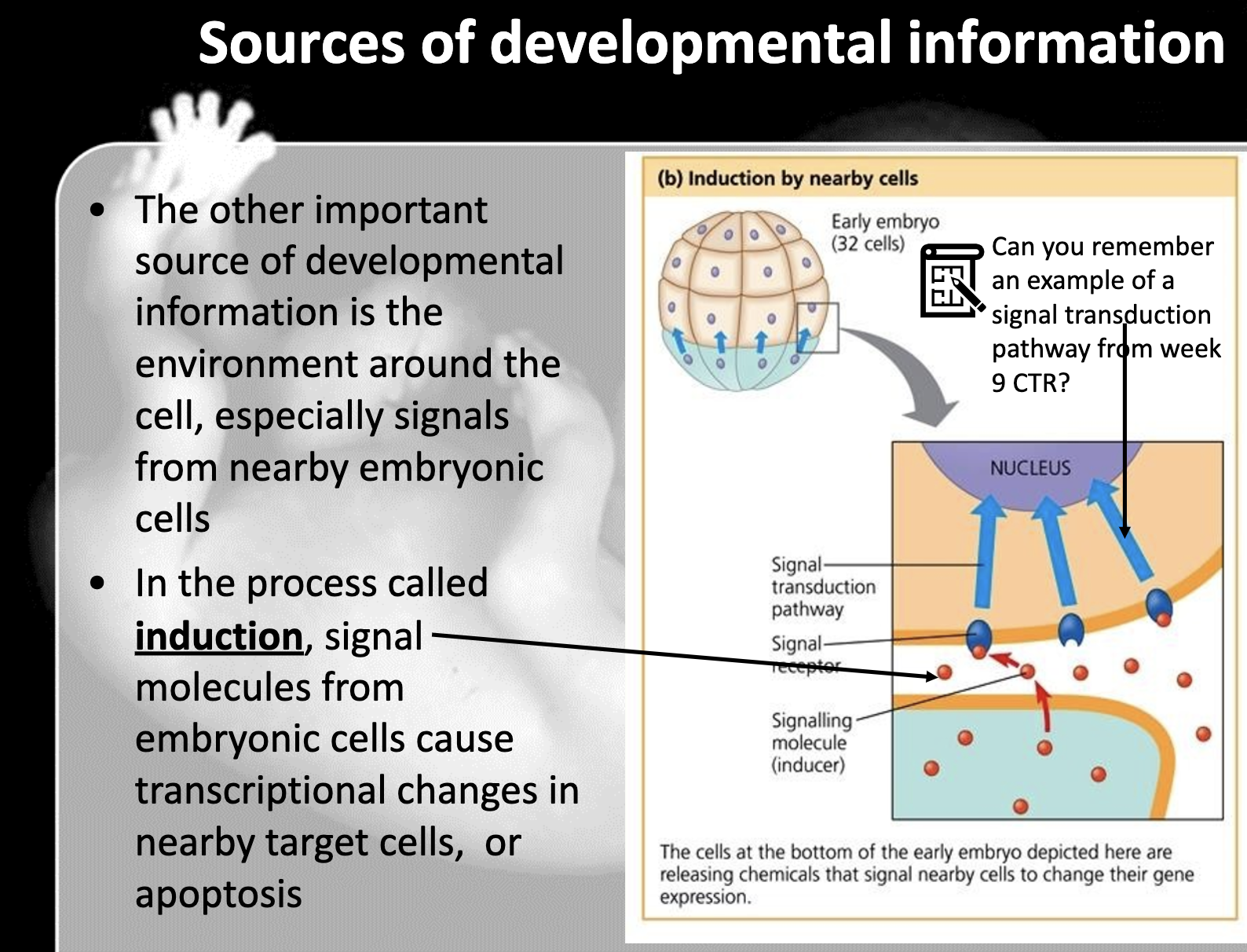
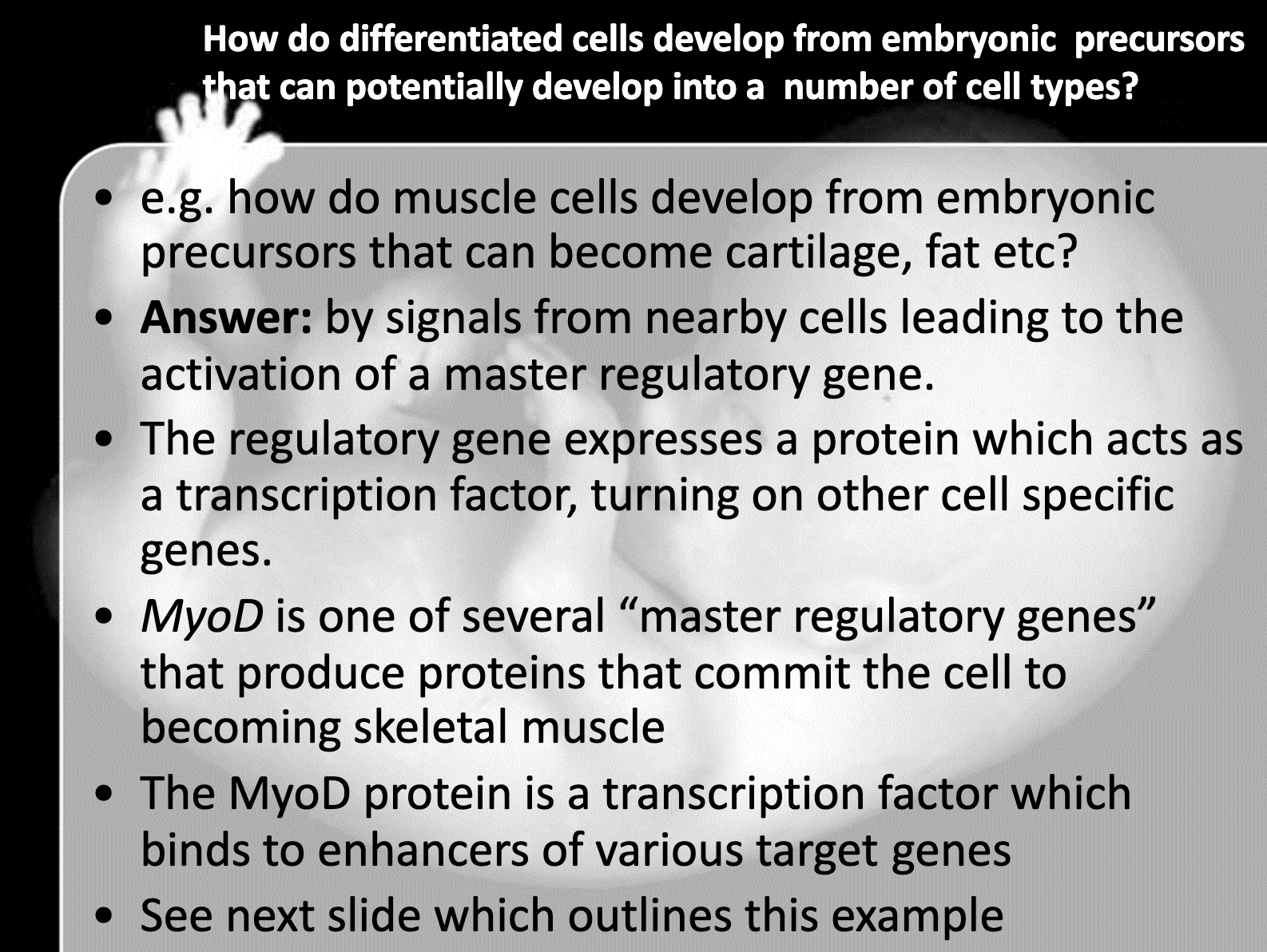
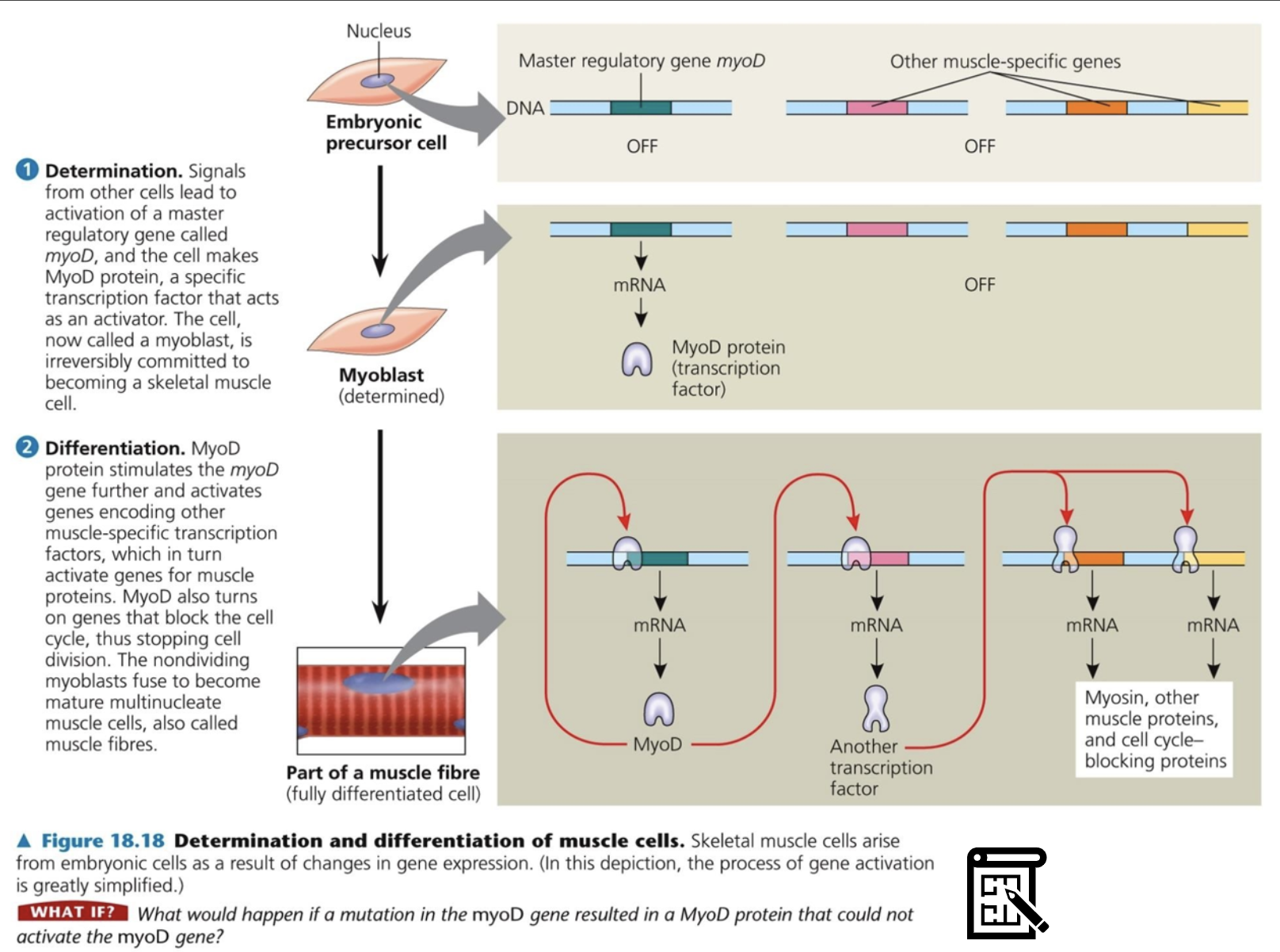
When the major transcription factor is produced by the induction of nearby cell, the cell is irreversibly commited to become the specific cell type. This is called determination
When the transcription factor stimulate other specific gene to produce transcription factors to produce protein that shows the cell's specific function, it is called cell differentiation
(muscle-actin myosin protein, liver-albumin protein, skin-melanin gene)
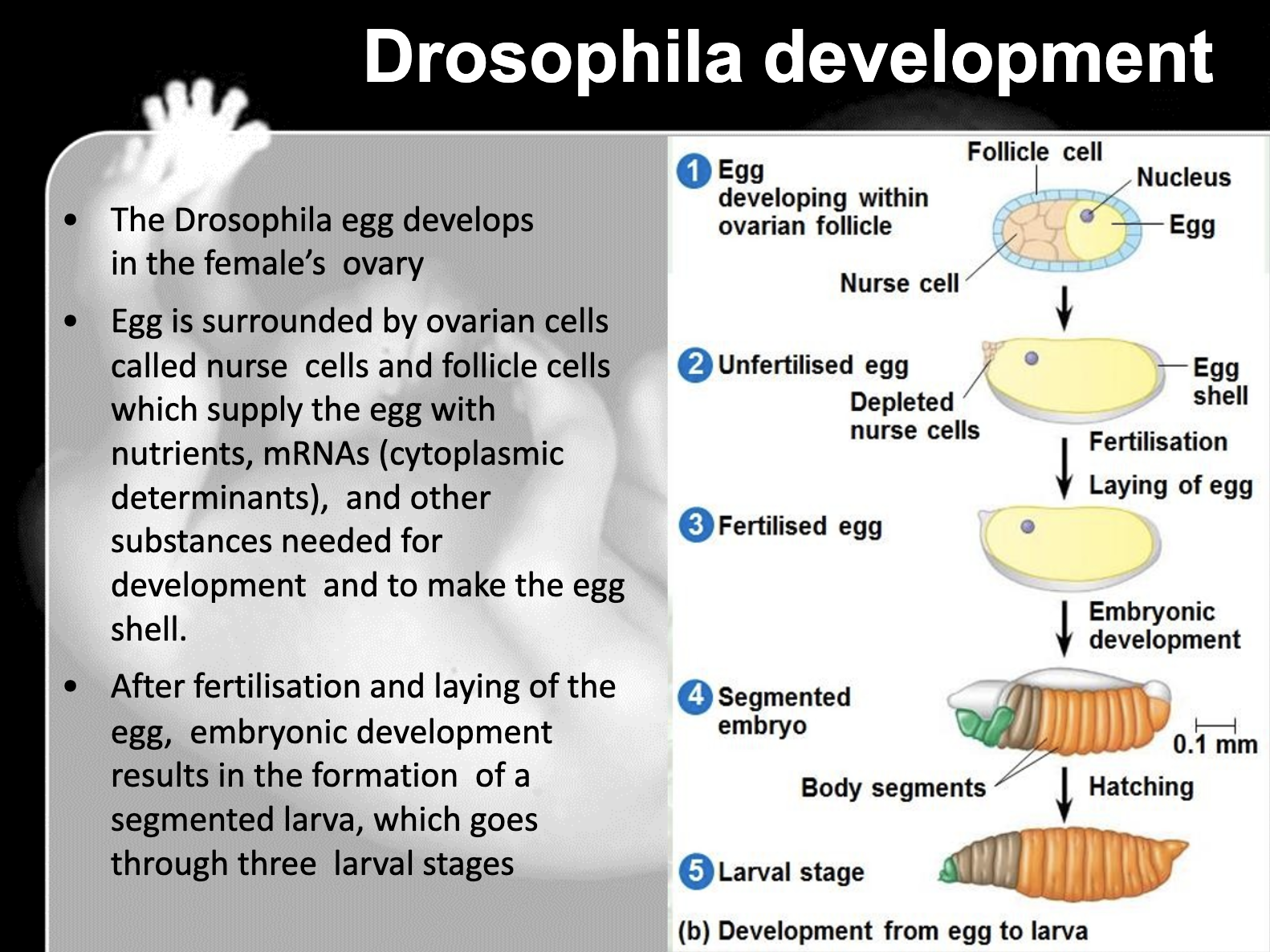
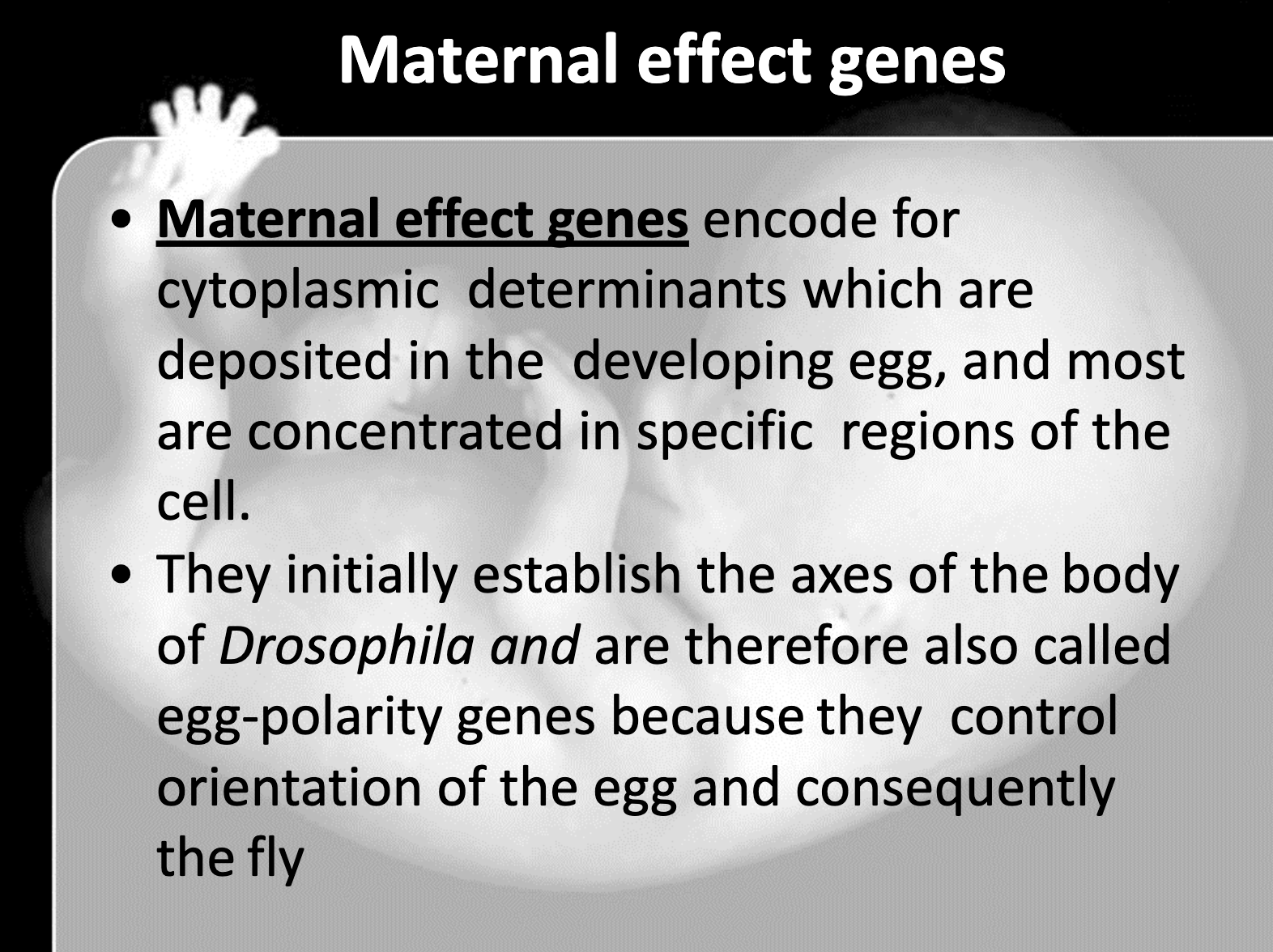
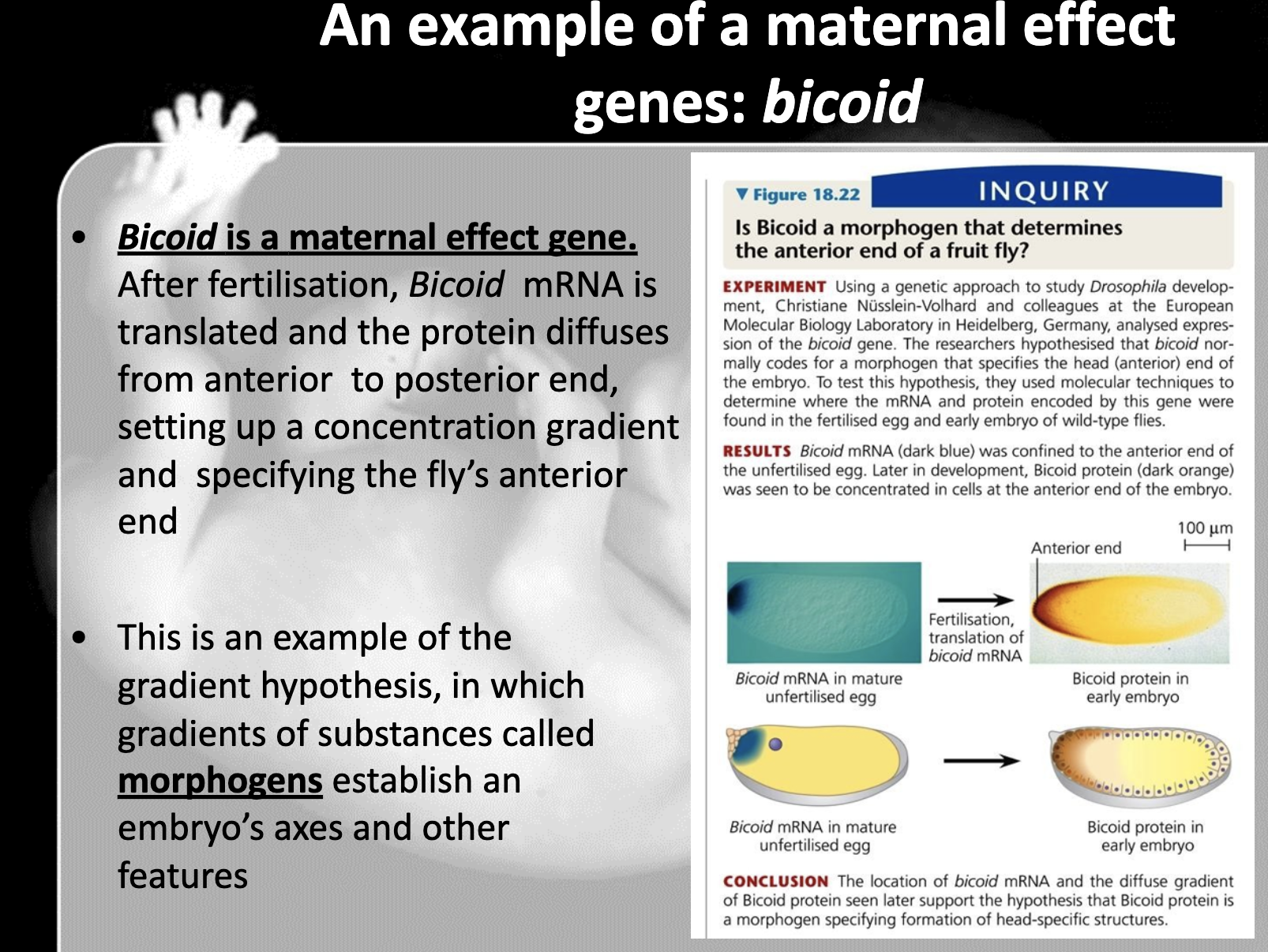
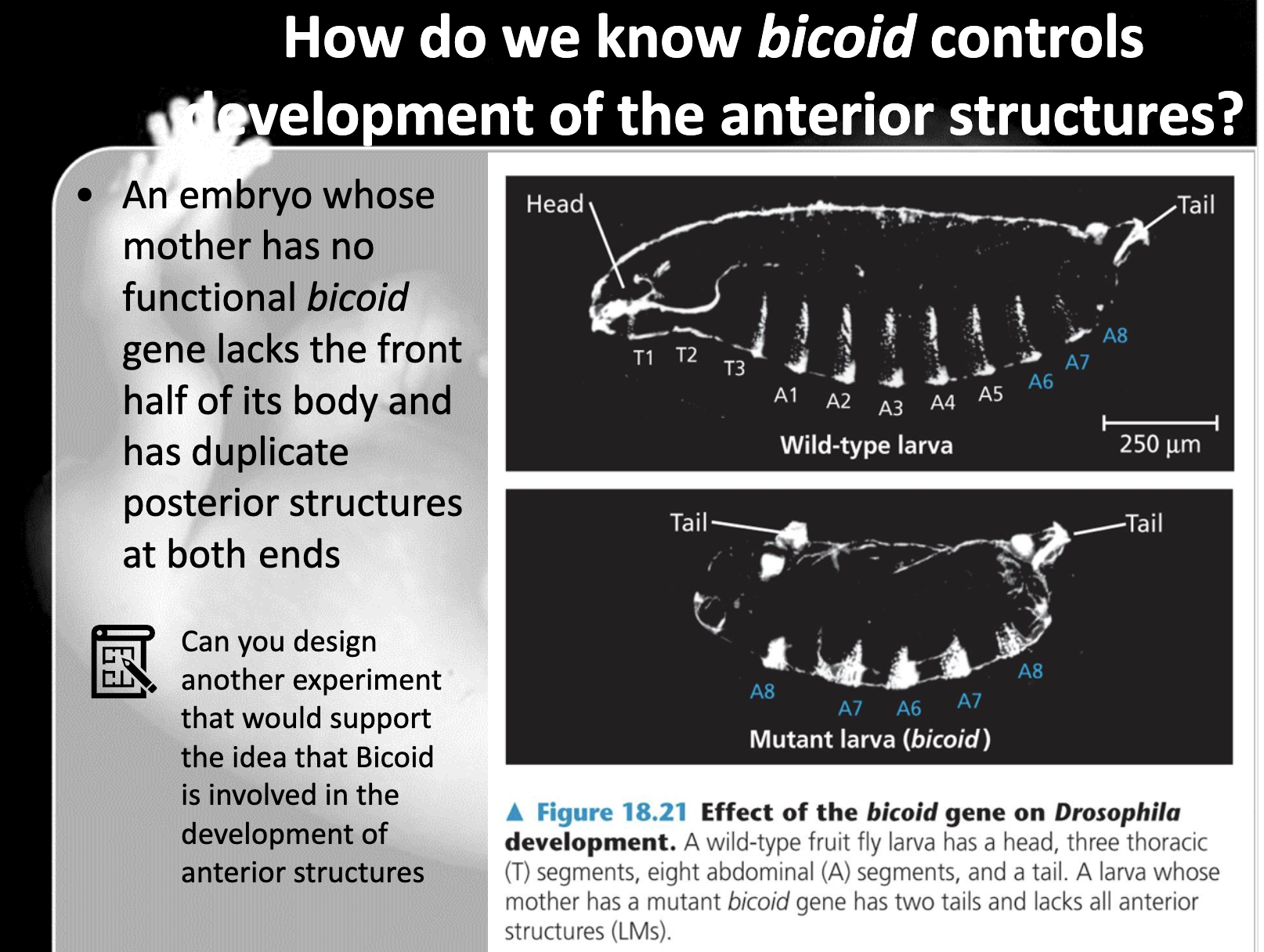
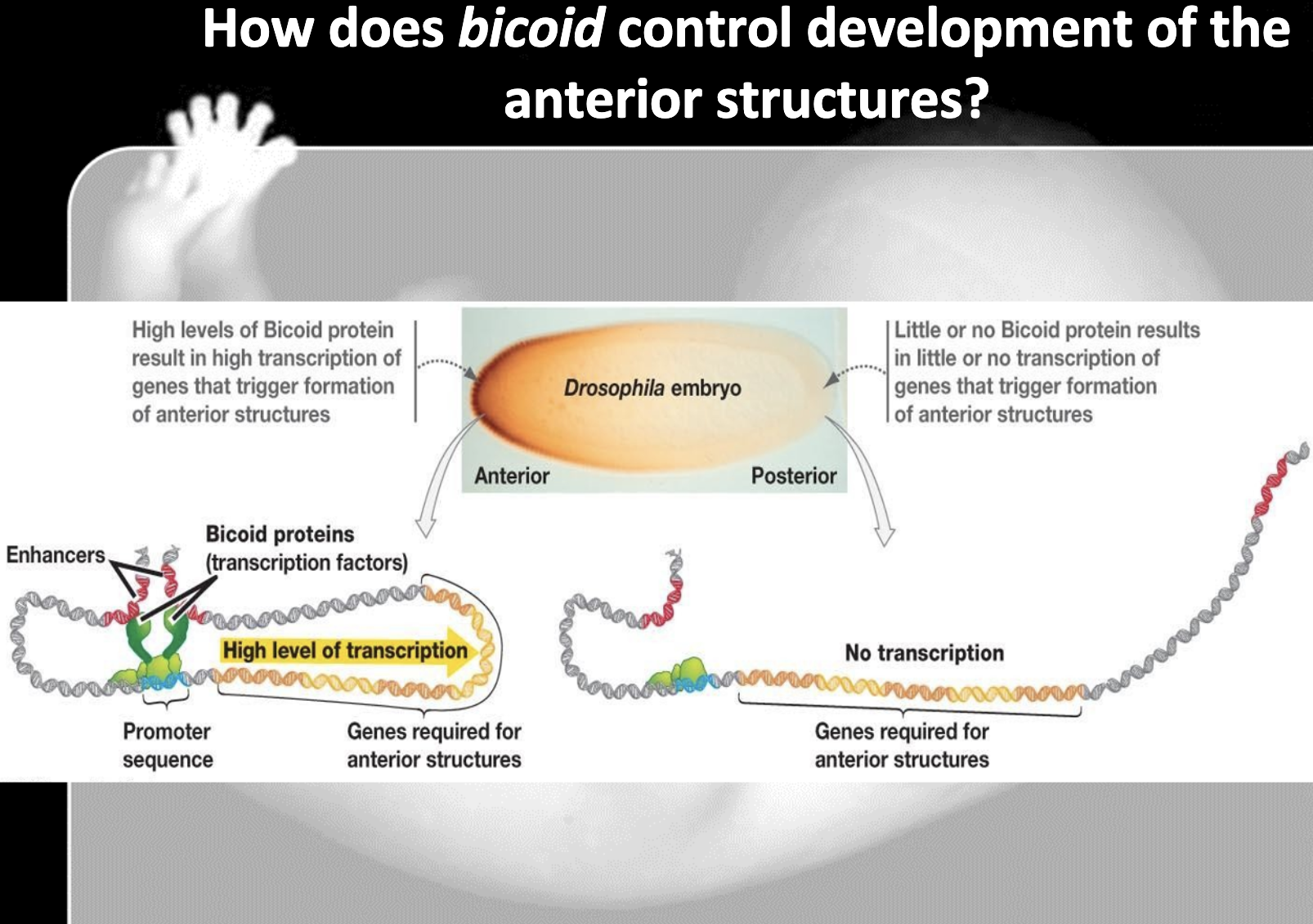
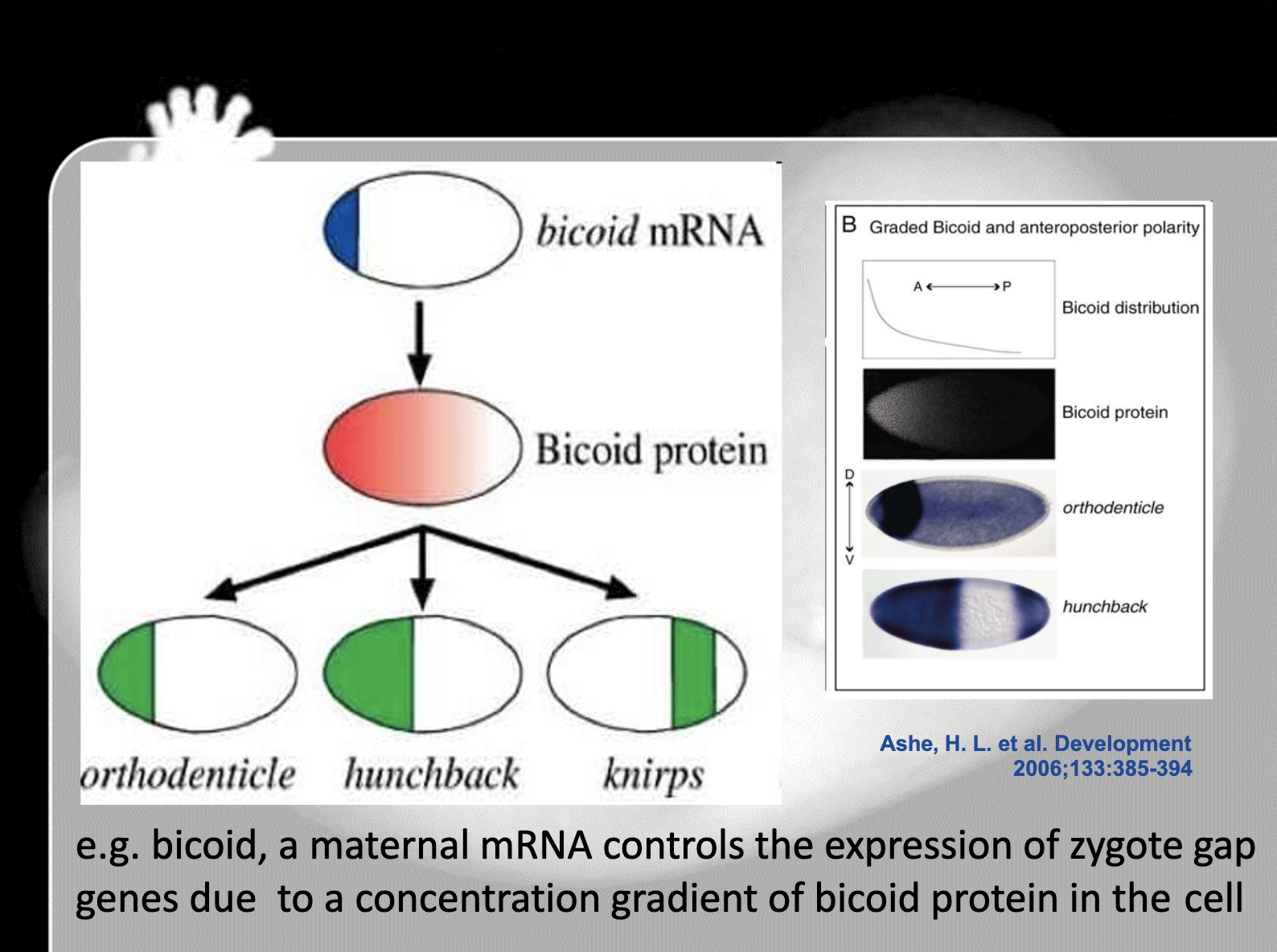
Outline the role of Bicoid and how it works to establish body axes in Drosophila.
-Bicoid is the maternal effect gene which encode the cytoplasmic determinant which is bicoid protein.
The gradient of bicoid gene and bicoid protein determines the anterior, posterior axes and structure of Drosophilia.
When there's a high level of bicoid, anterior structure of drosophilia is well developed
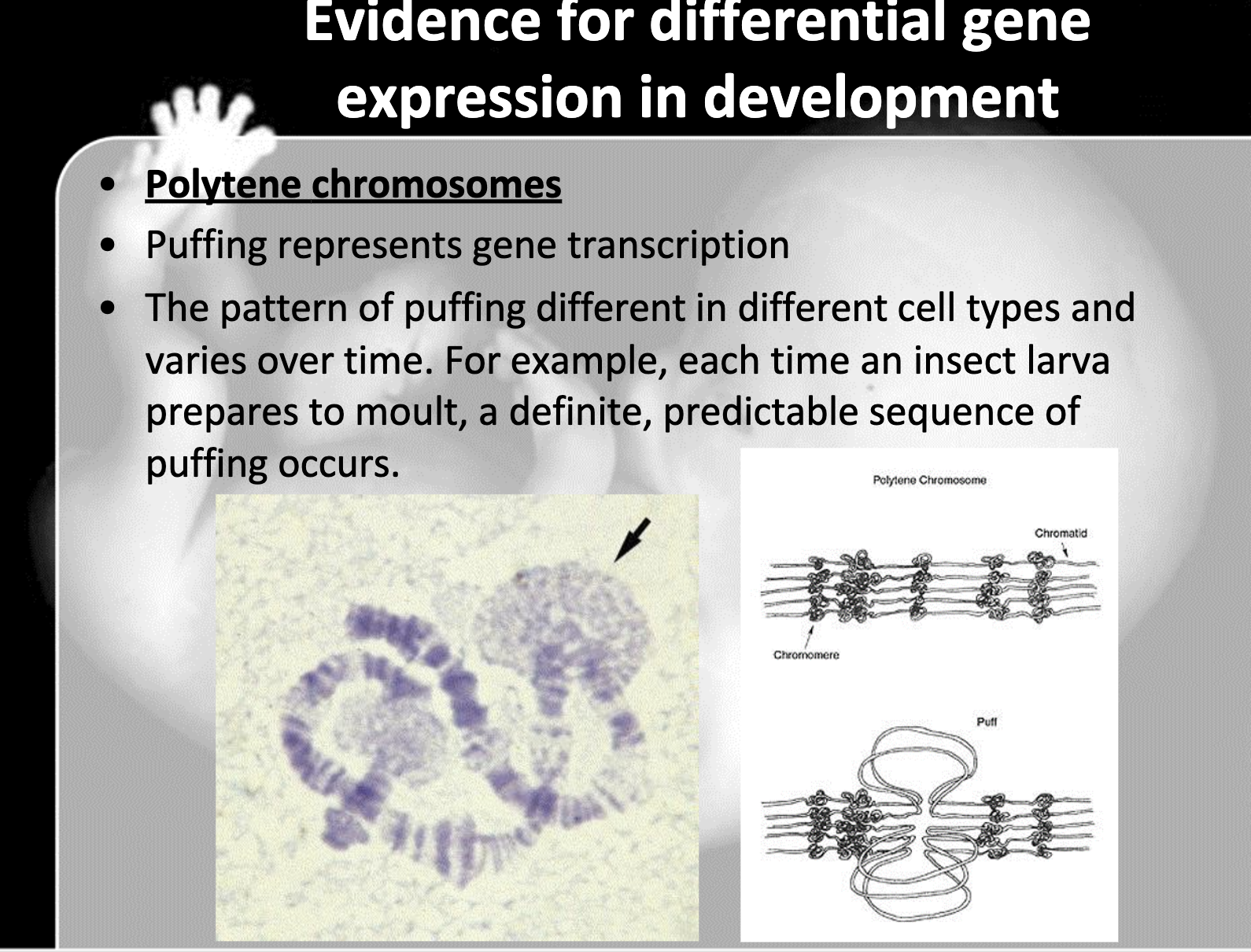
Describe one line of evidence for differential gene expression in development
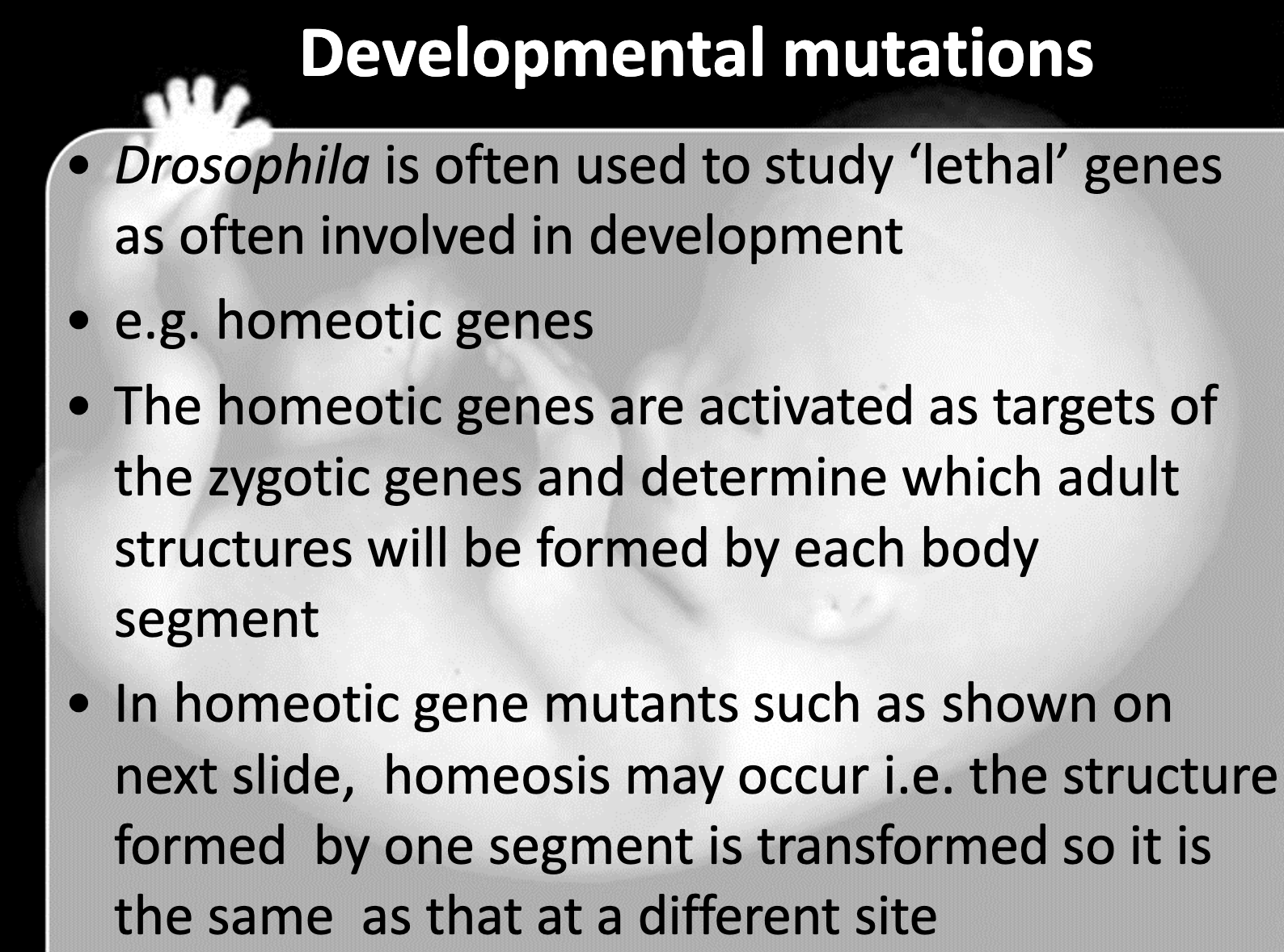
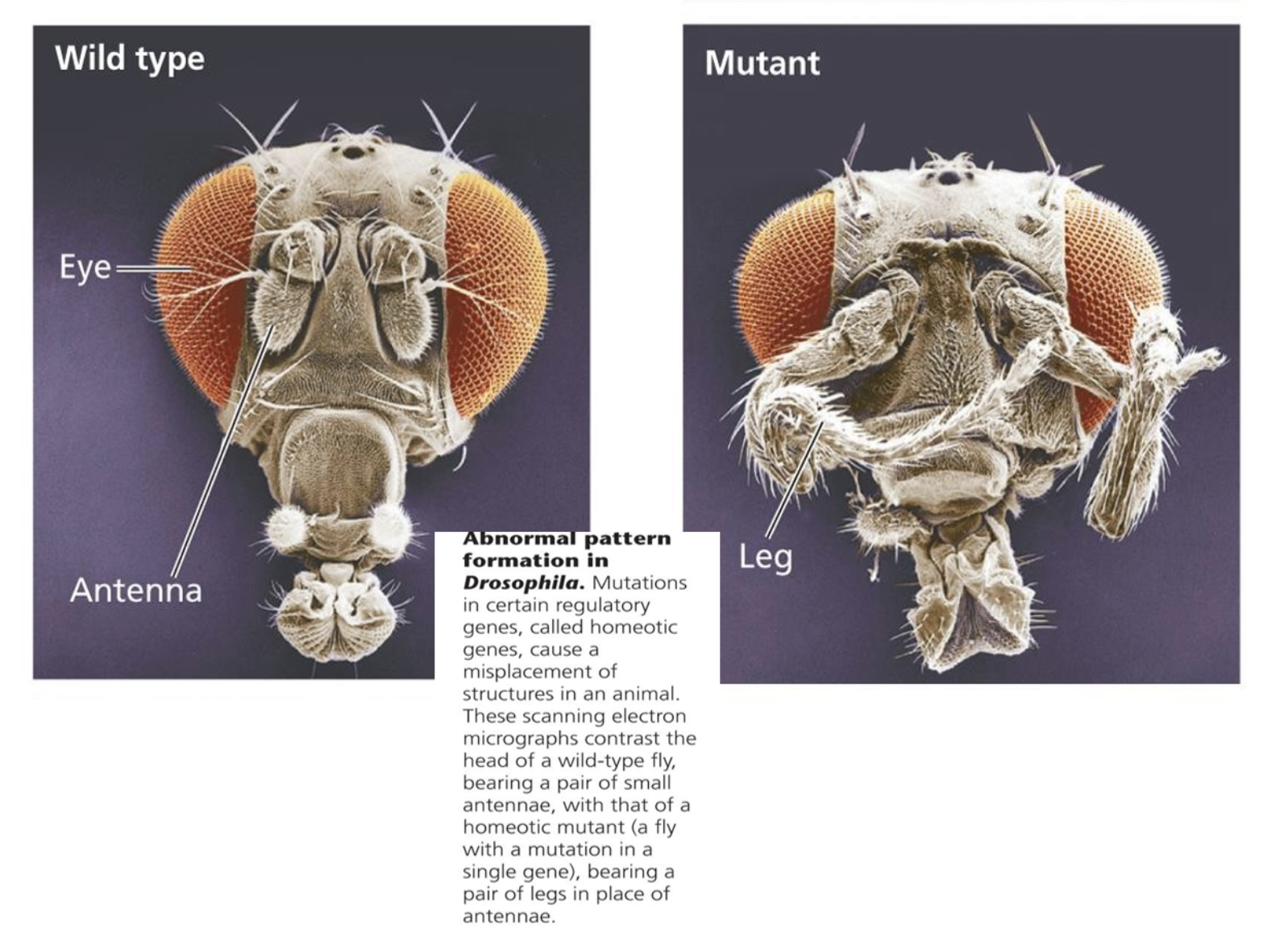
-Homeotic gene is the gene that determine the segment
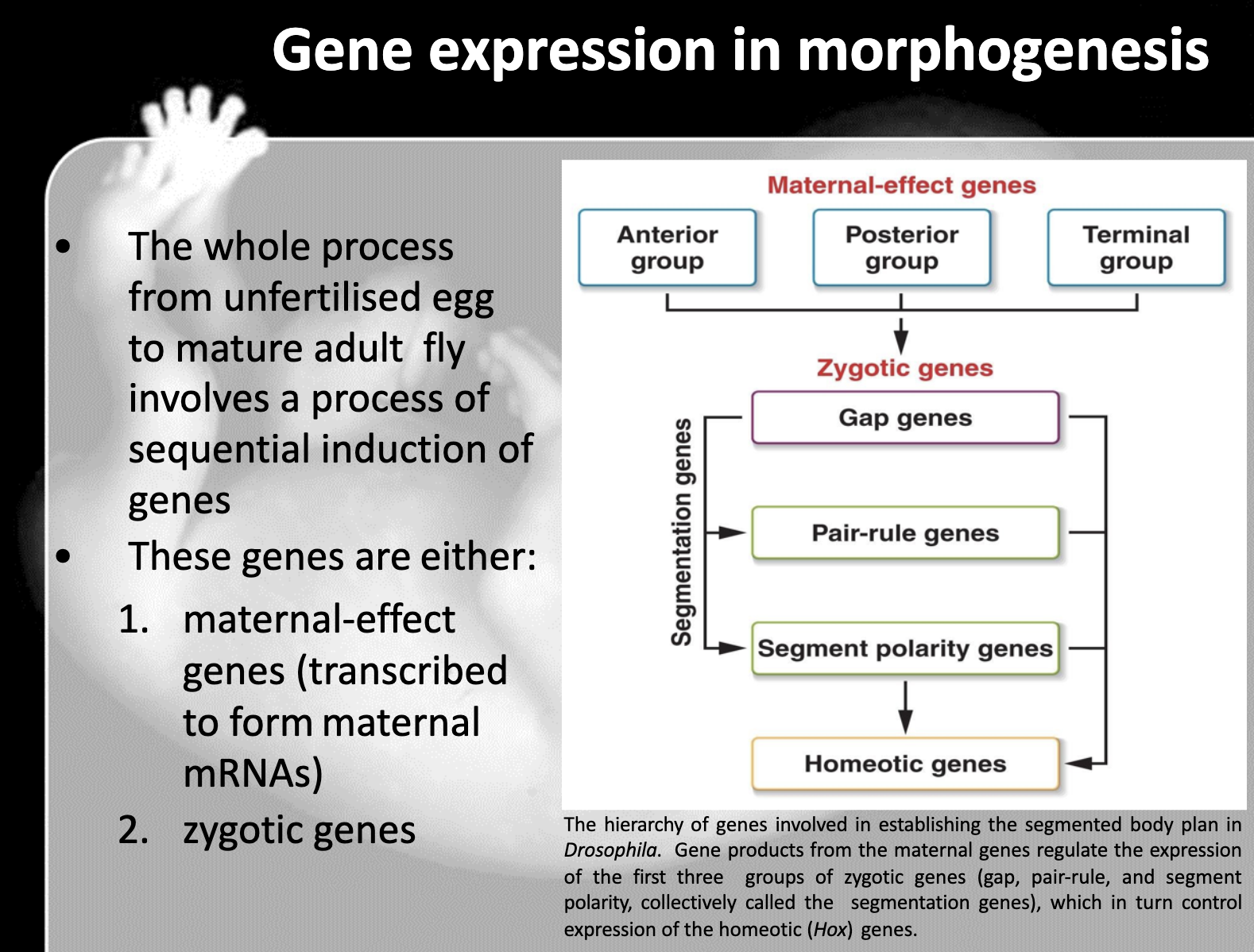
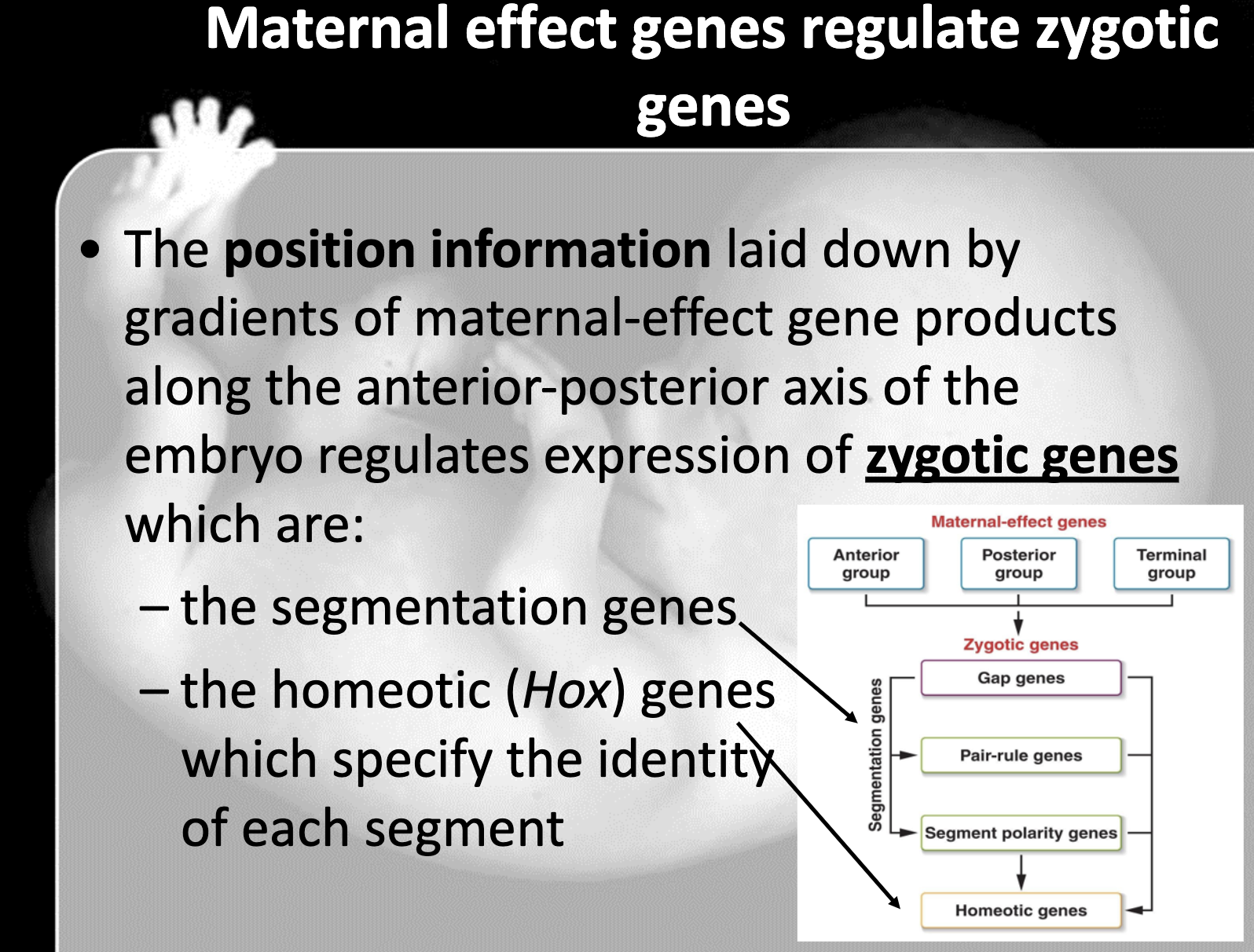
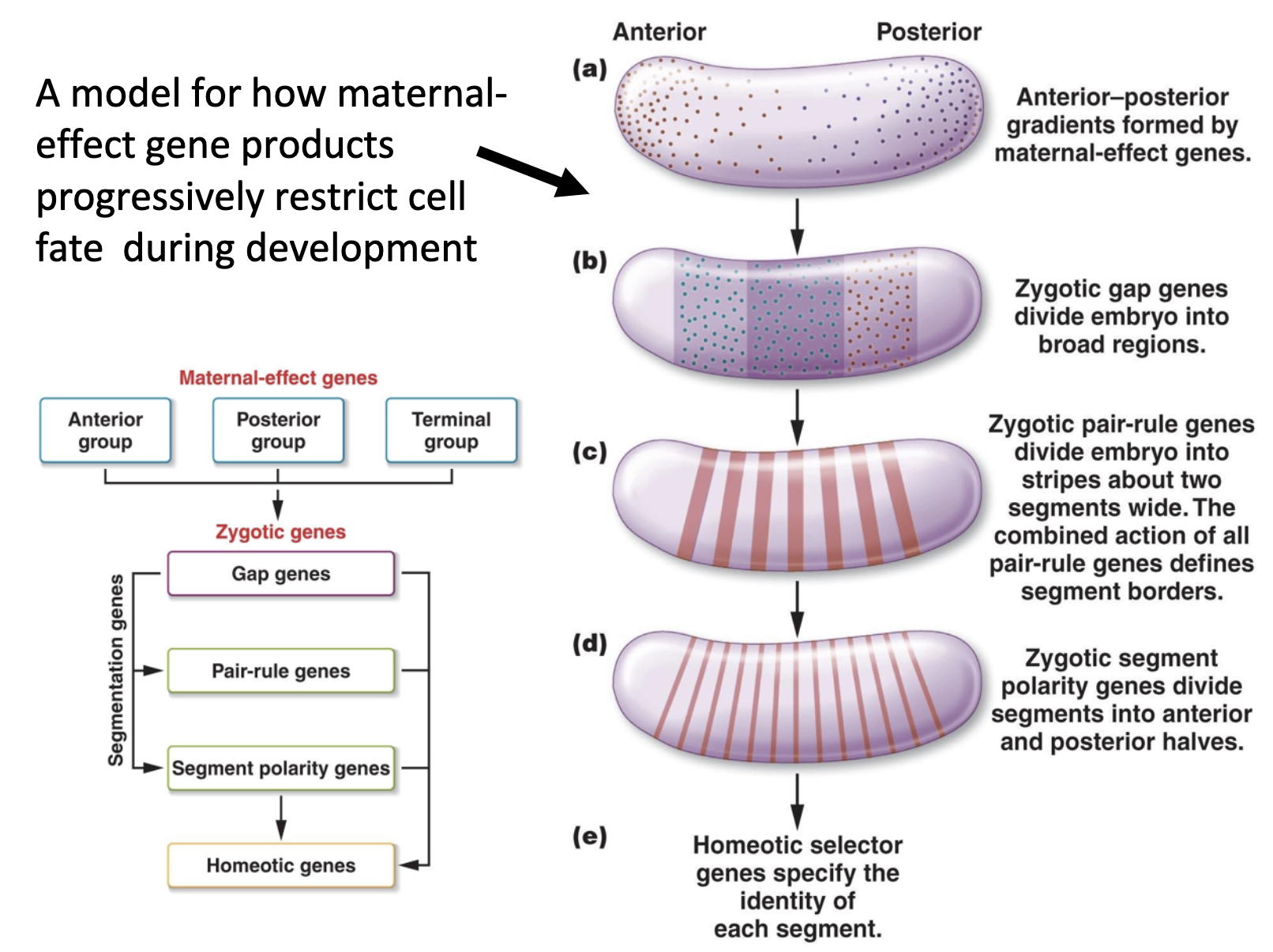
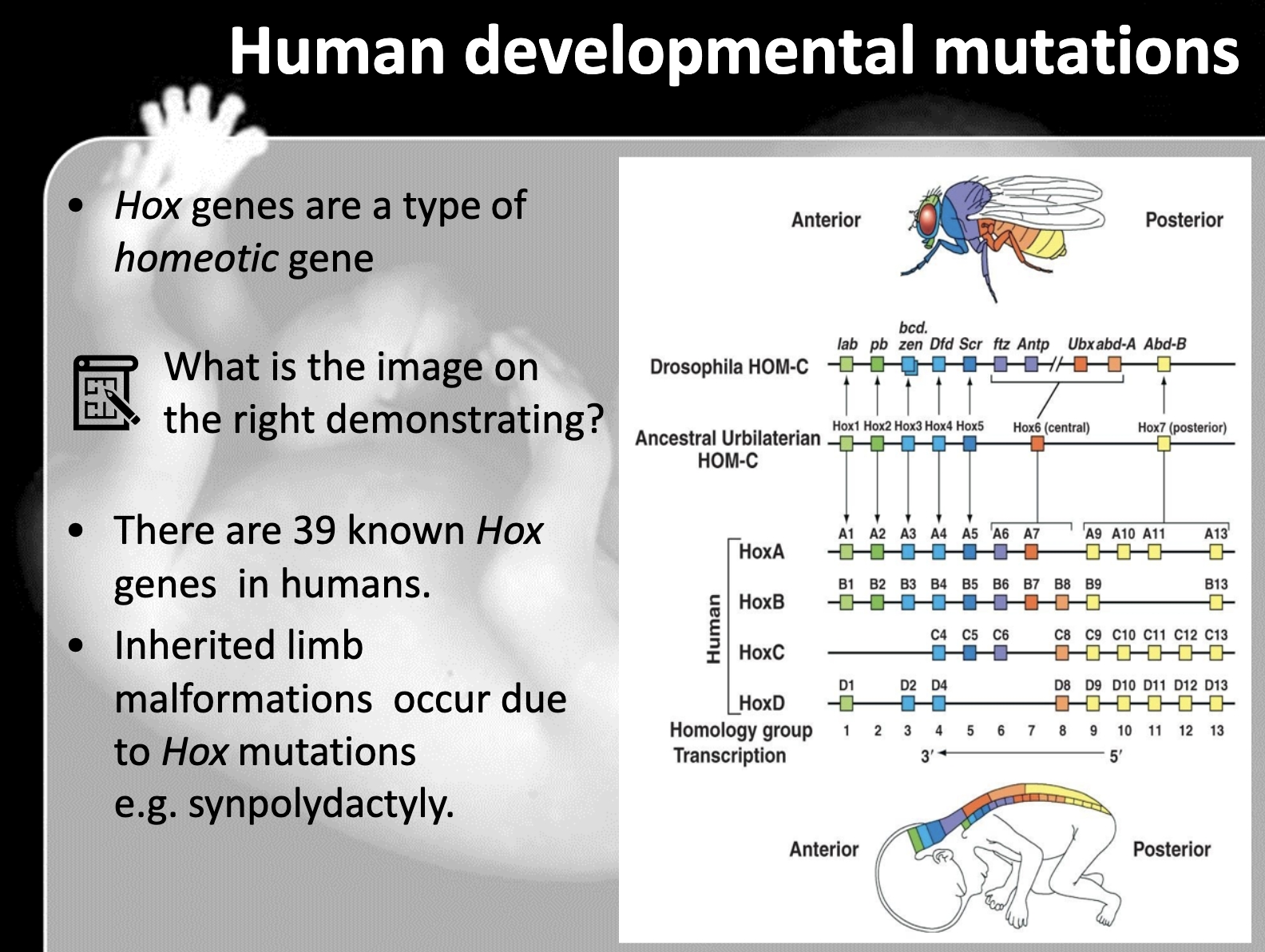
Know that Zygote genes include the segmentation genes (gap, pair-rule, and segment polarity genes) and the homeotic (Hox) genes that specify the fate of each segment, know the hierarchy of these genes
-gap gene -> pair rule -> segment polarity gene -> hox gene
gap gene divide into broader group
pair rule gene makes segment into two gap wides
Segment polarity gene divides each segment into two parts
Hox gene determines each segment the structure and function
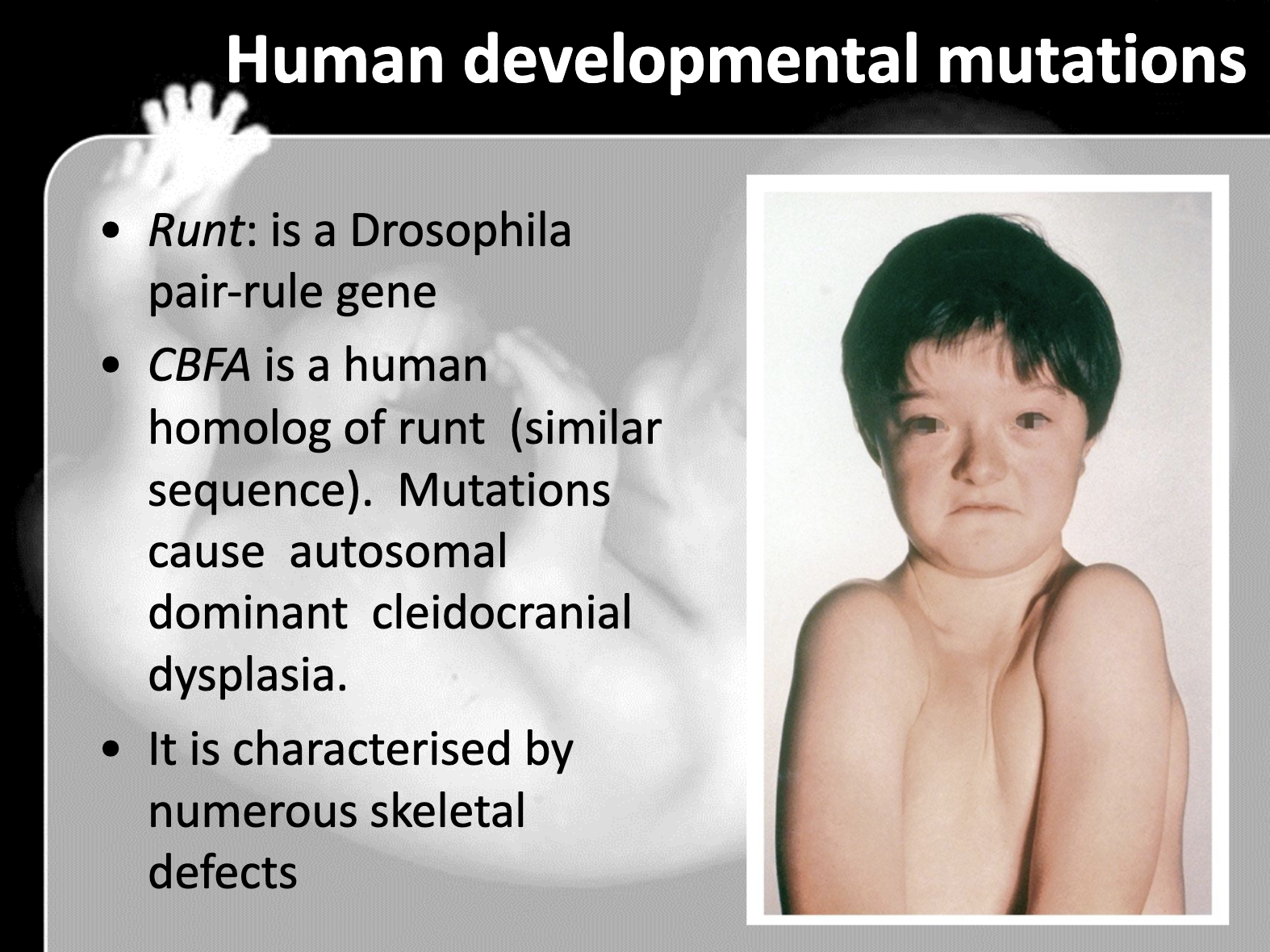
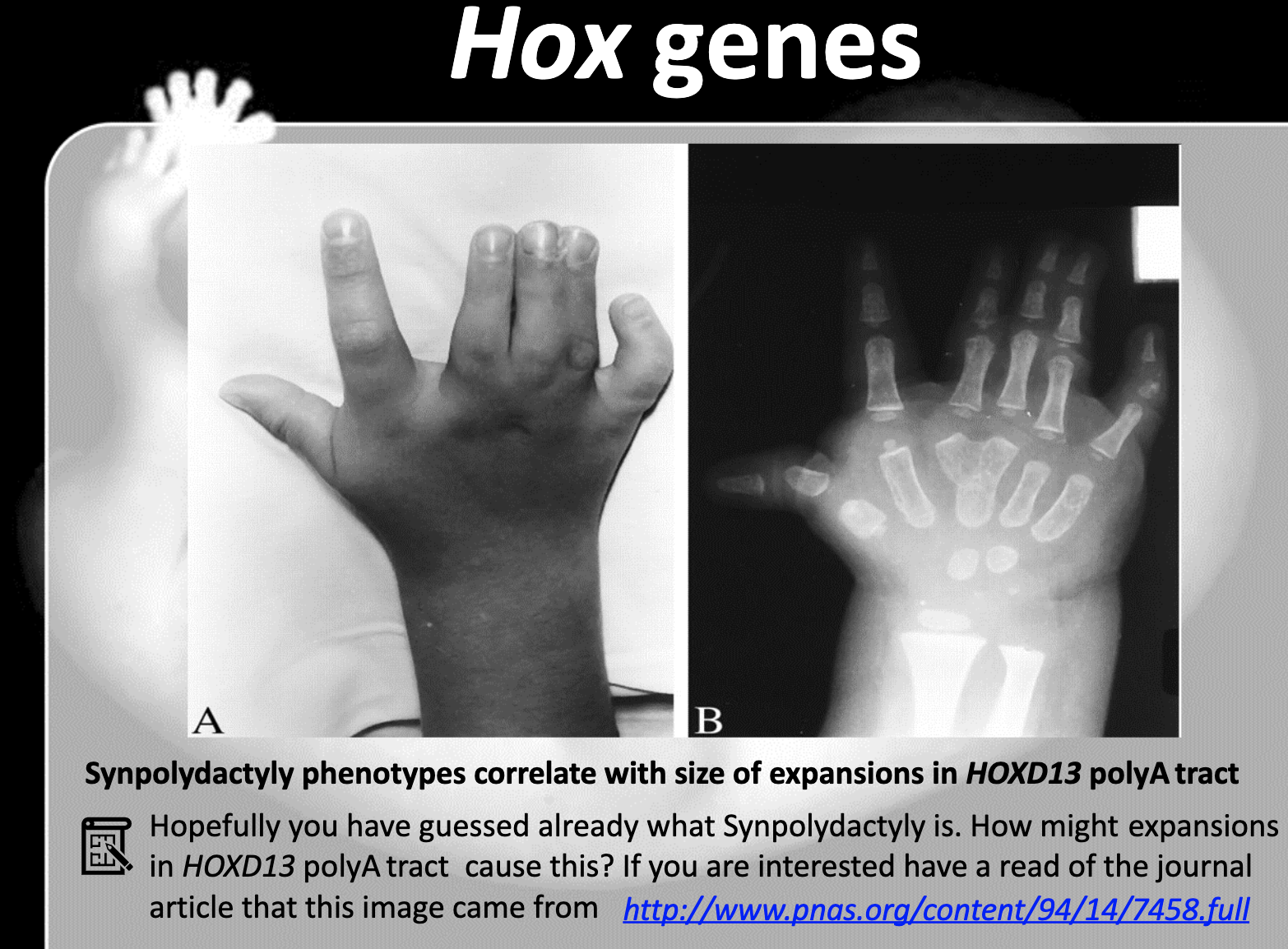
Describe the consequences of mutations in Hox genes. Give a human example
-Human has 39 hox genes. Synpolydactyly occurs as the mutation in hox gene of human. The size expansion of Hox gene 13 causes the limb malformation
Define a teratogen and list some human teratogens and examples of their effects
-Teratogen is a drug that can cause human malformation when the pregnant women exposed to it
wafarin is used to treat thrombosis but it causes the skeletal deformity, nasal hypoplasia, and skeletal deformity
retinoic acid is used to treat acne but it caused malformed children, spontaneous abortion, fatal abnormalities ..
alcohol, radiation, thalidomide are all teratogen
PPT


Embryonic development

Determination
Gene expression in morphogenesis

Developmental mutations
Tetratogens
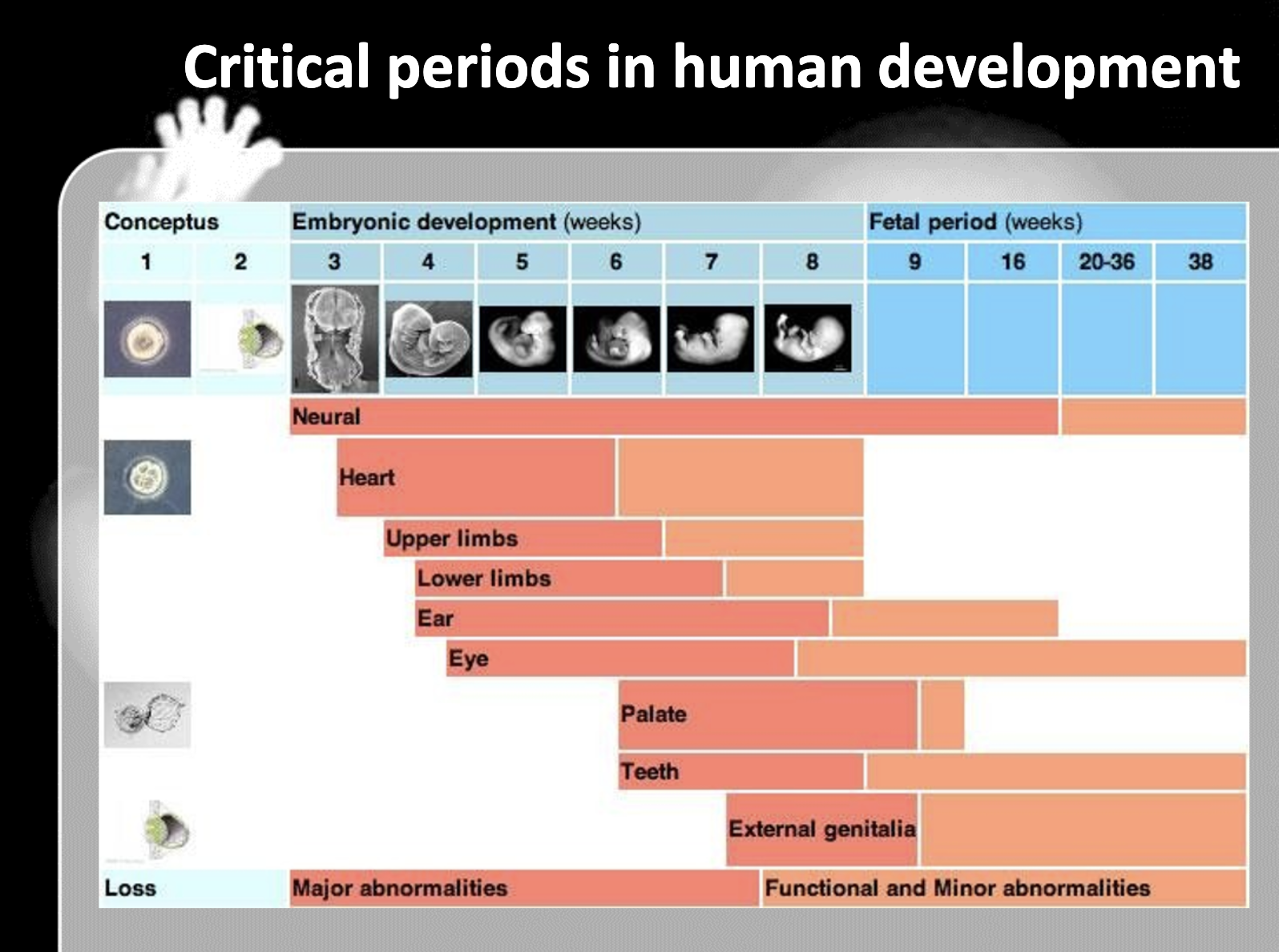



SPQ


1. Zygote goes through cell division, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis
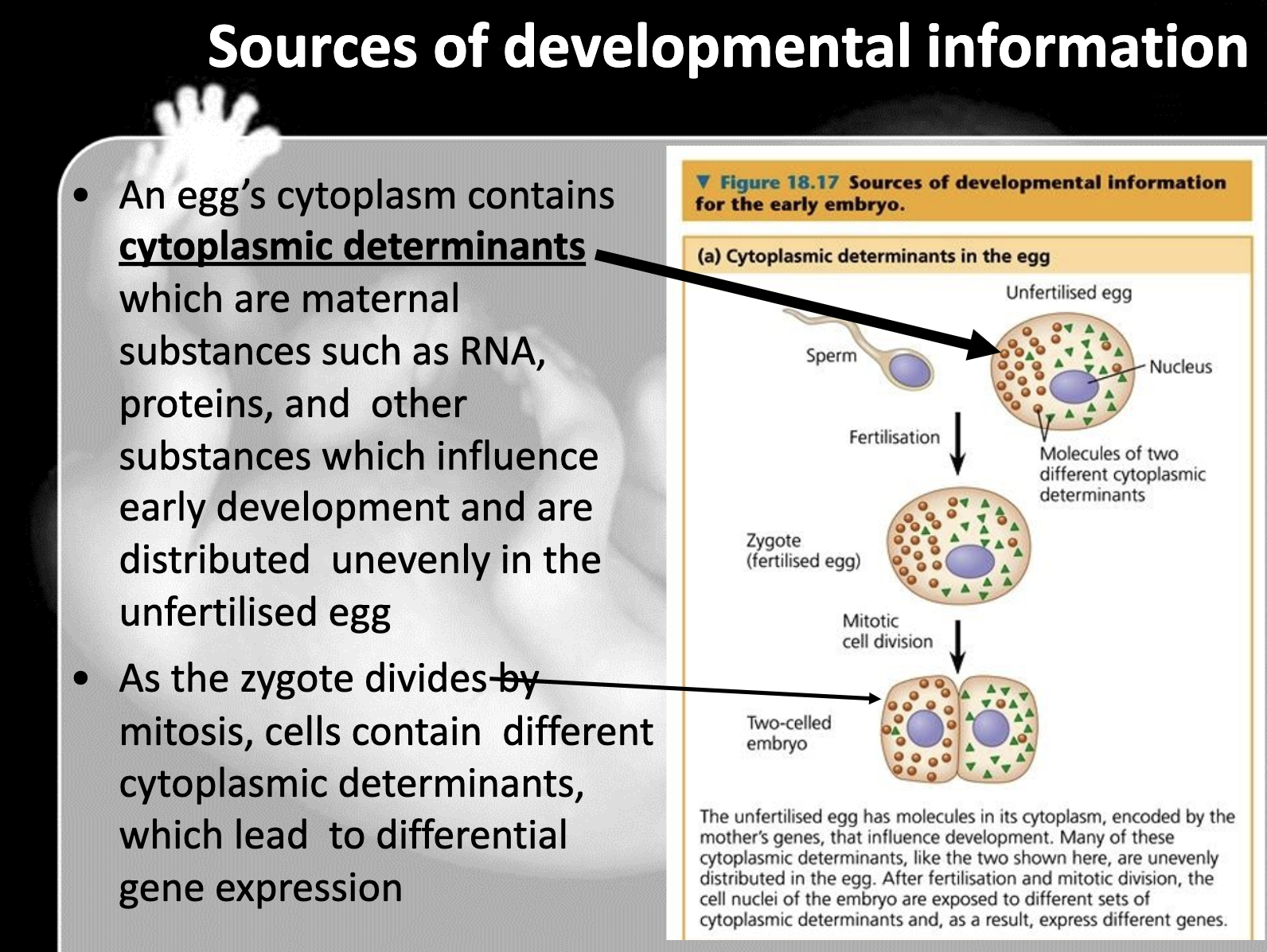
Before the egg is fetilised, maternal effect gene, which is a genetic substance in egg's cytoplasm such as mRNA and proteins, is unevenly distributed. This makes the gene expression differently after it fertilised with sperm and the cell starts to divide. Also during the cell division, induction happens, which is nearby cell send the signal to the cells' gene expression.
When it comes to cell differentiation, cell determination percedes the cell differentiation. When the regulatory gene is stimulated and transcribes transcription factor, the cell is now committed to become certain type of cell, and it is irreversible. It is called determination. When the master regulatory transcription factor activates other genes to transcribe other transcription factor which activates the genes to produce certain proteins which makes the cell's character, it is called differentiation
Morphogenesis is the process of an organism developing its shape. Maternal effect gene, zygotic gene(such as gap gene, pair-ruled gene, segment polarity gene), and homeotic gene affects the gene expression and affects the morphogenesis of the organism.


2. in organogenic period, 15-60 days


3. Segmentation genes in Drosophilia include gap genes -> pair ruled genes -> segment polarity genes
(Maternal effect gene determine the group of the drosophilia by the gradient, anterior posterior terminal)


4. Embryonic deveopment <- cell division, cell differentiation, morphogenesis
5. Morphogenesis is the term for giving rise to the shape of an organism
Differentiation is the process of cell becoming more specific cell by producing protein by stimulating specific gene with transcription factor
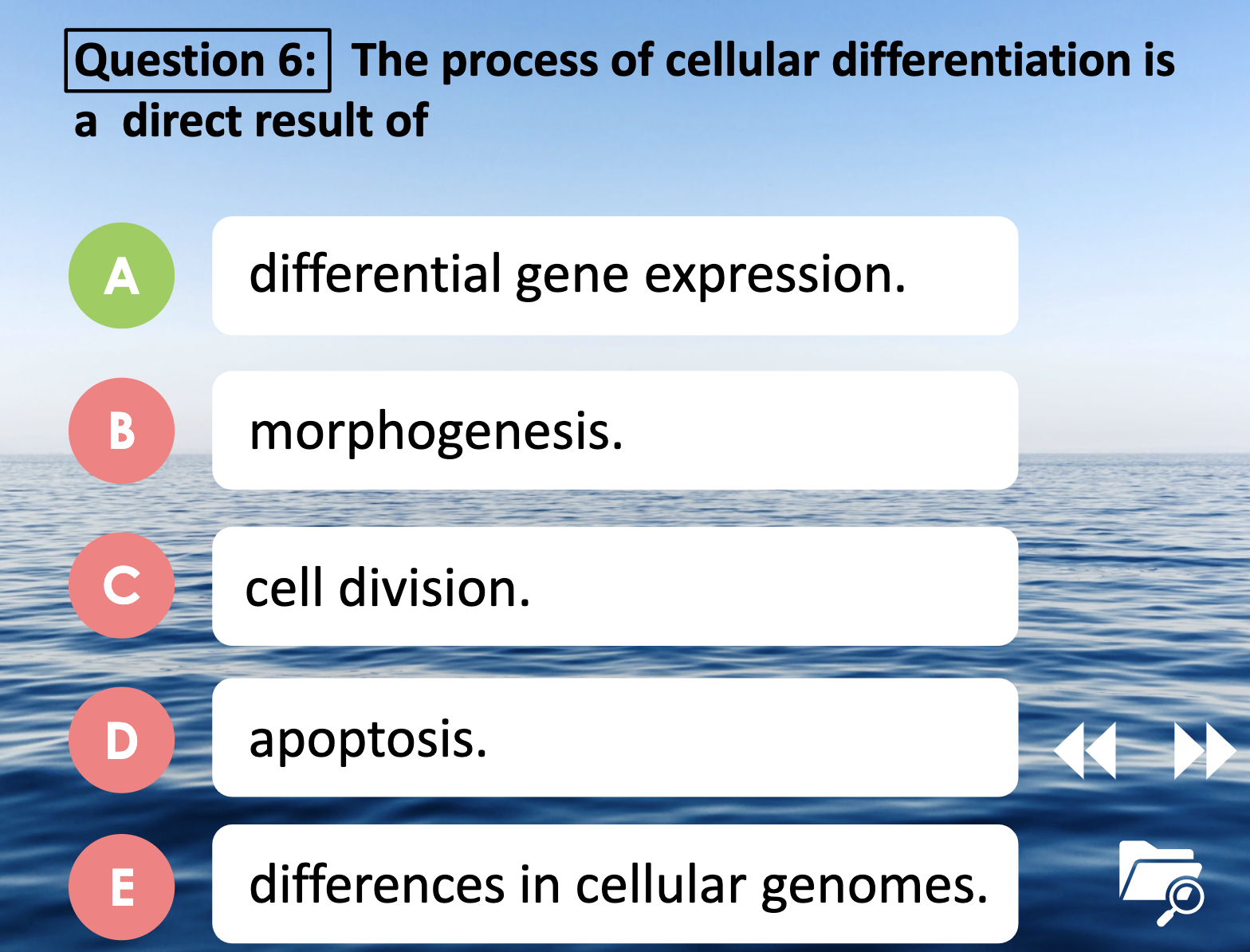

6. The process of cellular differentiation is a direct result of producing specific protein stimulated by transcription factor which is differential gene expression
7. Cytoplasmic determinants such as mRNAs and proteins produced before fertilisation, and signal molecules produced by neighboring cell give the different gene expression
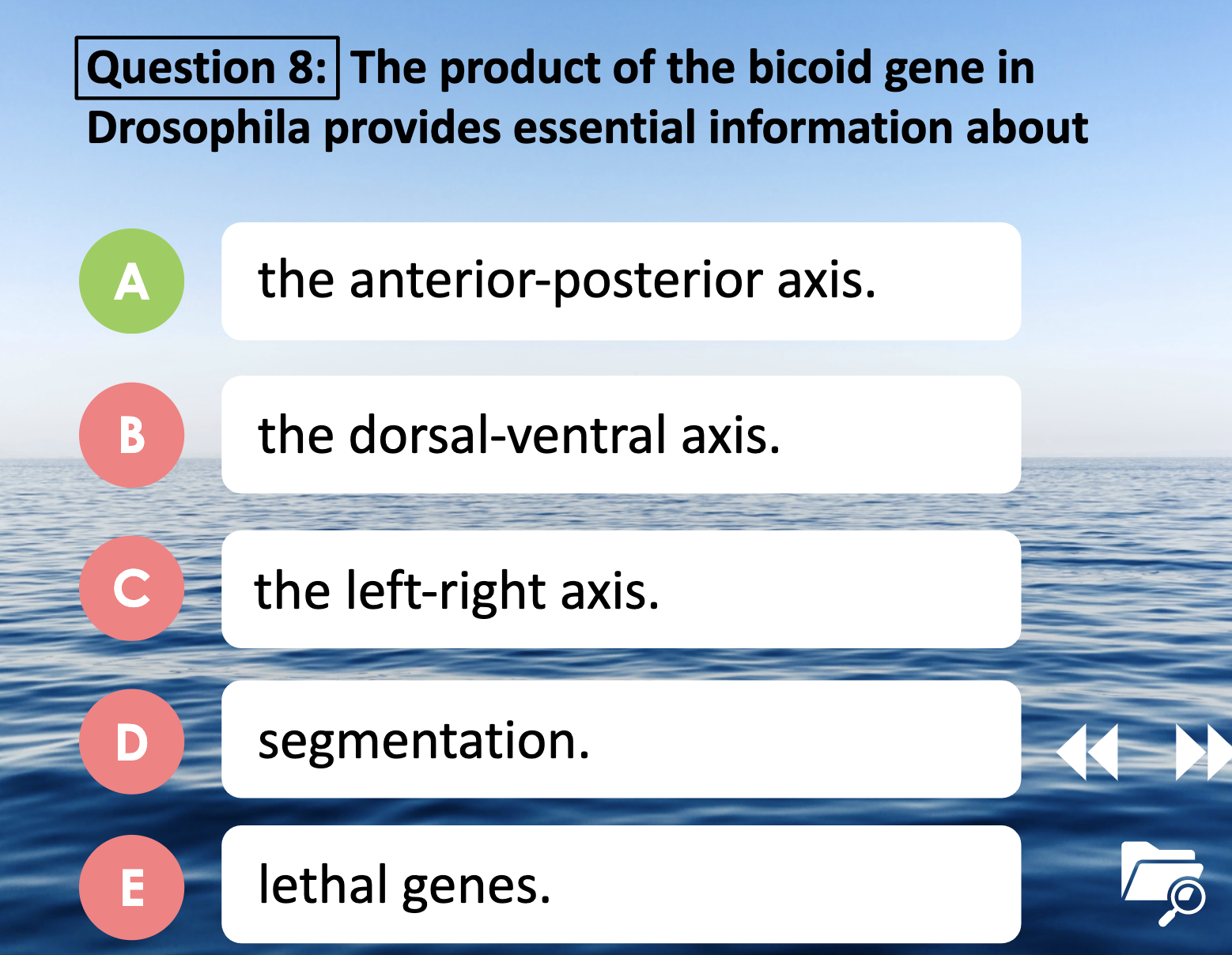

8. Bicoid gene is the maternal effect gene which encode the cytoplasmic determinants which affect the gene expression. It determines the anterior-posterior axis. High bicoid concentration develops anterior structure
9. Then all of the cytoplasmic determinants, the materials in the egg's cytoplasm which determines differential gene expression, will be all homozygous mutants. For drosophilia, bicoid, for example, the morphogen is all mutant so despite their genotype to determine other phenotype, their axes and other features will be all mutant..

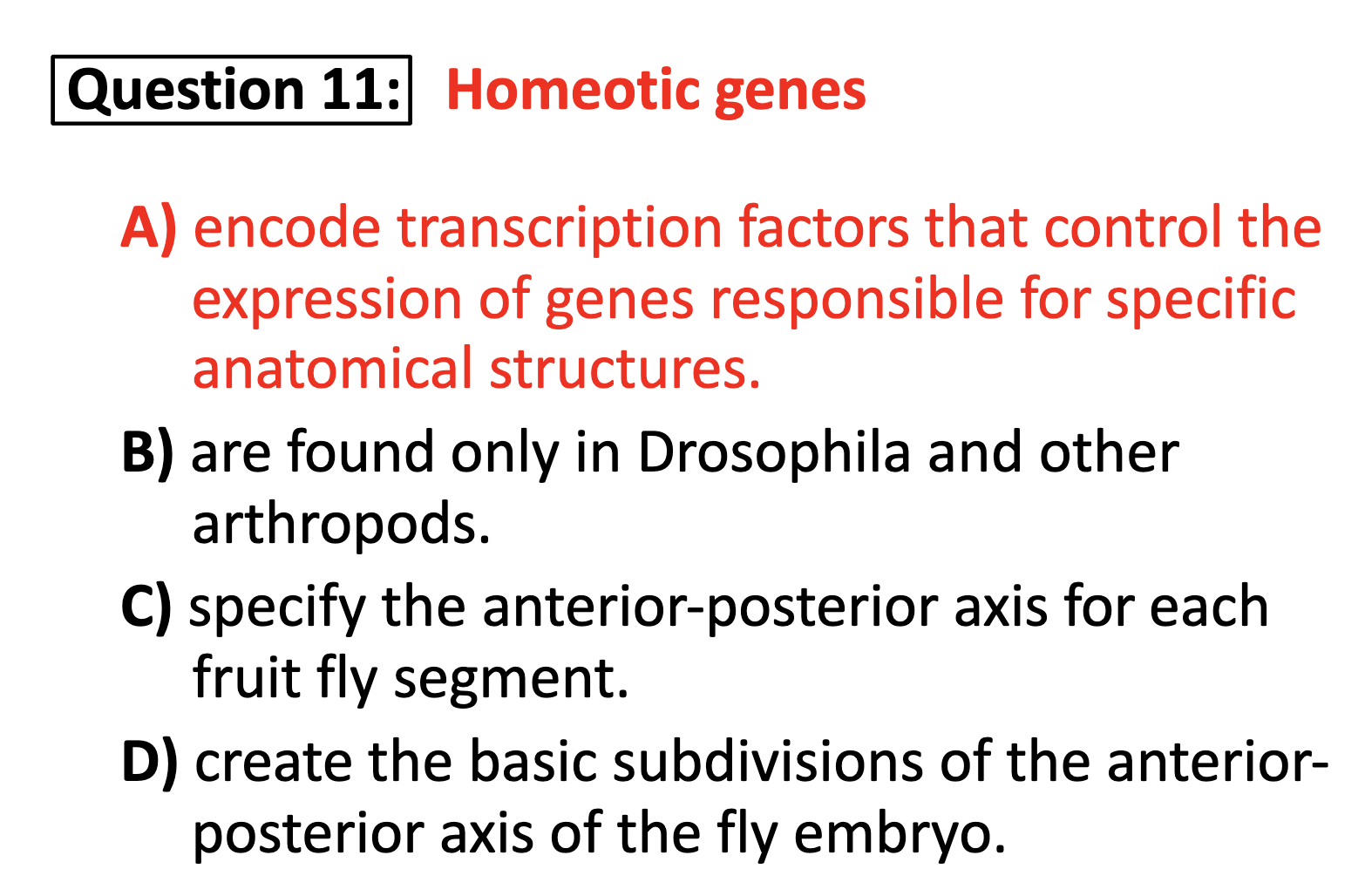
10. maternal effect gene -> zygotic gene (gap gene, pair ruled gene, segment polarity gene)->Homeotic genes
11. Homeotic genes determine the segment to become which structure
Homeotic genes encode transcription factors that control the expression of genes responsible for specific anatomical structure
'Griffith college Tri1 2023 > 1005 QBT (GnD)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [WEEK10] How did life start on Earth? (0) | 2023.05.13 |
|---|---|
| [WEEK10] Charles Darwin and the theory of evolution (0) | 2023.05.13 |
| [WEEK6] Part 1 Gene Expression (0) | 2023.04.12 |
| [WEEK5] Part 3 Molecular Basis of Inheritance (0) | 2023.04.01 |
| [WEEK4] Part 2 Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance (0) | 2023.04.01 |



