Learning objectives
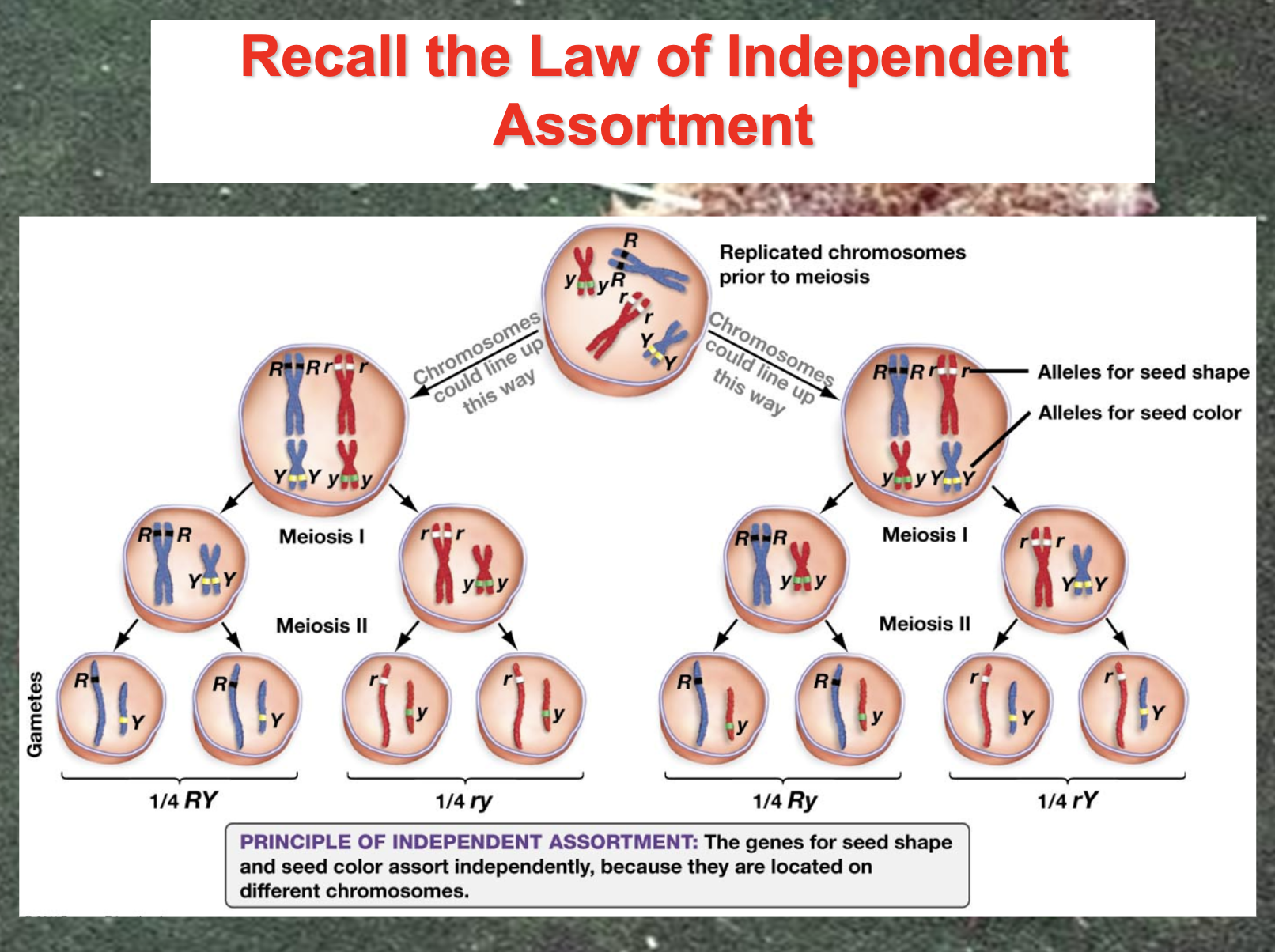
Understand Mendel’s laws (segregation and independent assortment) and describe how they can be explained by the behaviour of chromosomes during meiosis.
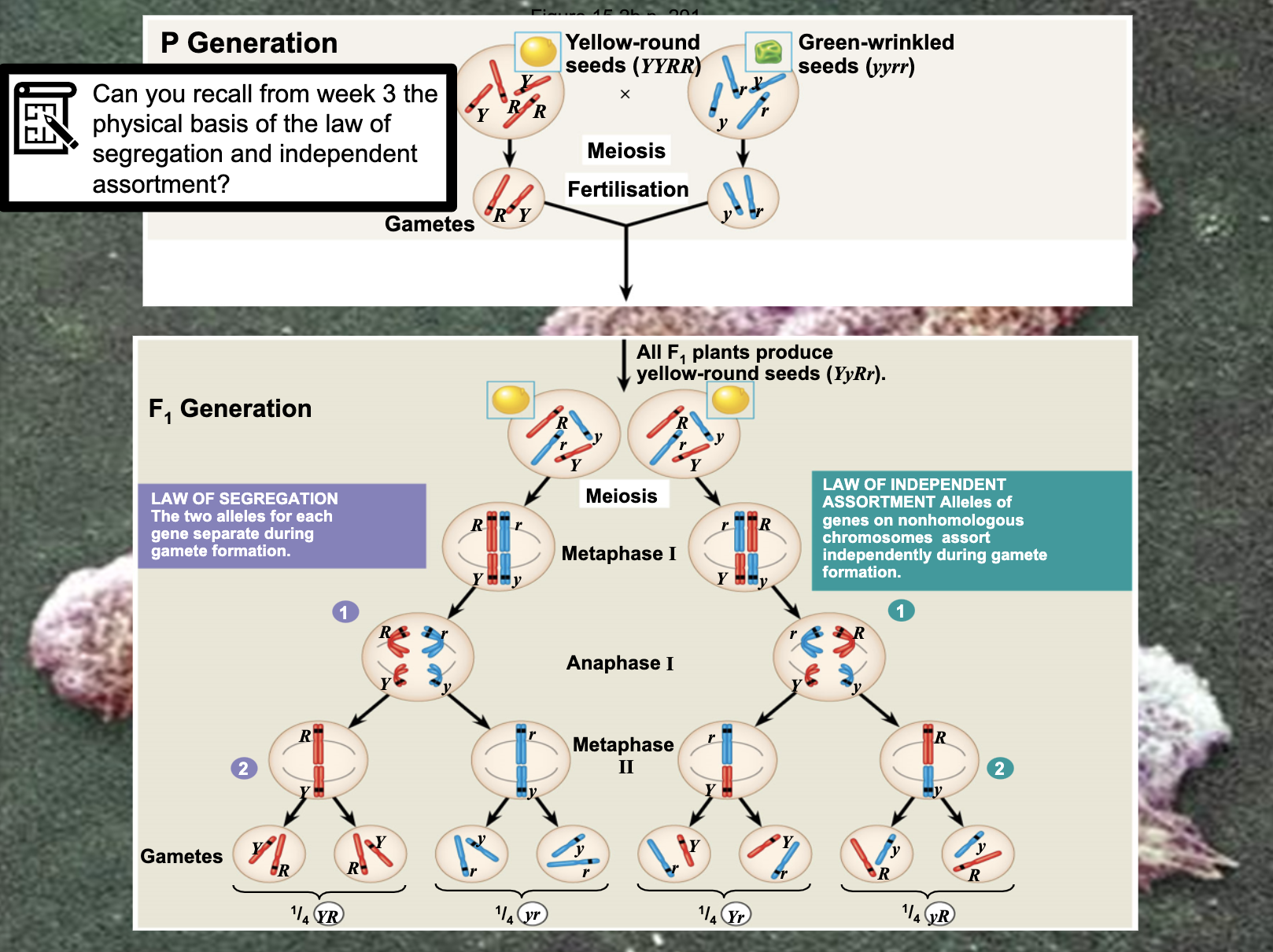
The law of segregation = The allele seperate during meiosis 1
->Chromosome split into each of the gamete and produce haploid cell
The law (principle) of independent assortment = Each of the allele in the different chromosome doesn't affect to other chromosomes when they are spliting.
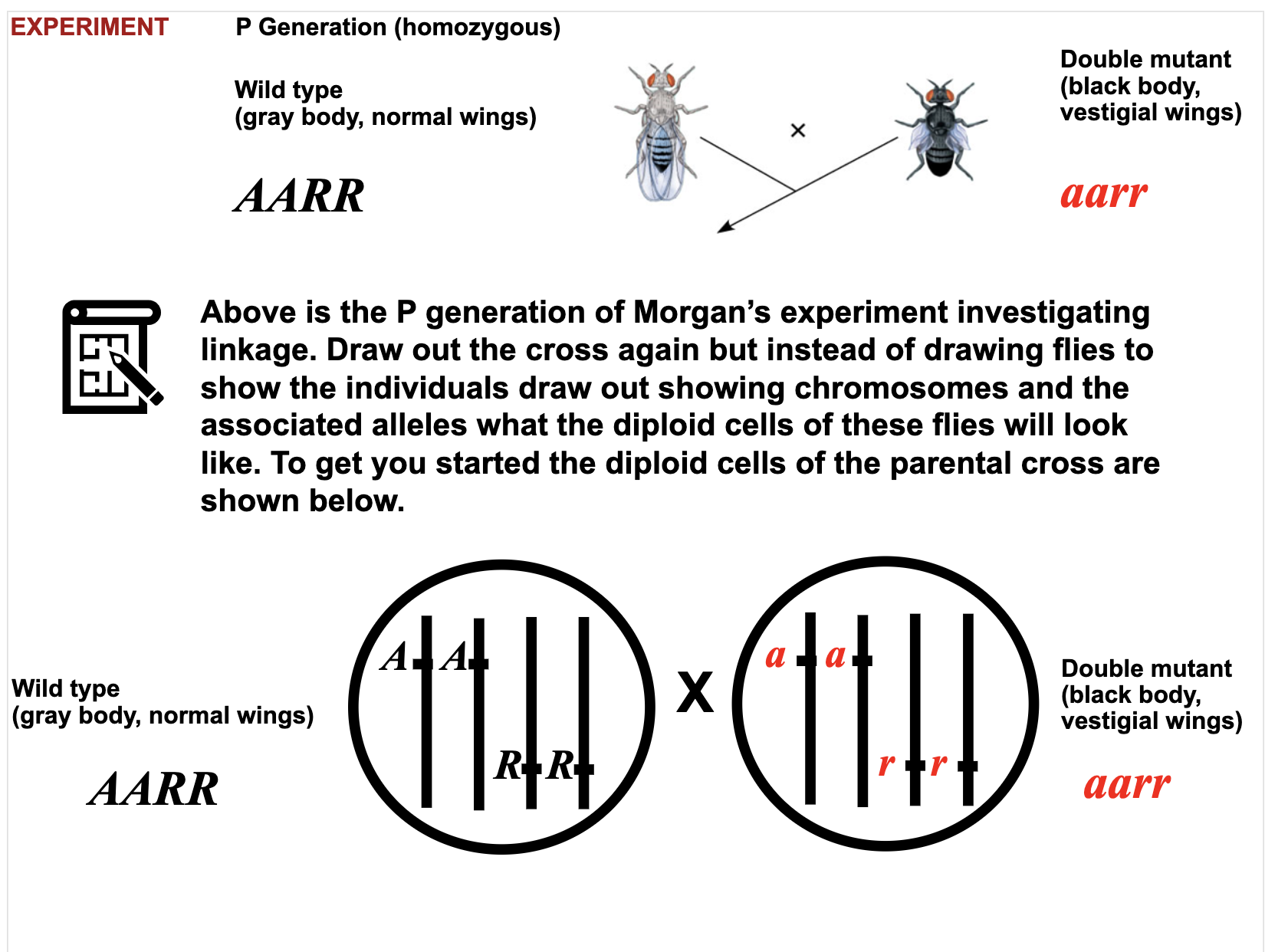
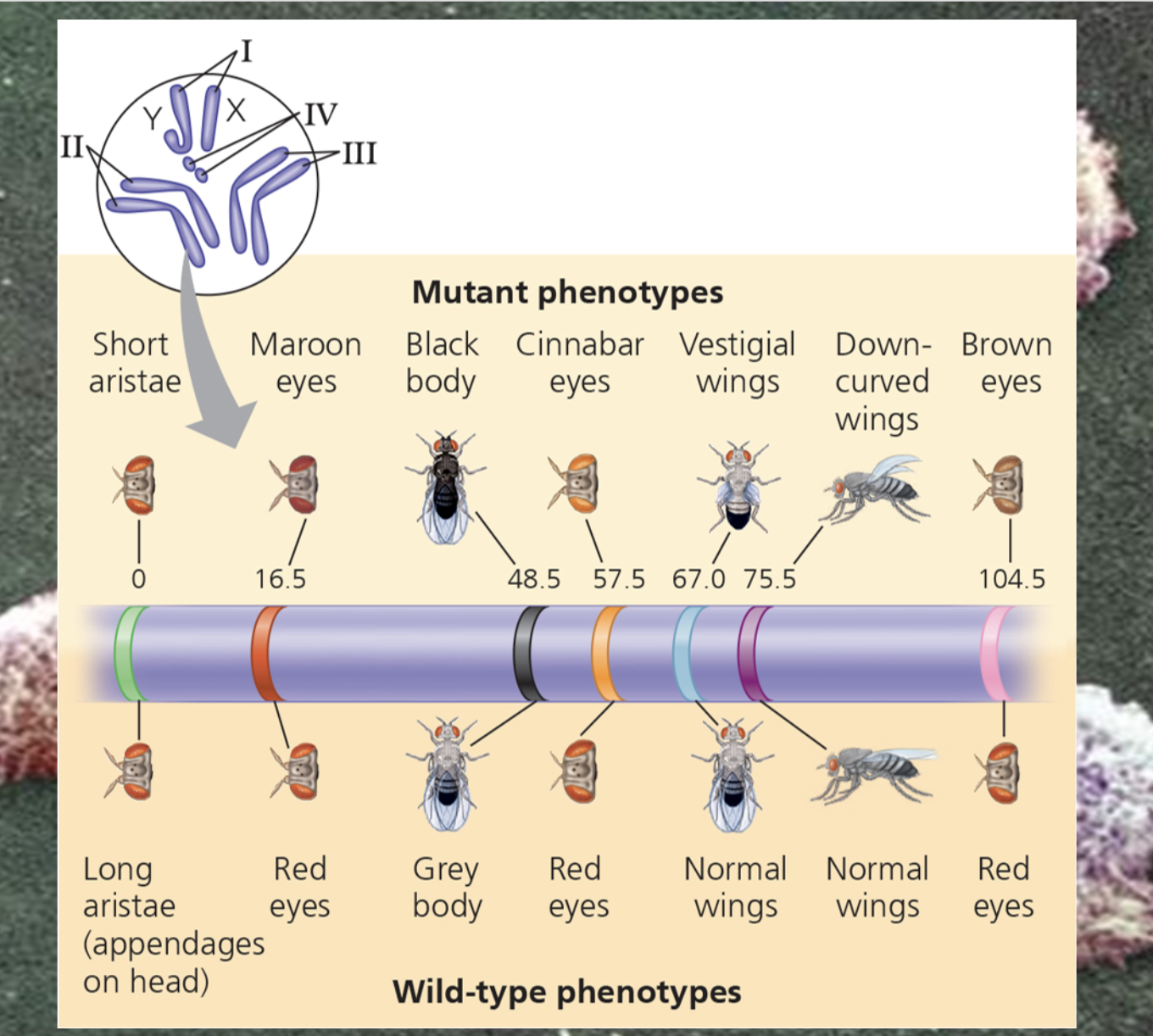
Describe Morgan’s experiments that provided evidence that genes exist on chromosomes.
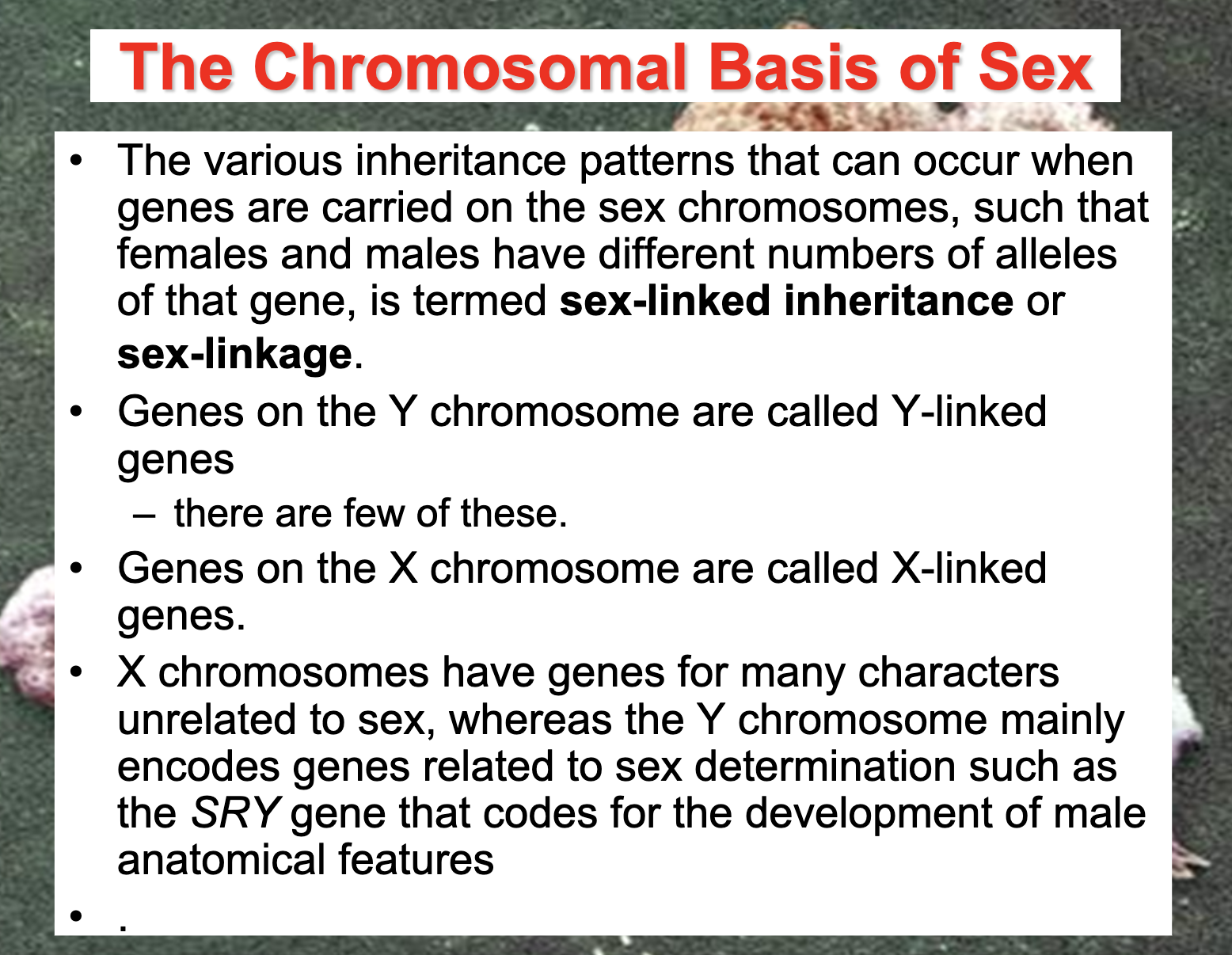
Describe the chromosomal basis of sex and define sex-linkage.
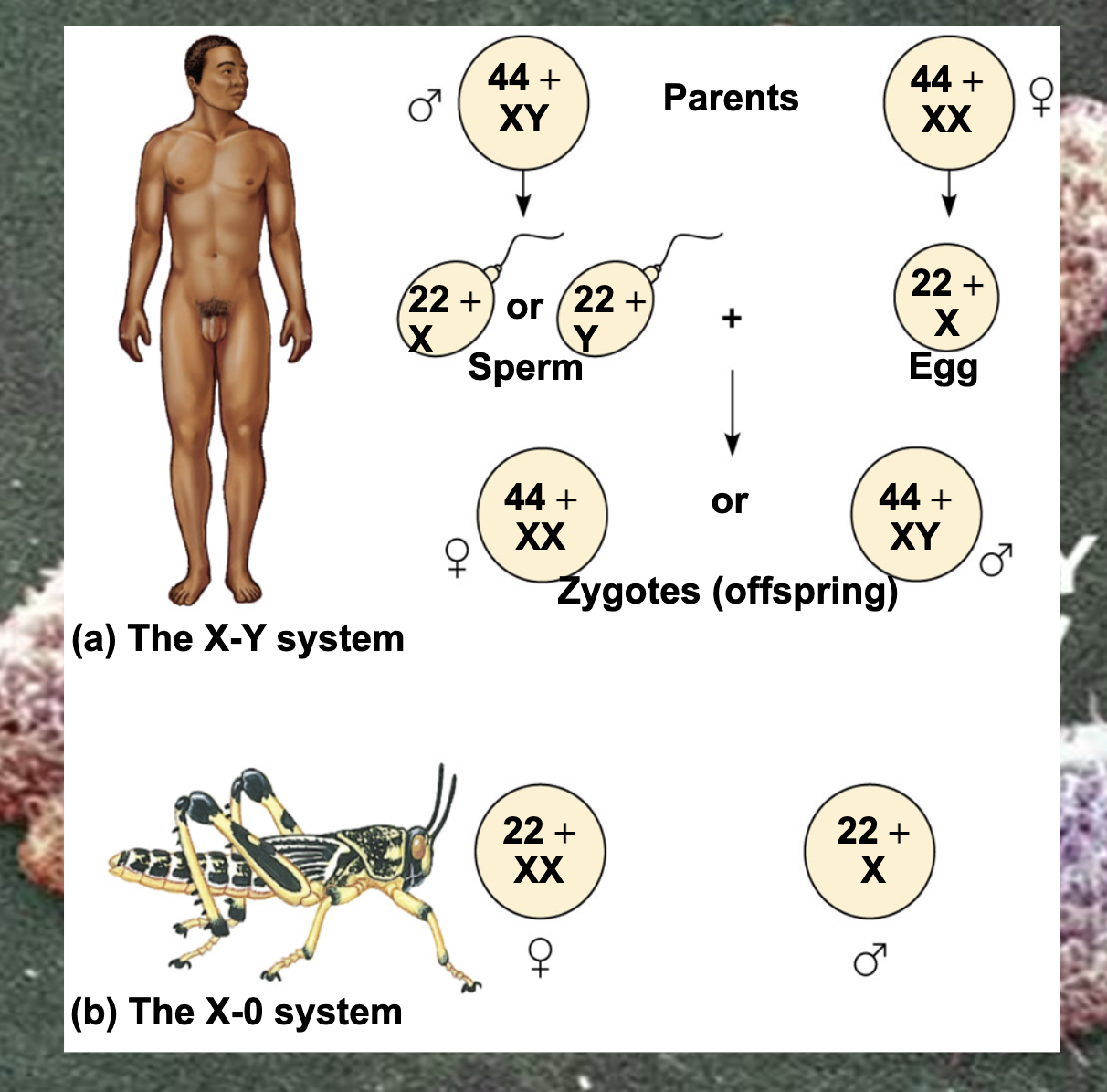
-X and Y chromosomes are called sex chromosomes because they determine the sex of the offspring
-Females are XX and males are XY
-Sex chromosomes pair during meiosis1 and then segregte during meiosis2
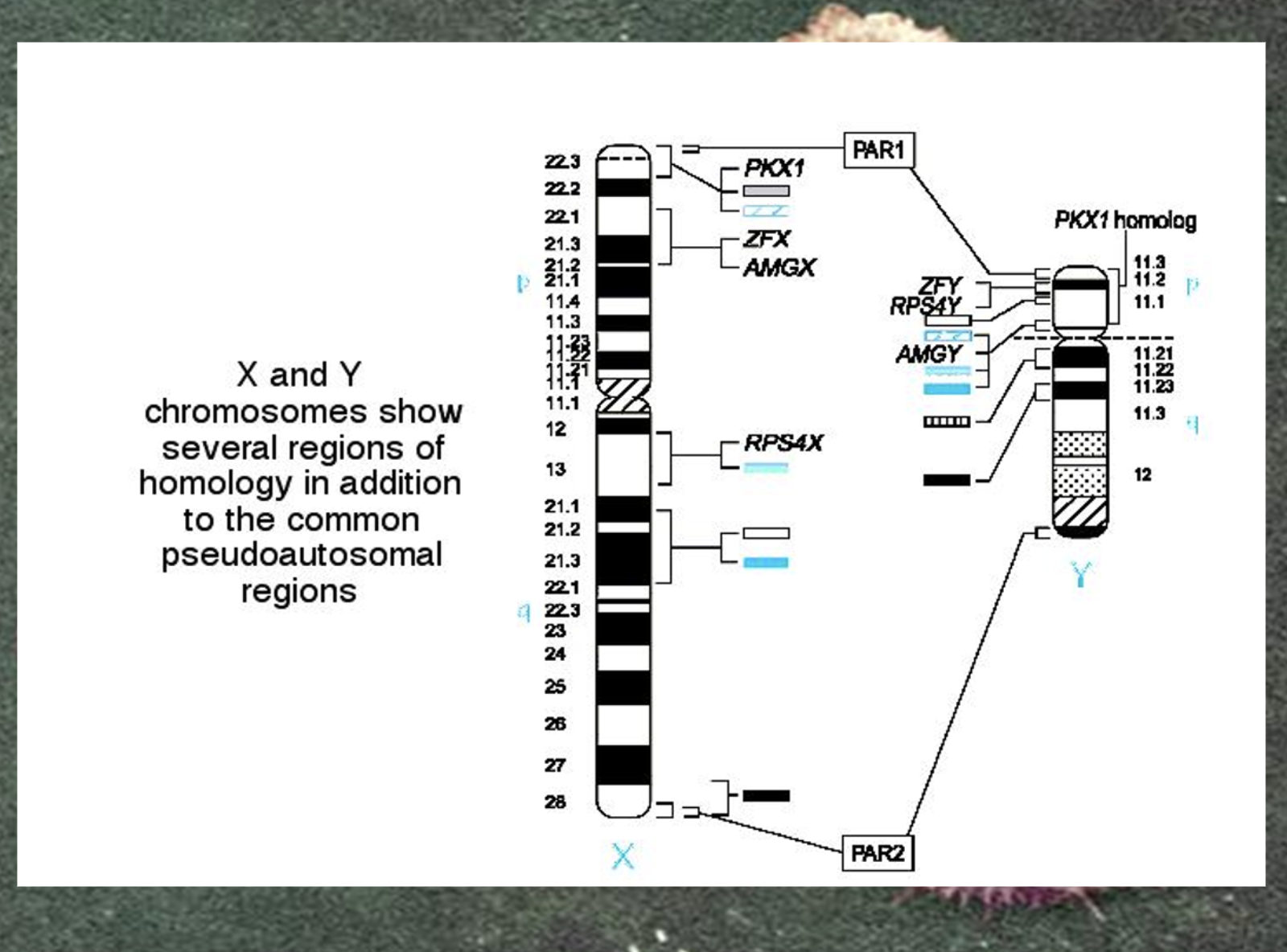
-Only the ends of the Y chromosome have regions that are homologous with corresponding regions of the X chromosome
-Each ovum contains an X chromosome, while a sperm may contain either an X or a Y chromosome
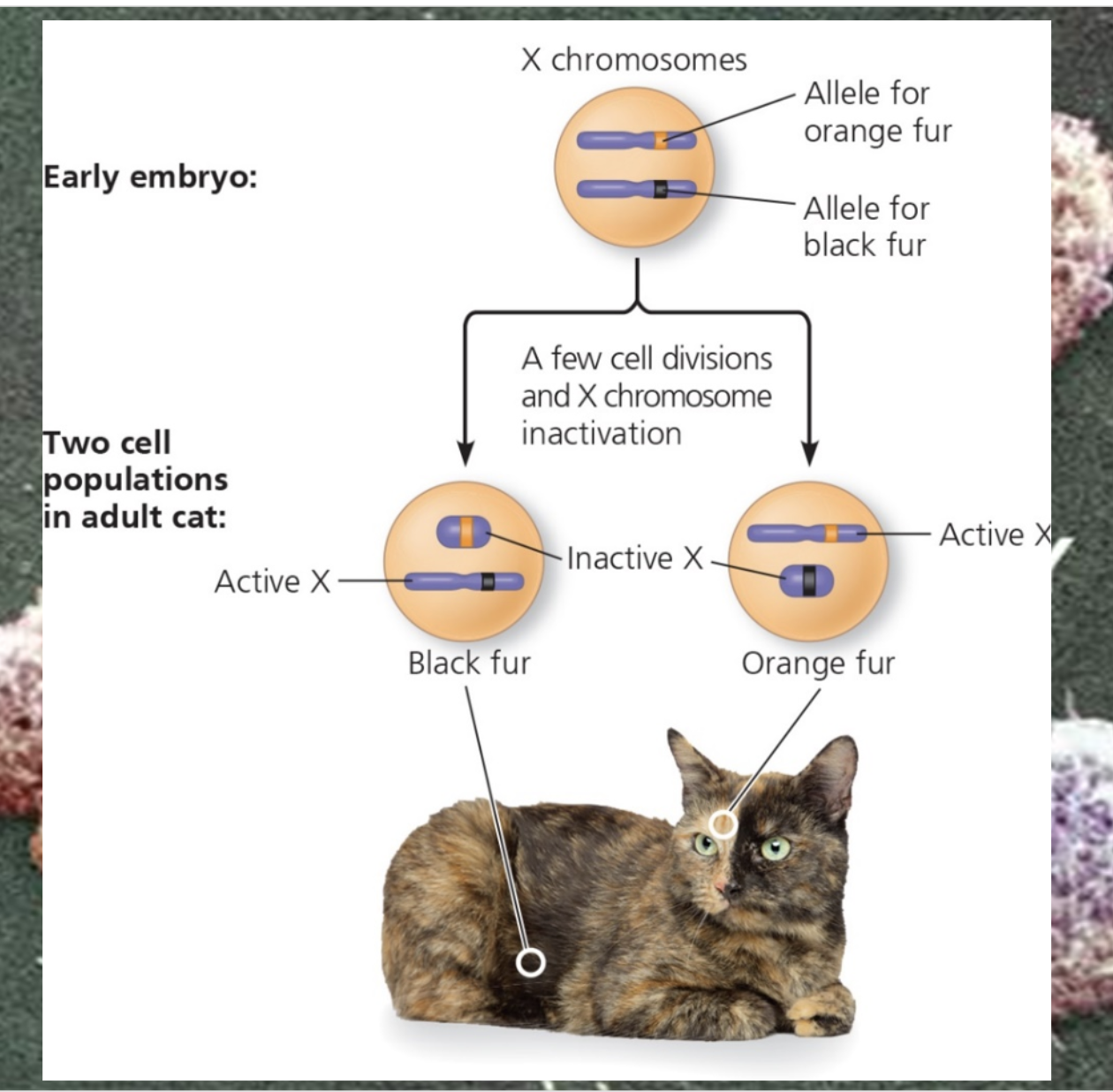
-The various inheritance patterns that can occur when genes are carried on the sex chromosomes, such that females and males have different numbers of alleles of that gene, is termed sex-linked inheritance or sex-linkage
-Genes on the Y chromosome are called Y-linked genes
-Genes on the X chromsome are called X-linked genes
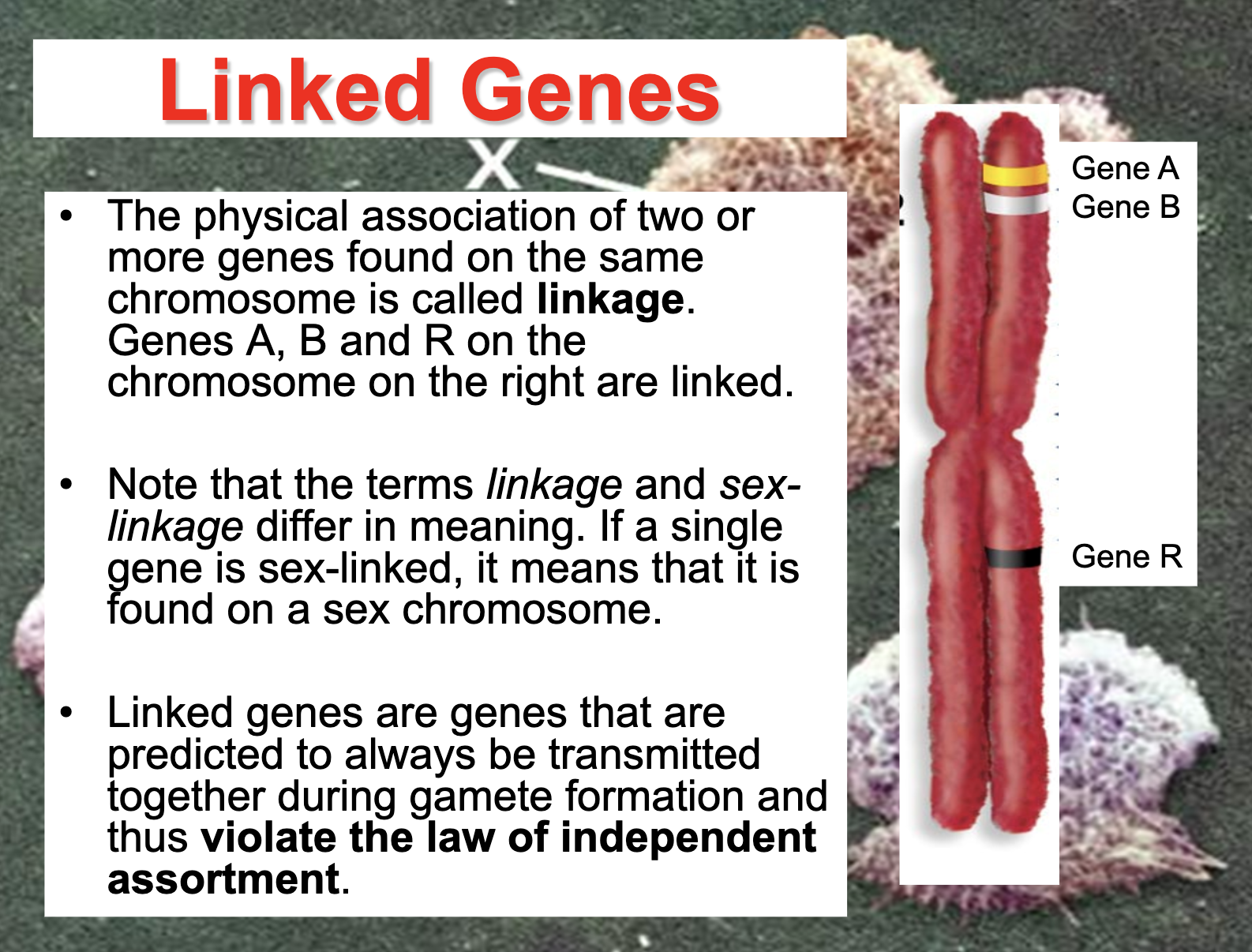
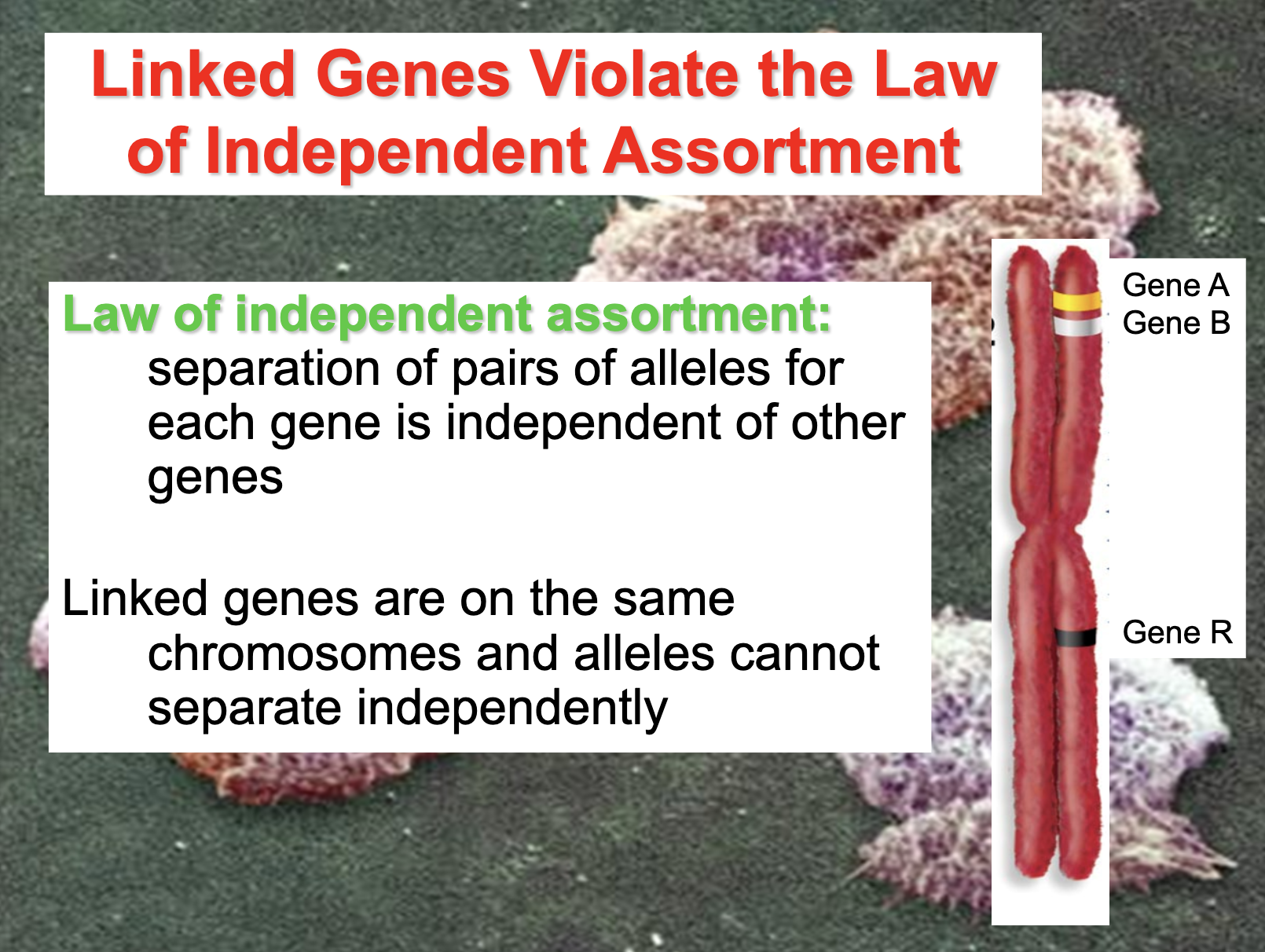
Understand the term linkage (and how it differs from sex linkage).
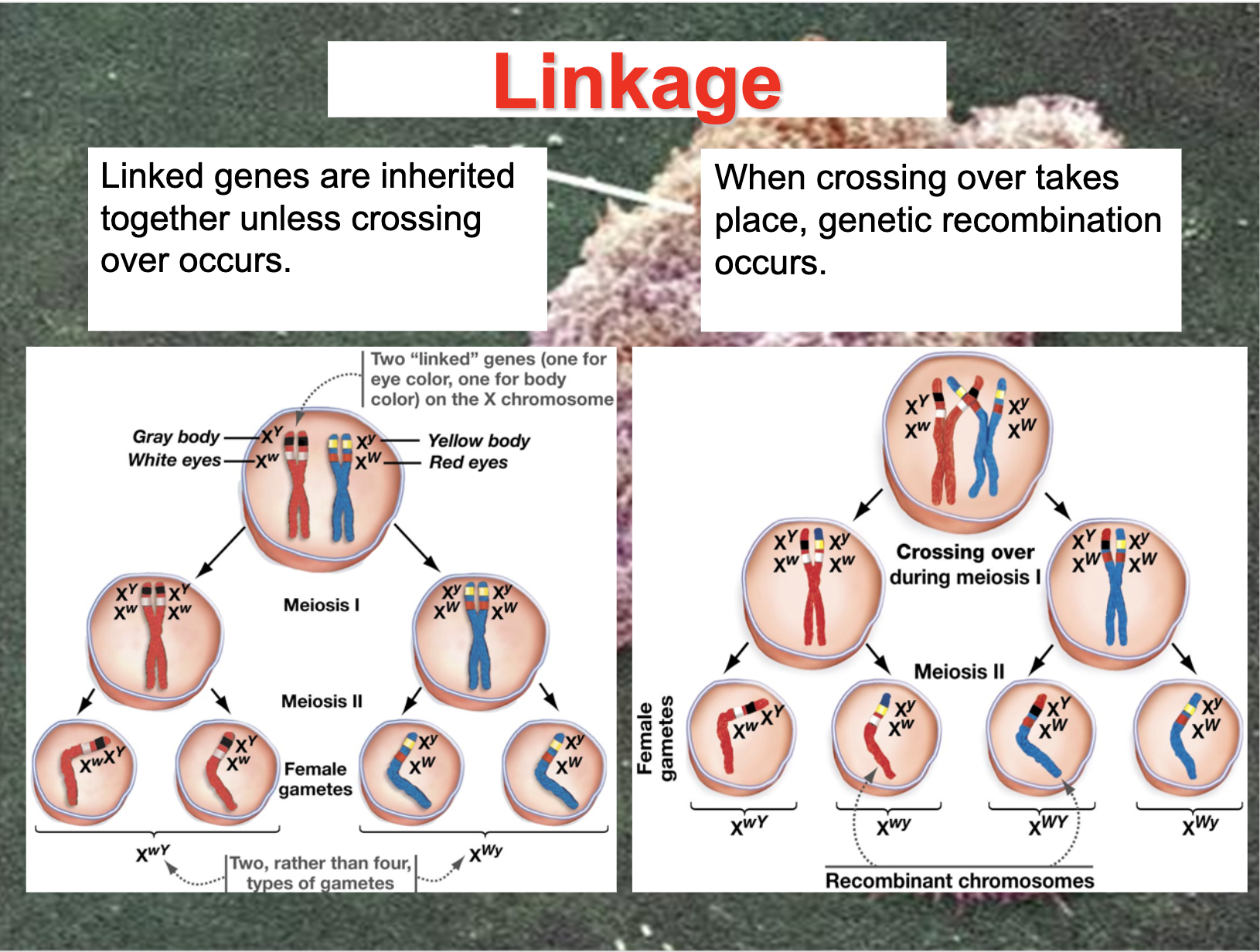
*Linkage means that the gene is on the same chromosome which makes it violate the principle of segregation
*Sex linkage means that the gene is located in the sex chromosome
Be able to detect linkage and determine offspring ratios in crosses between linked genes.
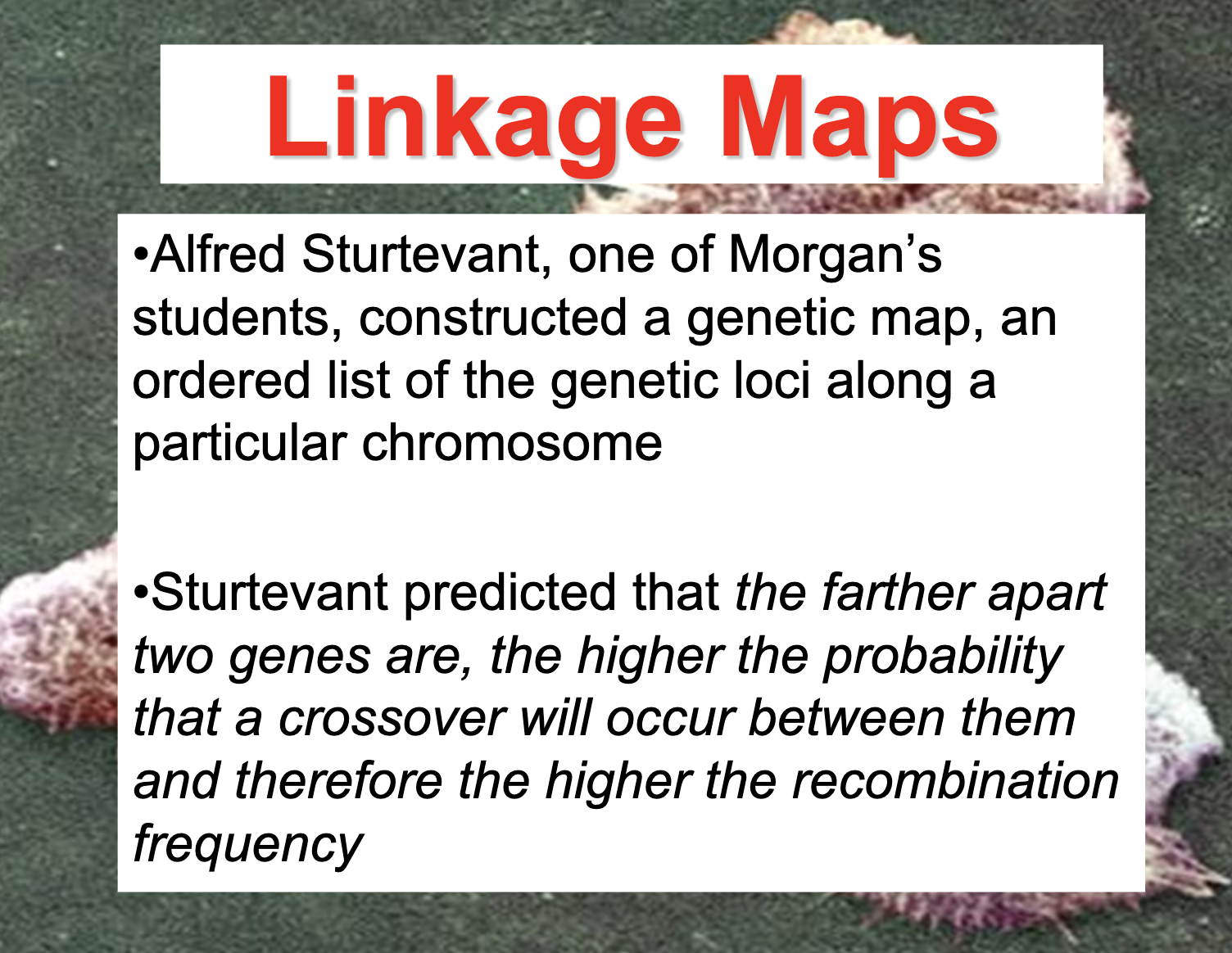
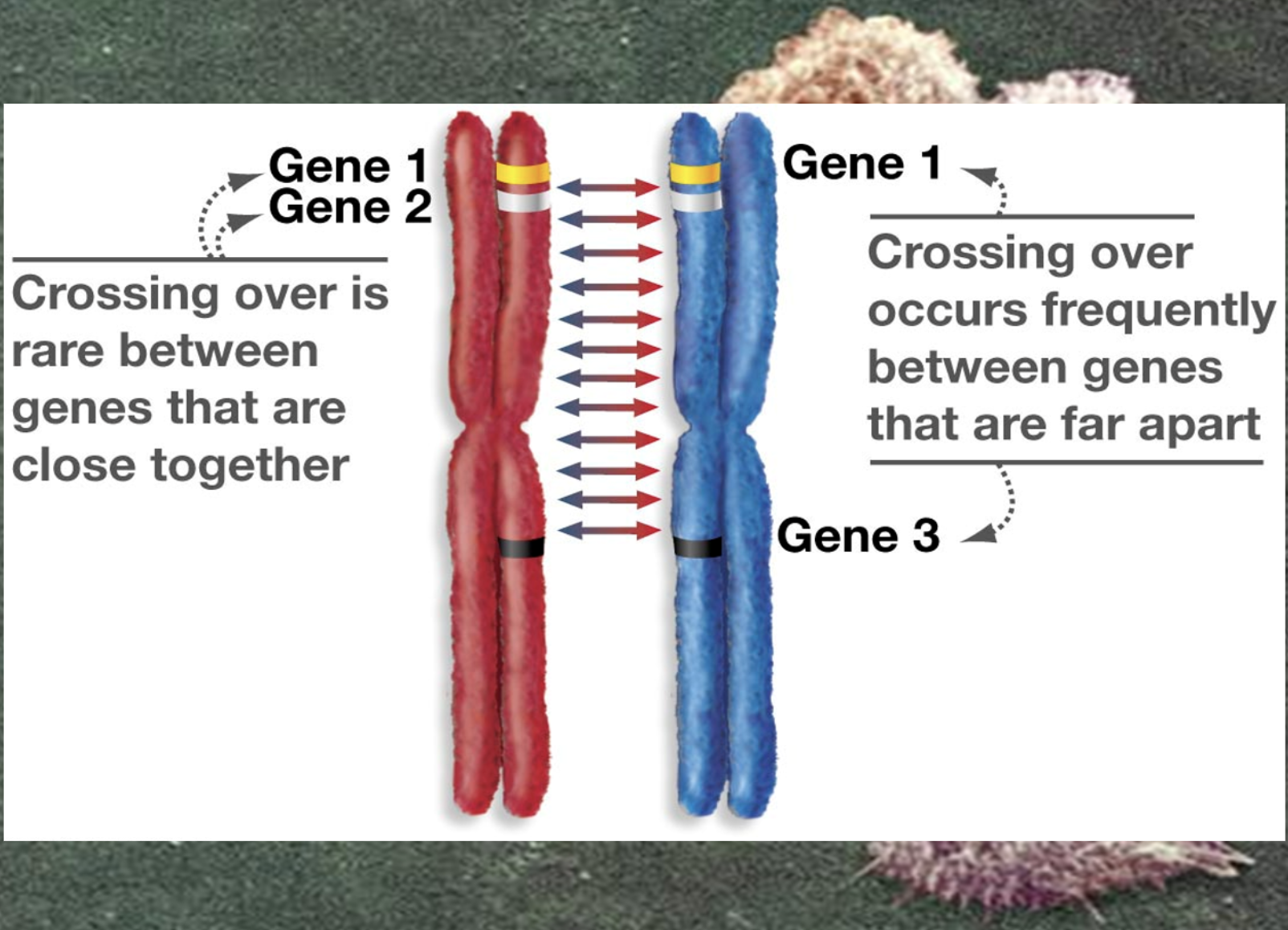
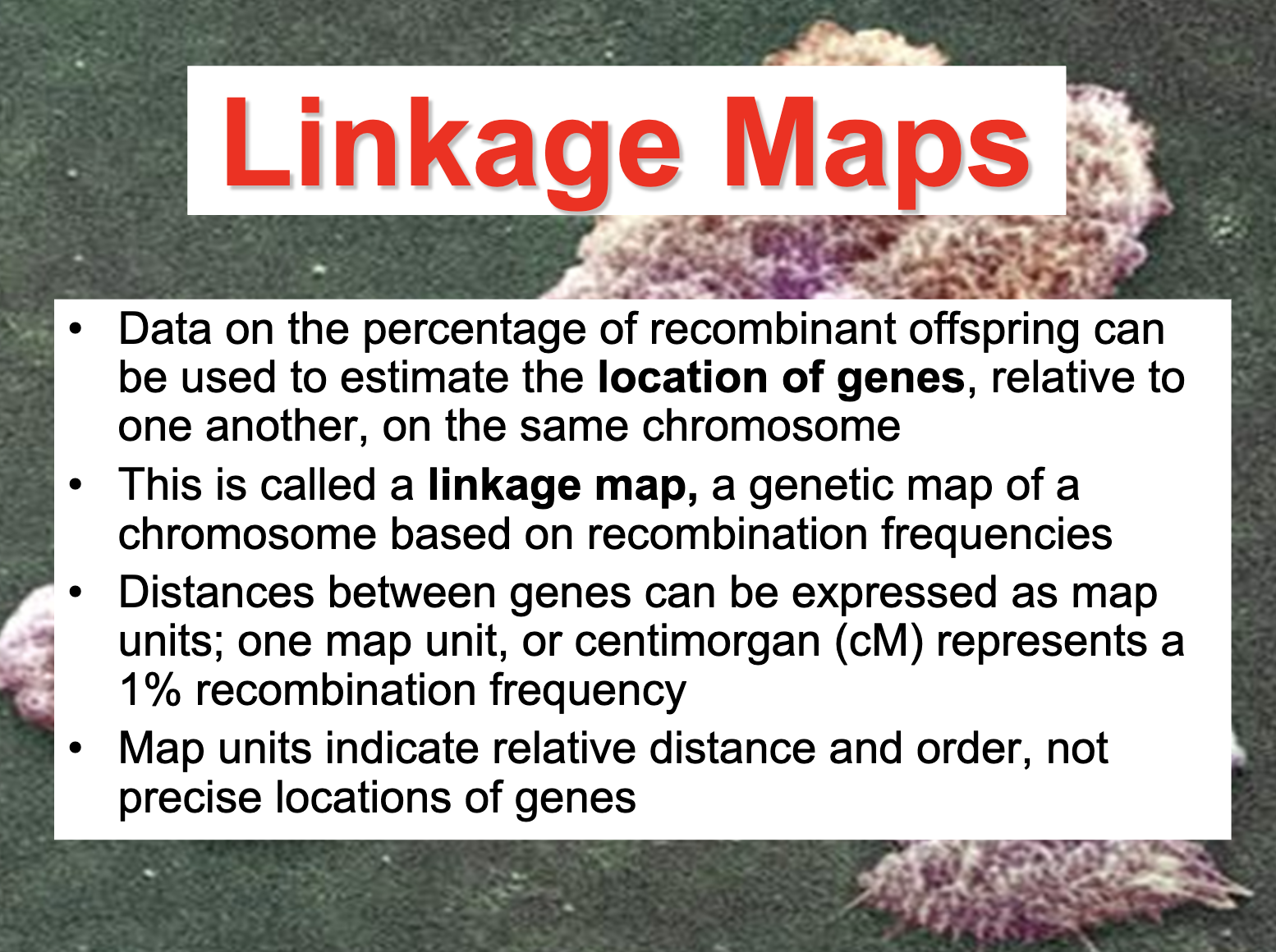
Determine the distance between linked genes.
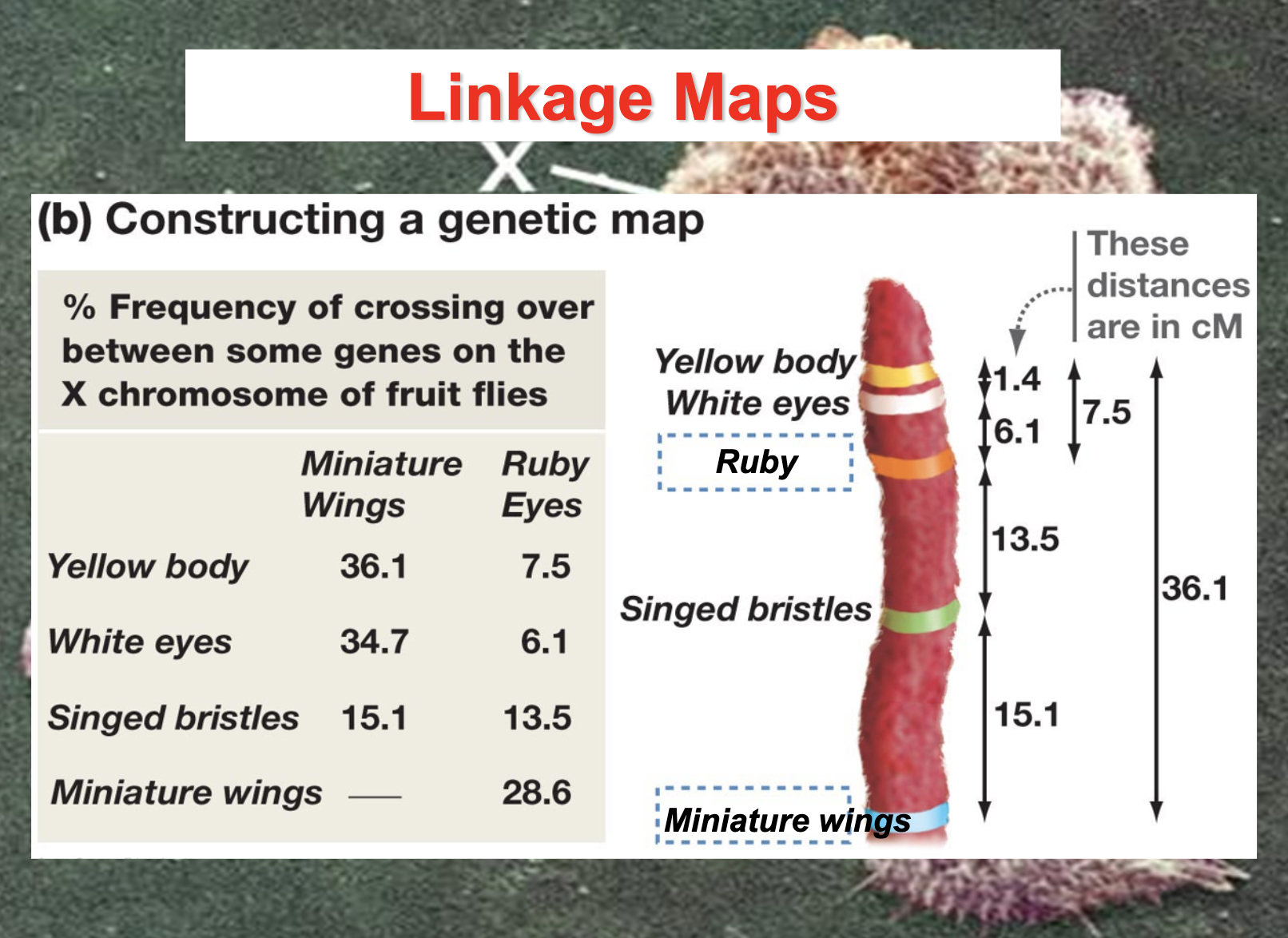
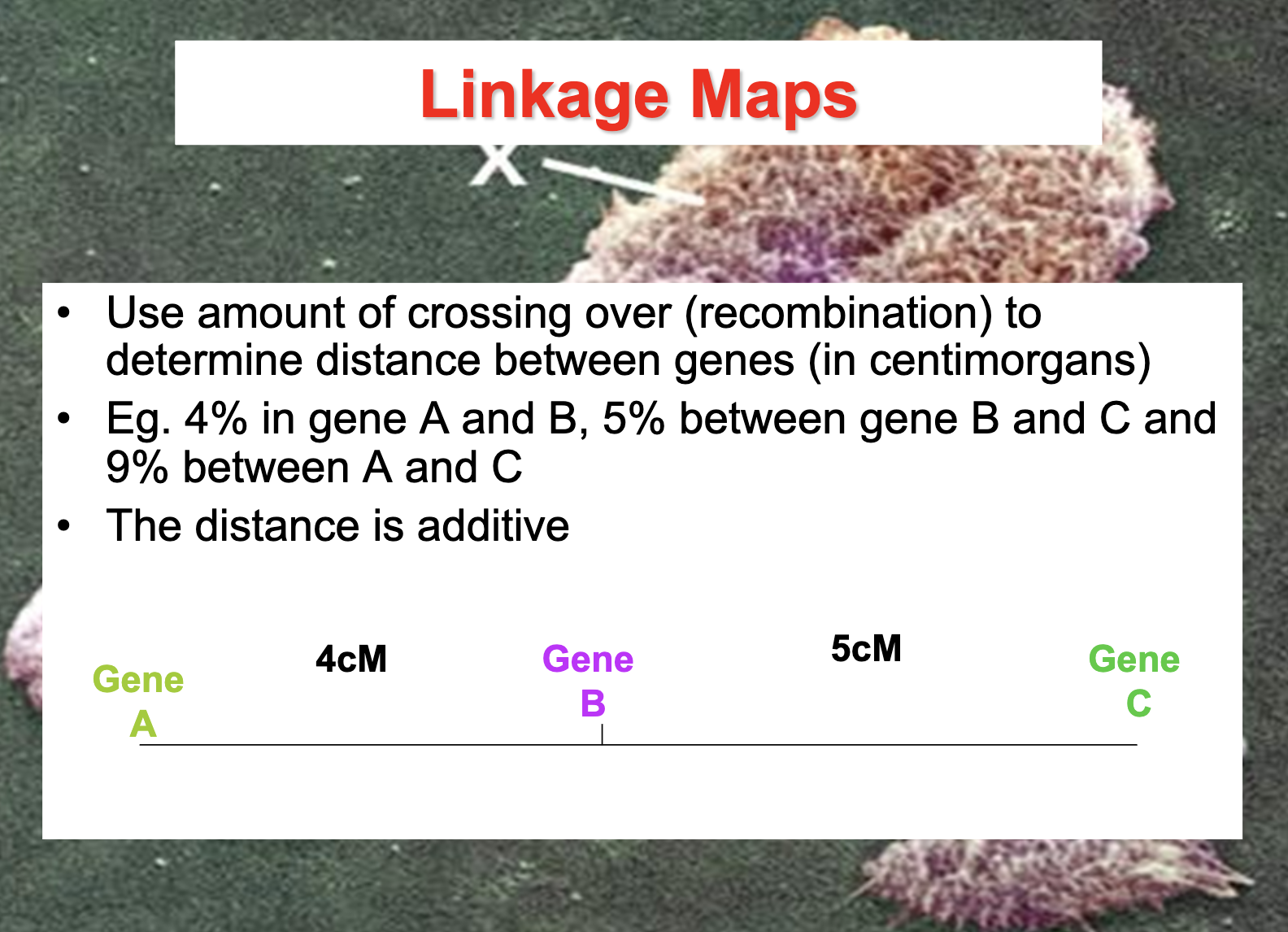
The distance between linked genes are expressed as cM and it expresses the probability to be crossed over. (recombination frequency)
Define the term centimorgan and its relationship to recombinant frequency.
Distances between genes can be expressed as map unit, 1cM represents a 1% recombination frequency
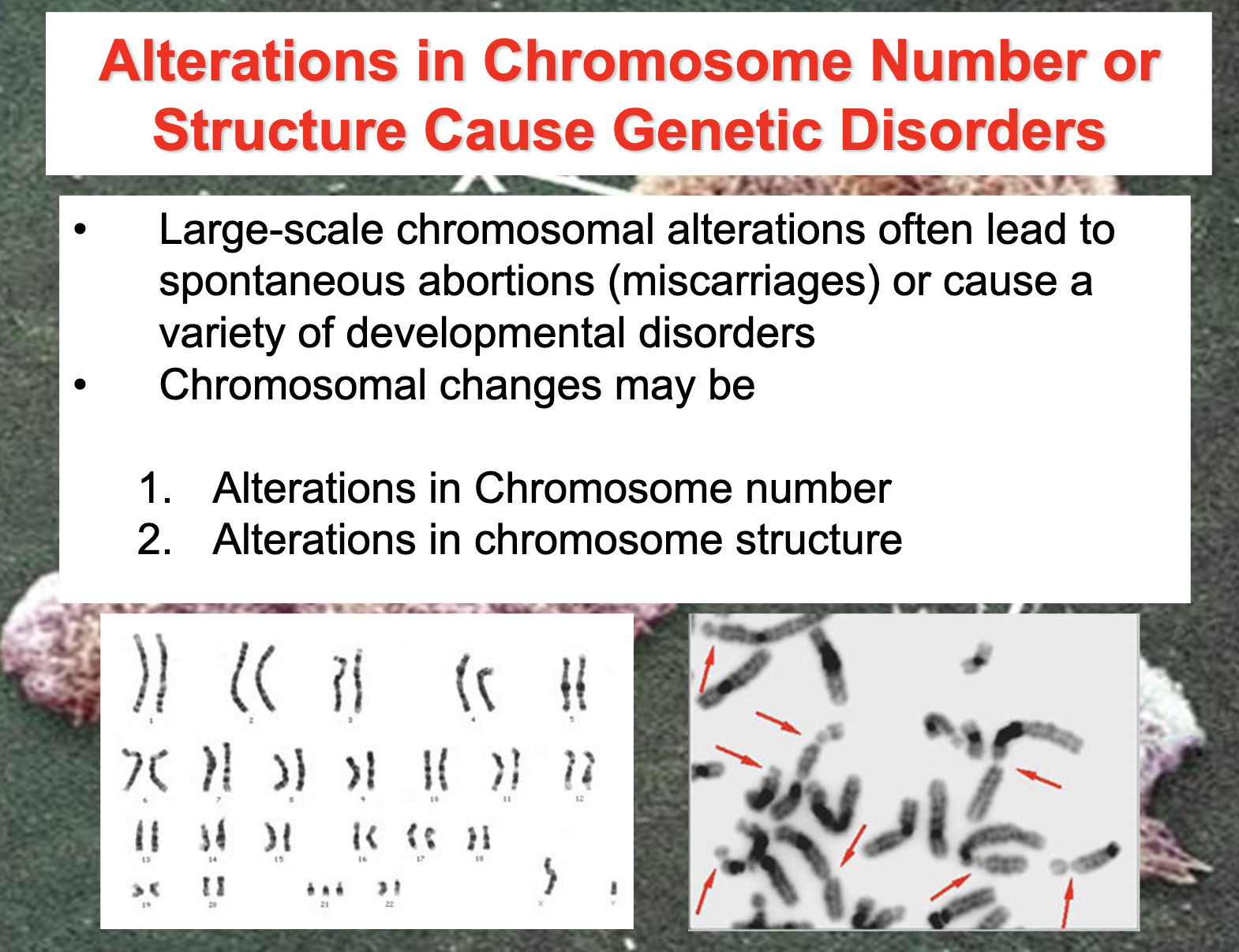
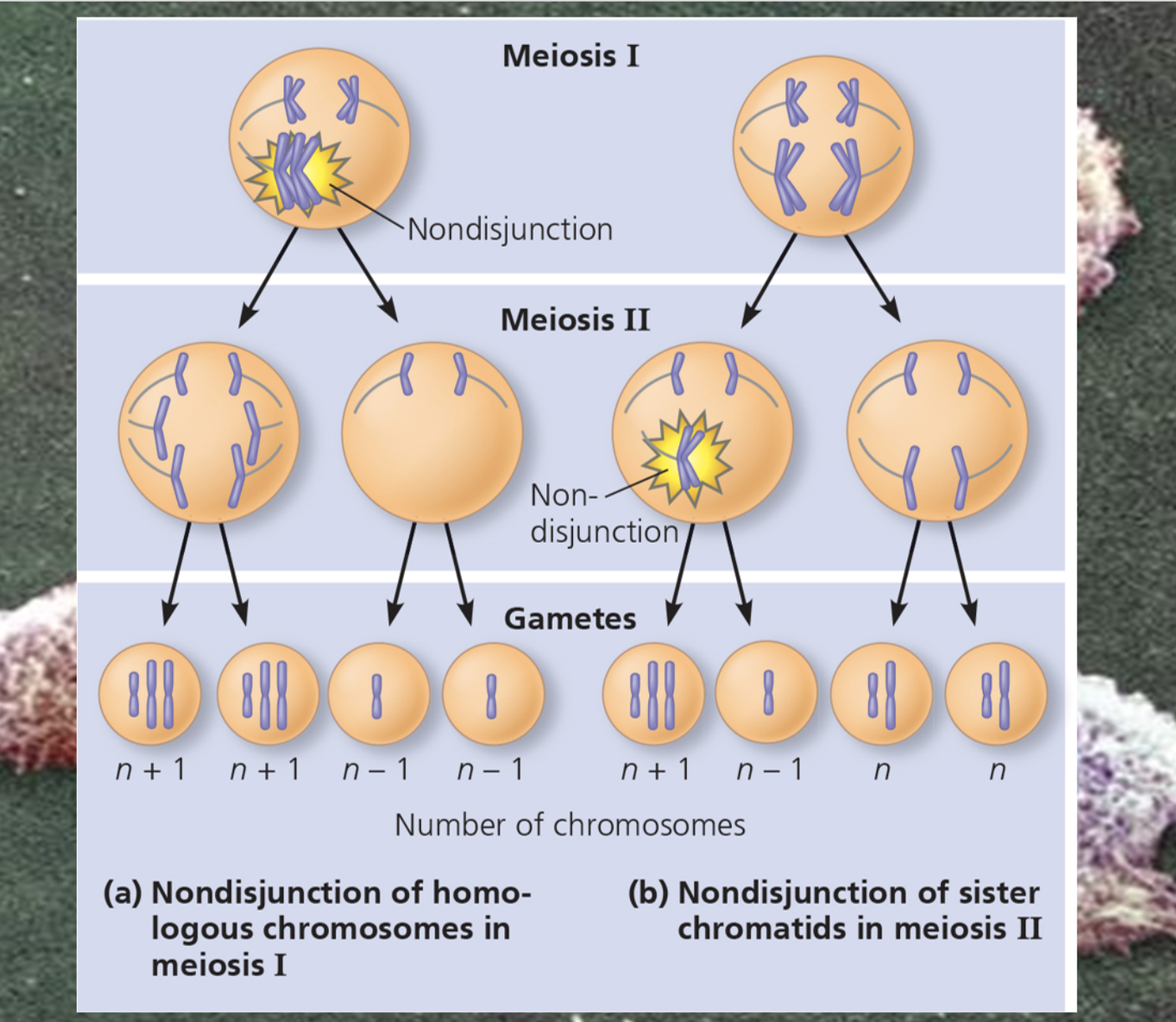
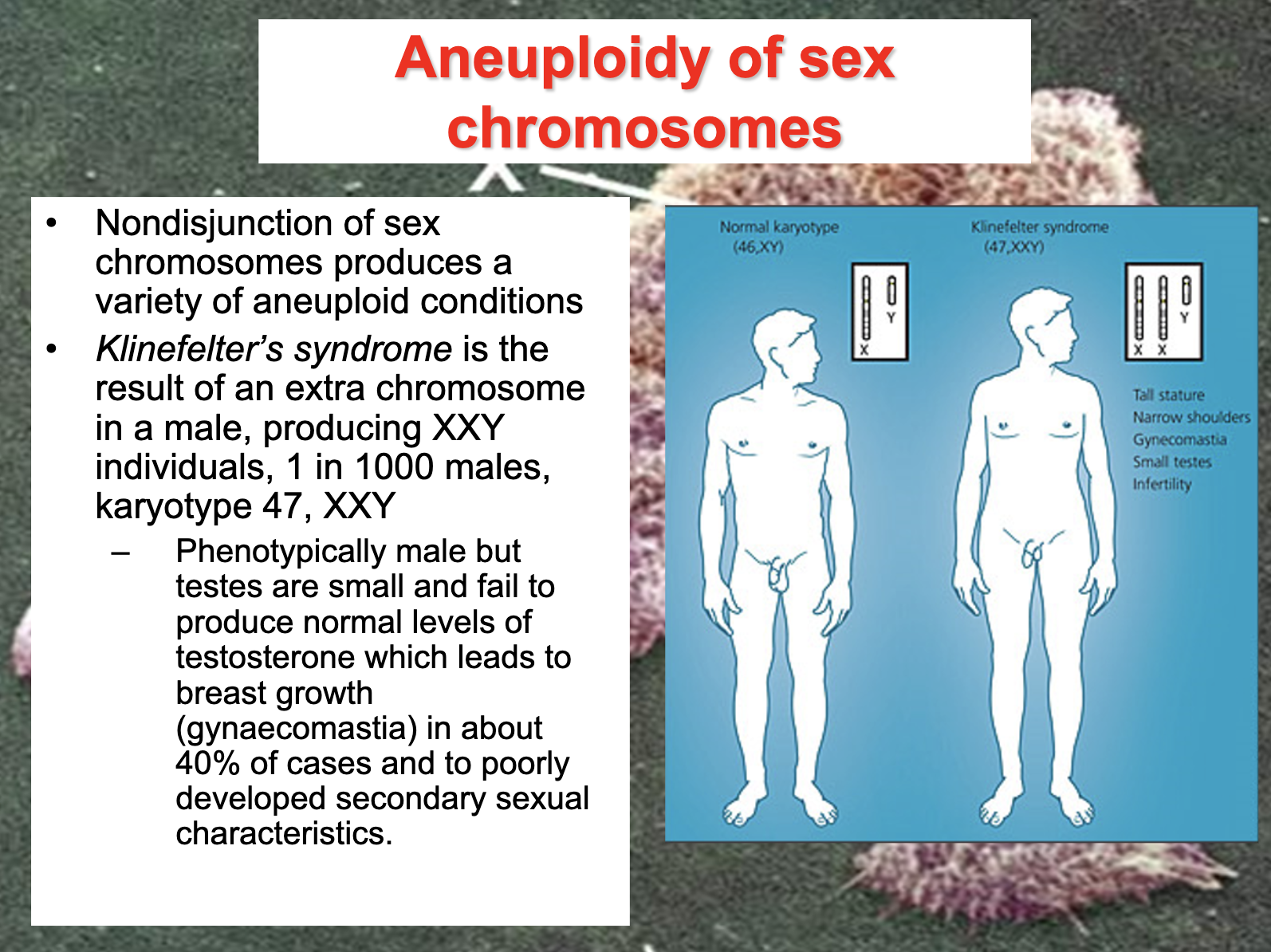
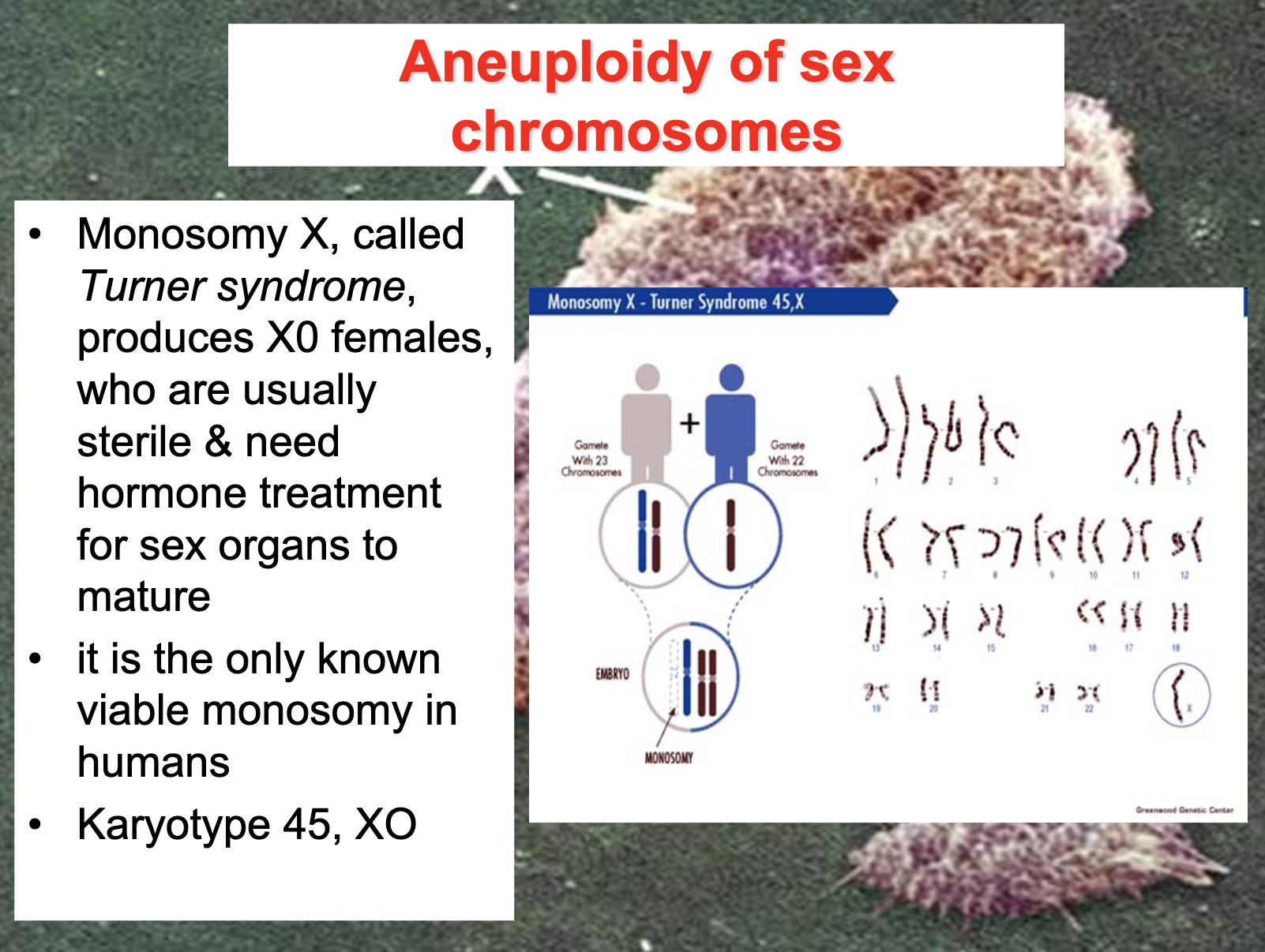
Describe the various aneuploid human conditions and describe and write out their karyotype
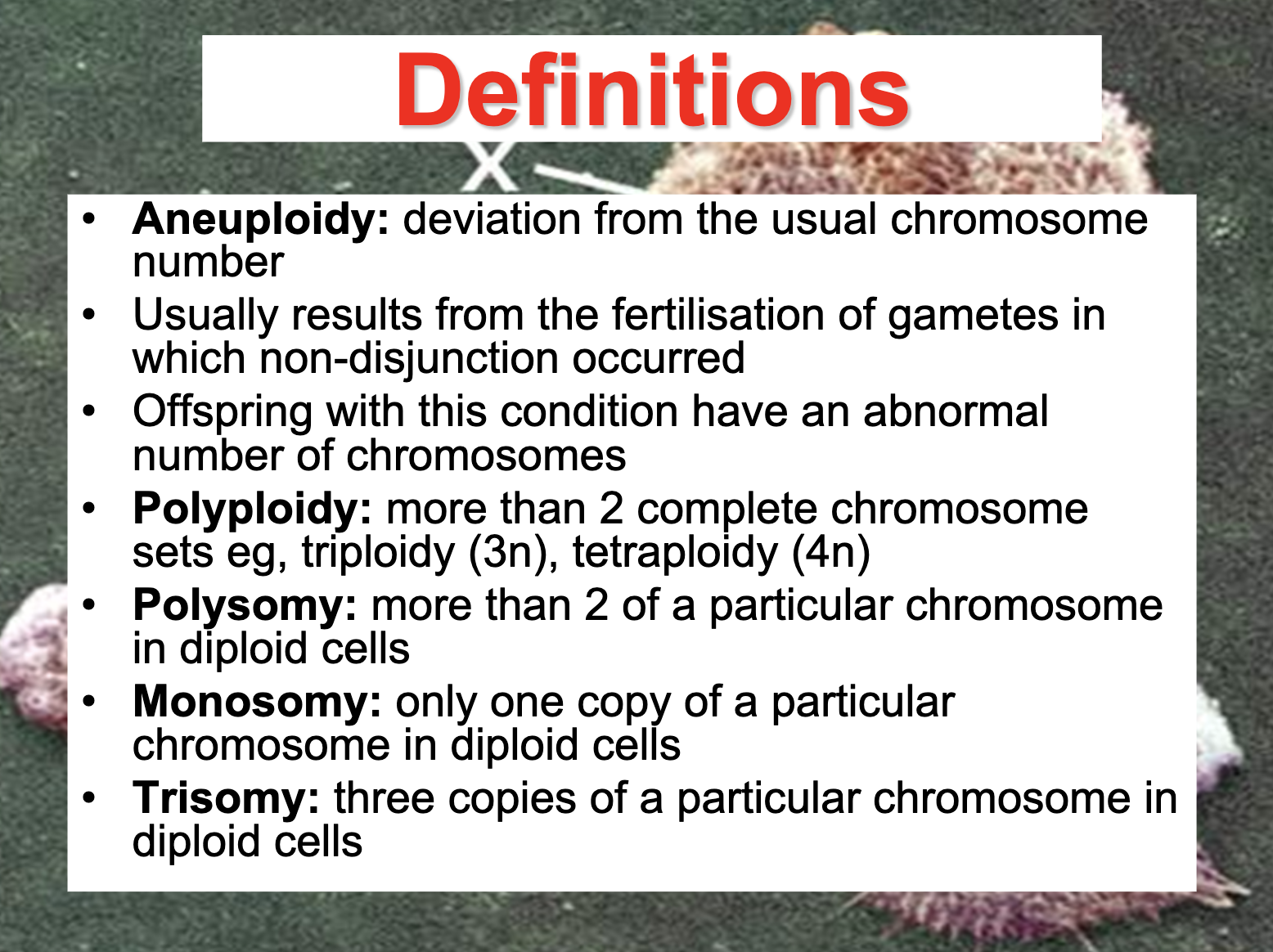
-Aneuploidy : deviation from the usual chromosome number
-Polyploidy : more than 2 complete chromosome sets (3n, 4n)
-Polysomy : more than 2 of a particular chromosome in diploid cells
-Monosomy : only one copy of a particular chromosome in diploid cells
-Trisomy : three copies of a particular chromosome in diploid cells
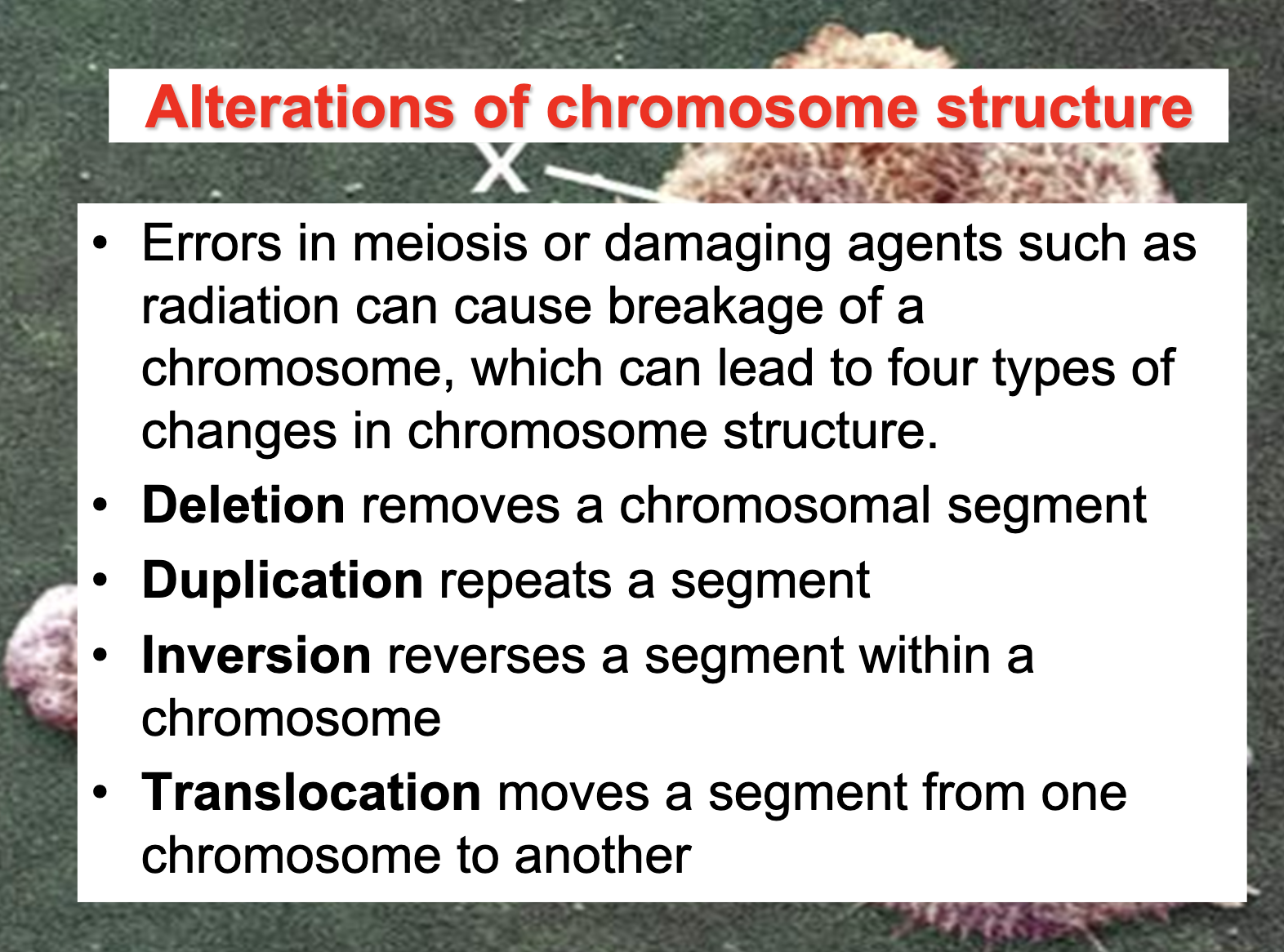
Describe the types of changes that can occur in chromosome structure due to damage and describe a human condition that results from one of these.
-Deletion : removes a chromosomal segment
-Duplication : repeats a segment
-Inversion : reverses a segment within a chromosome
-Translocation : moves a segment from one chromosome to another
PPT

Meiosis and Mendel's Laws

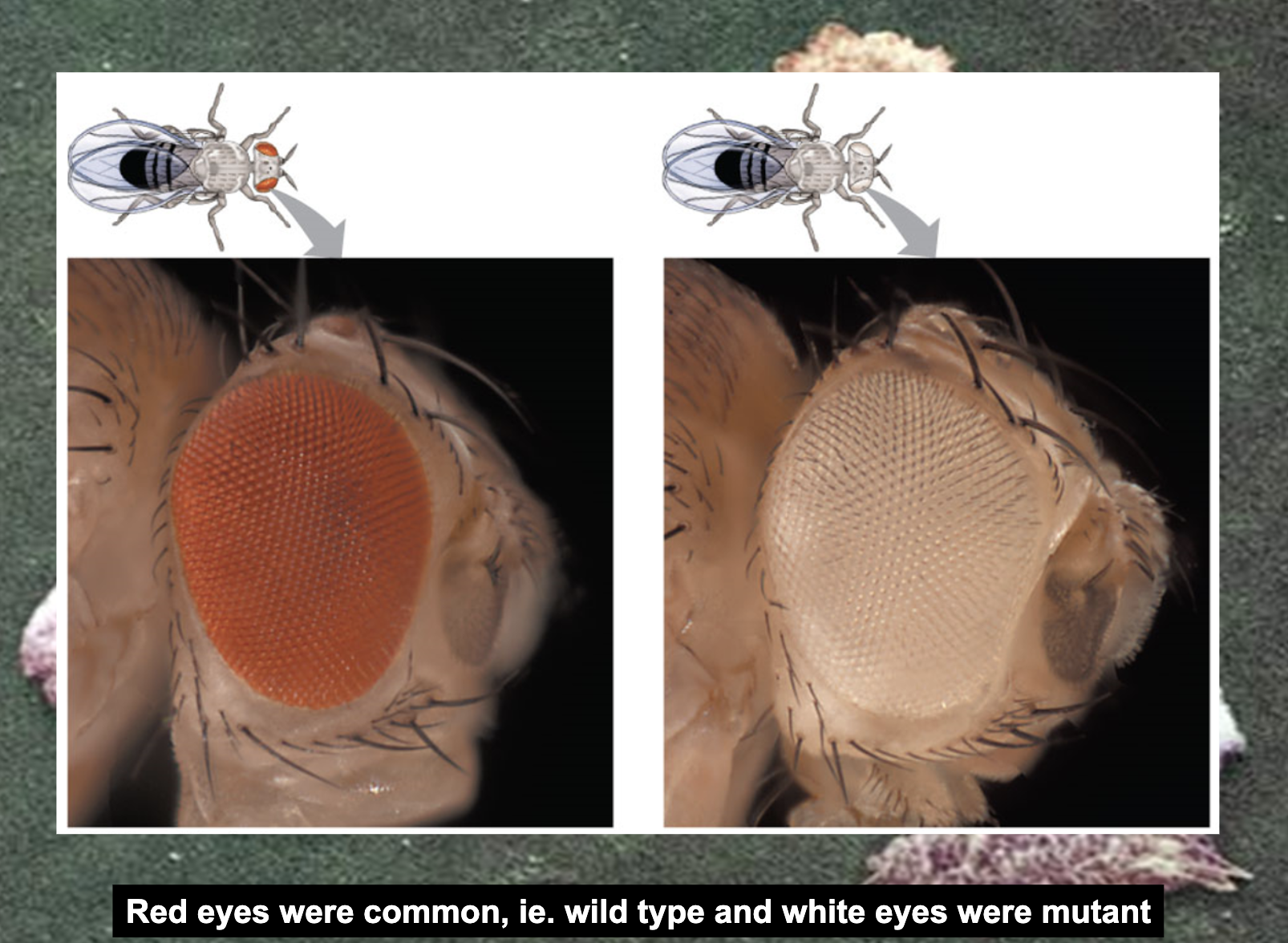
Thomas Hunt Morgan's Experiment




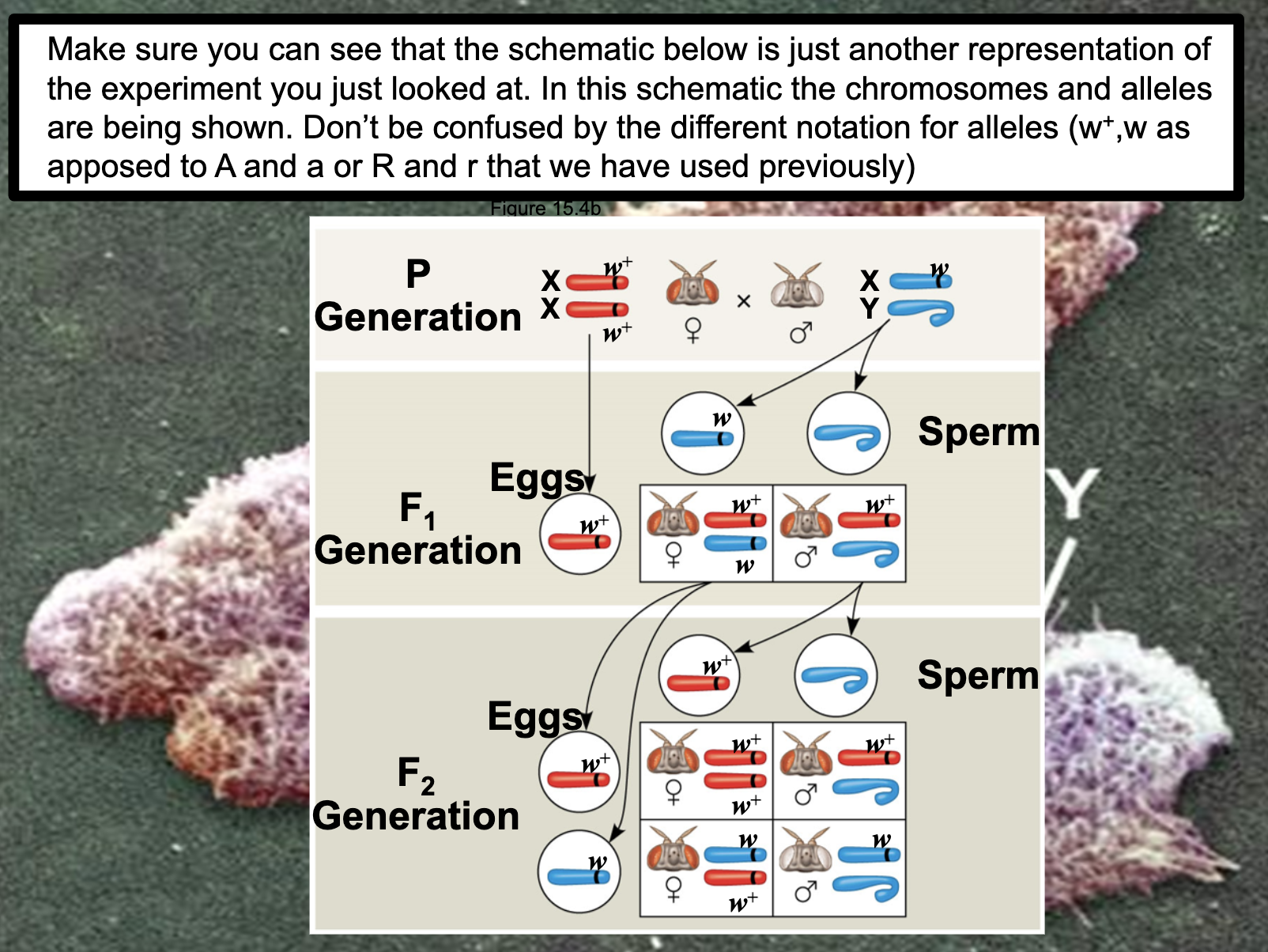

The Chromosomal Basis of Sex

How linkage affects inheritance

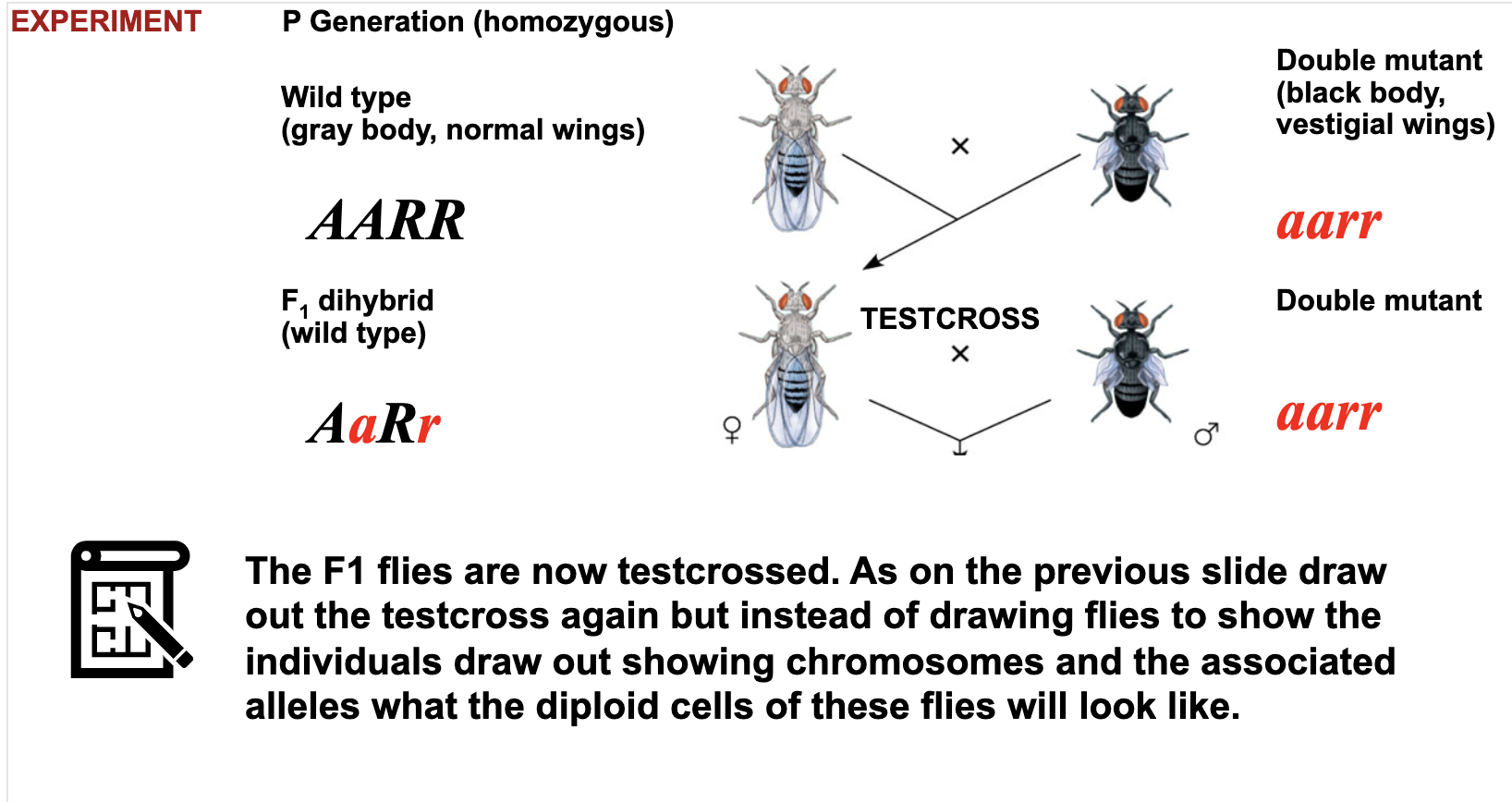
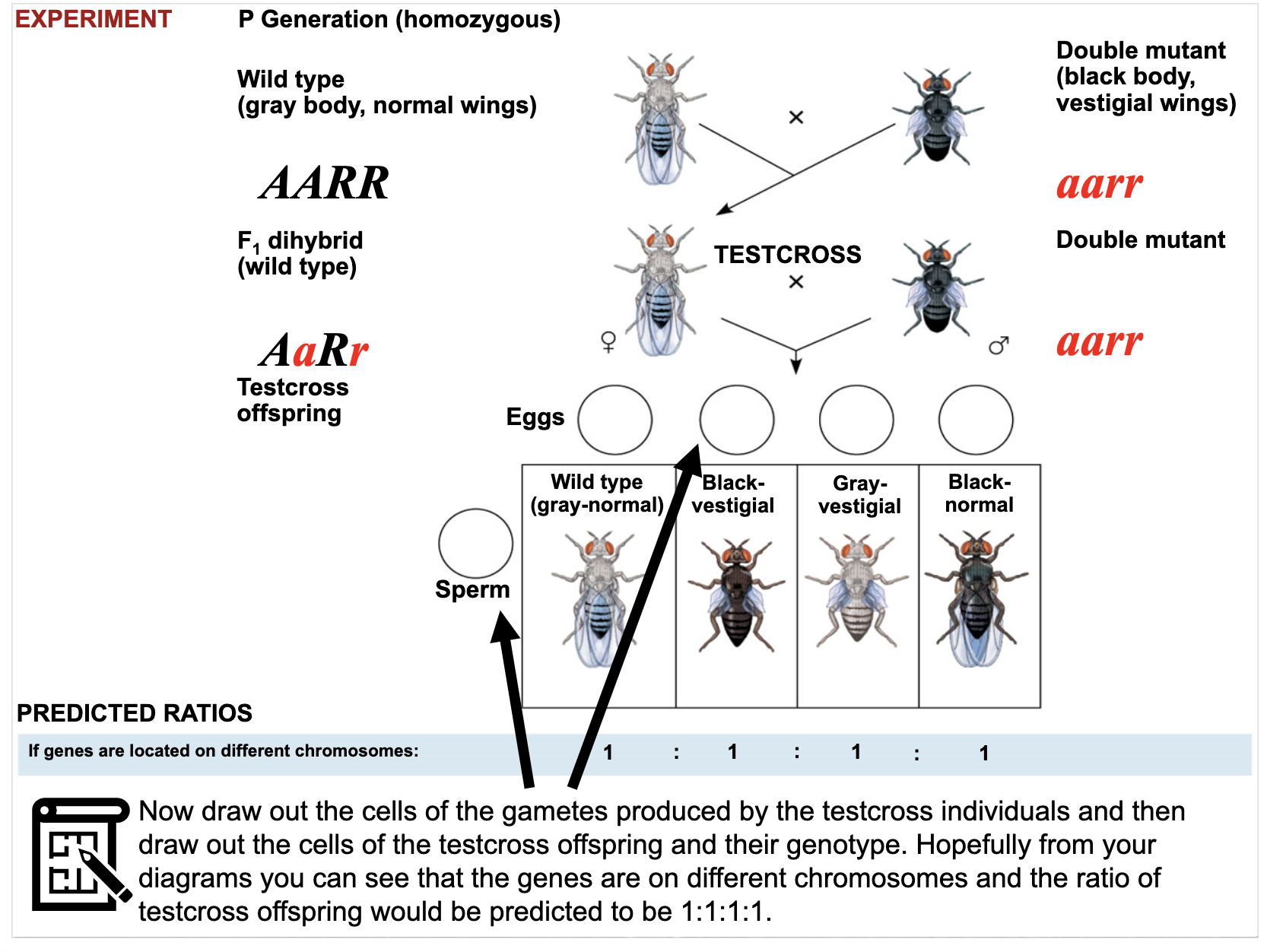

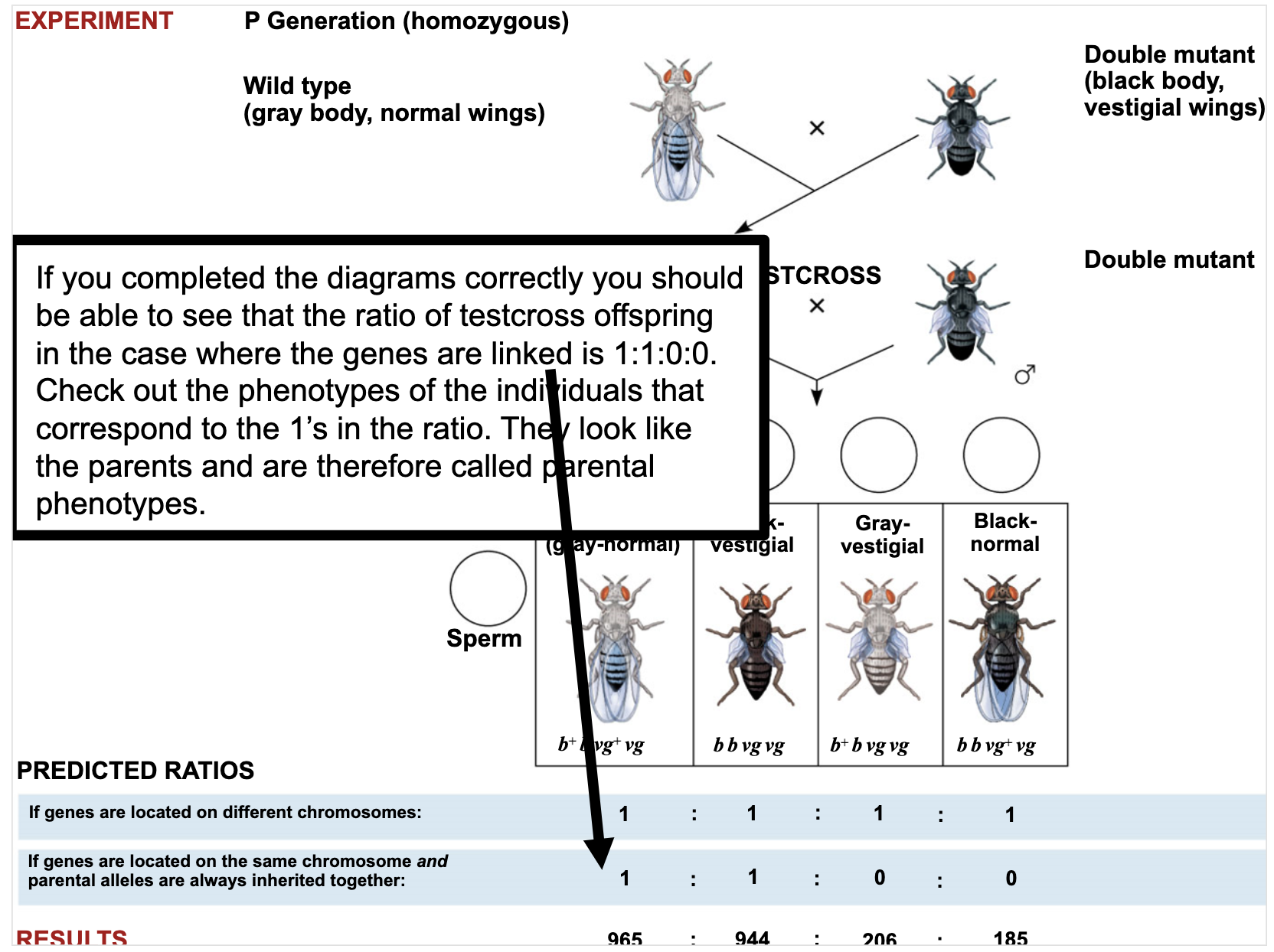
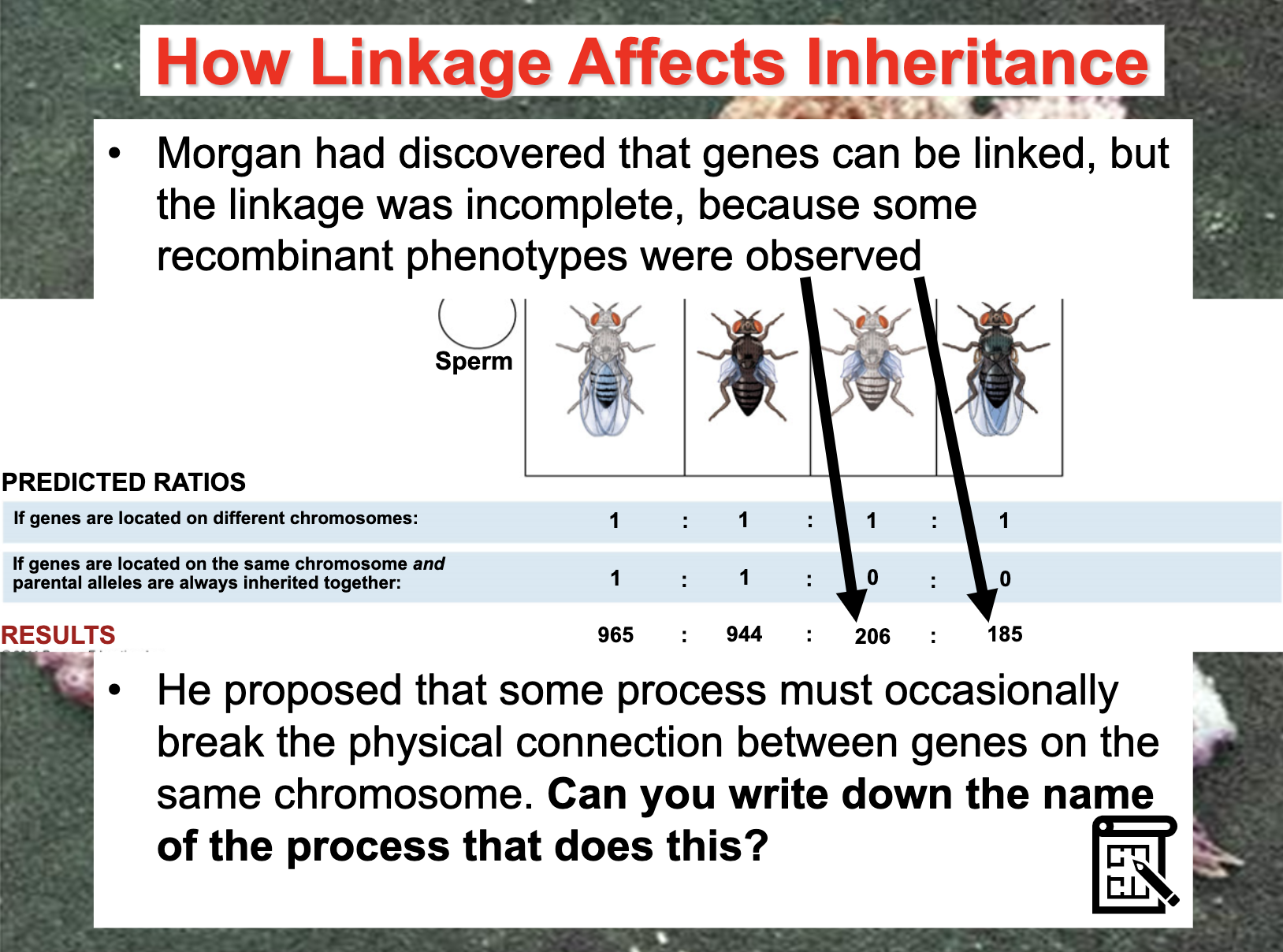

Linkage maps
Distances between genes can be expressed as map unit, 1cM represents a 1% recombination frequency

Alteration in chrosome number or structure case genetic disorders


SELF PACED QUIZ


-polysomy
: abnormal number of chromosomes in a specific number of chromosome set
: more than 2 of a particular chromosome in diploid cells
-polyloidy
: like 2n, 3n.. deviated set of chromosome from 2n
: more than 2 complete chromosome sets in somatic cells
: triploidy means 3 chromosomes are considered as one set, tetraploidy means 4 chromosomes are binded as one set
-A triploid human somatic cell would contain 46 + an extra 23 chromosomes


-cM is the unit to express the genetic distance
-genetic distance does not represent the actual distance, it expresses the 1% of recombination of frequency

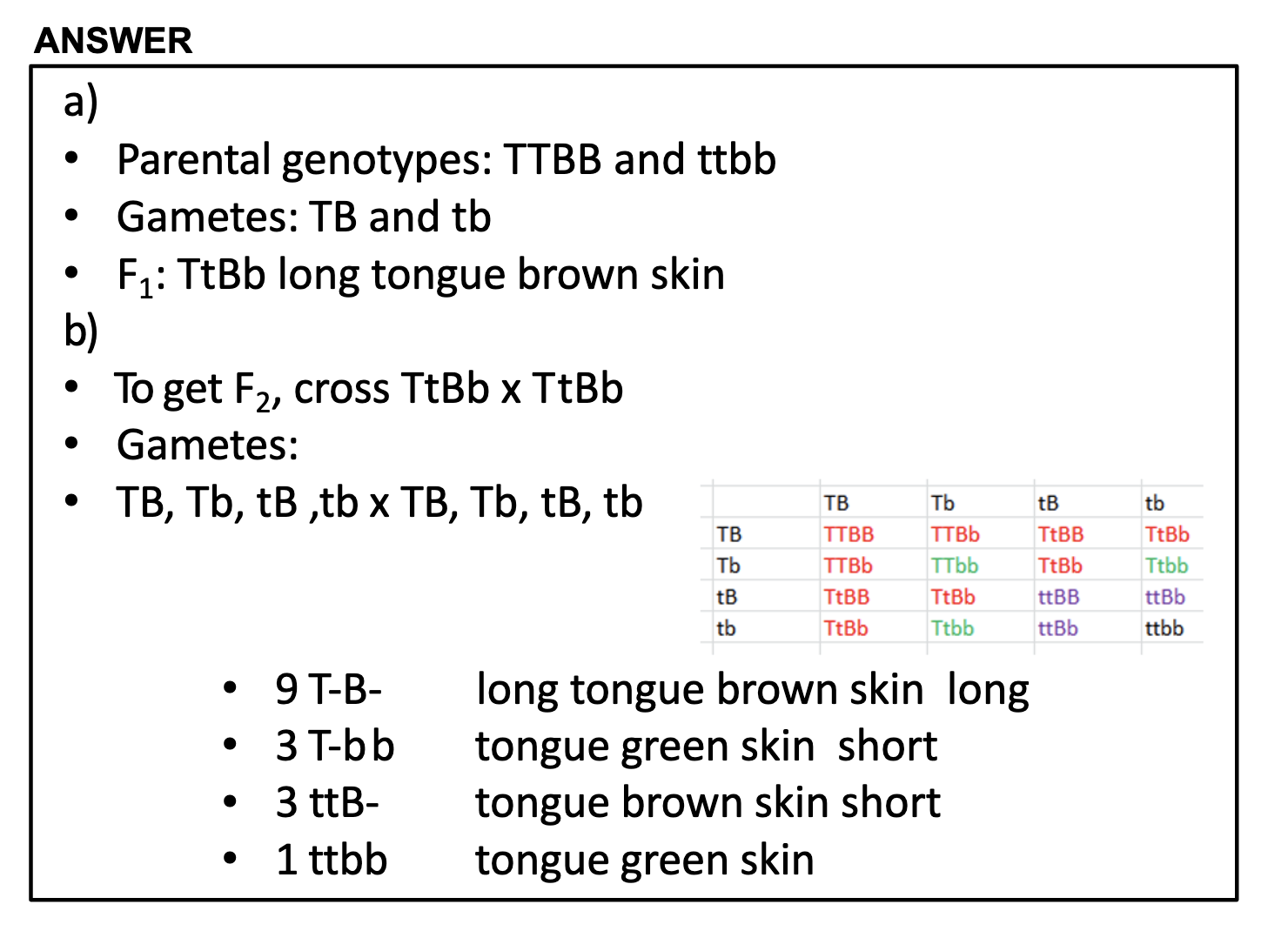
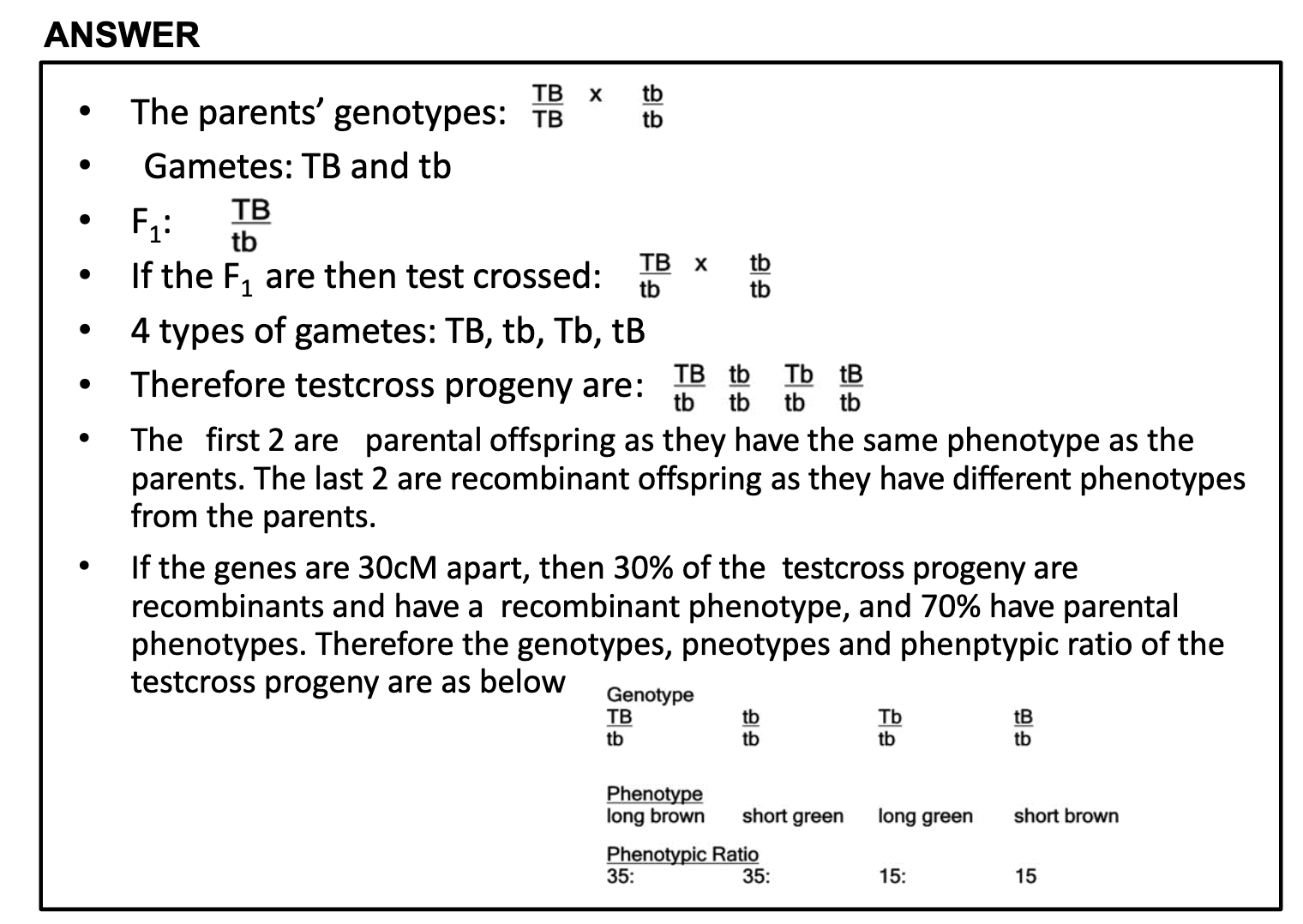
a) TTBB x ttbb -> TB x tb => TtBb is the genotype of F1 , long tongue brown skin for a phenotype
b) TtBb x TtBb => TB, Tb, tB, tb x TB, Tb, tB, tb => T-B-: T-bb : ttB- : ttbb = 9:3:3:1
Long tongue, brown skin : Long tongue, green skin : Short tongue, brown skin : Short tongue, green skin


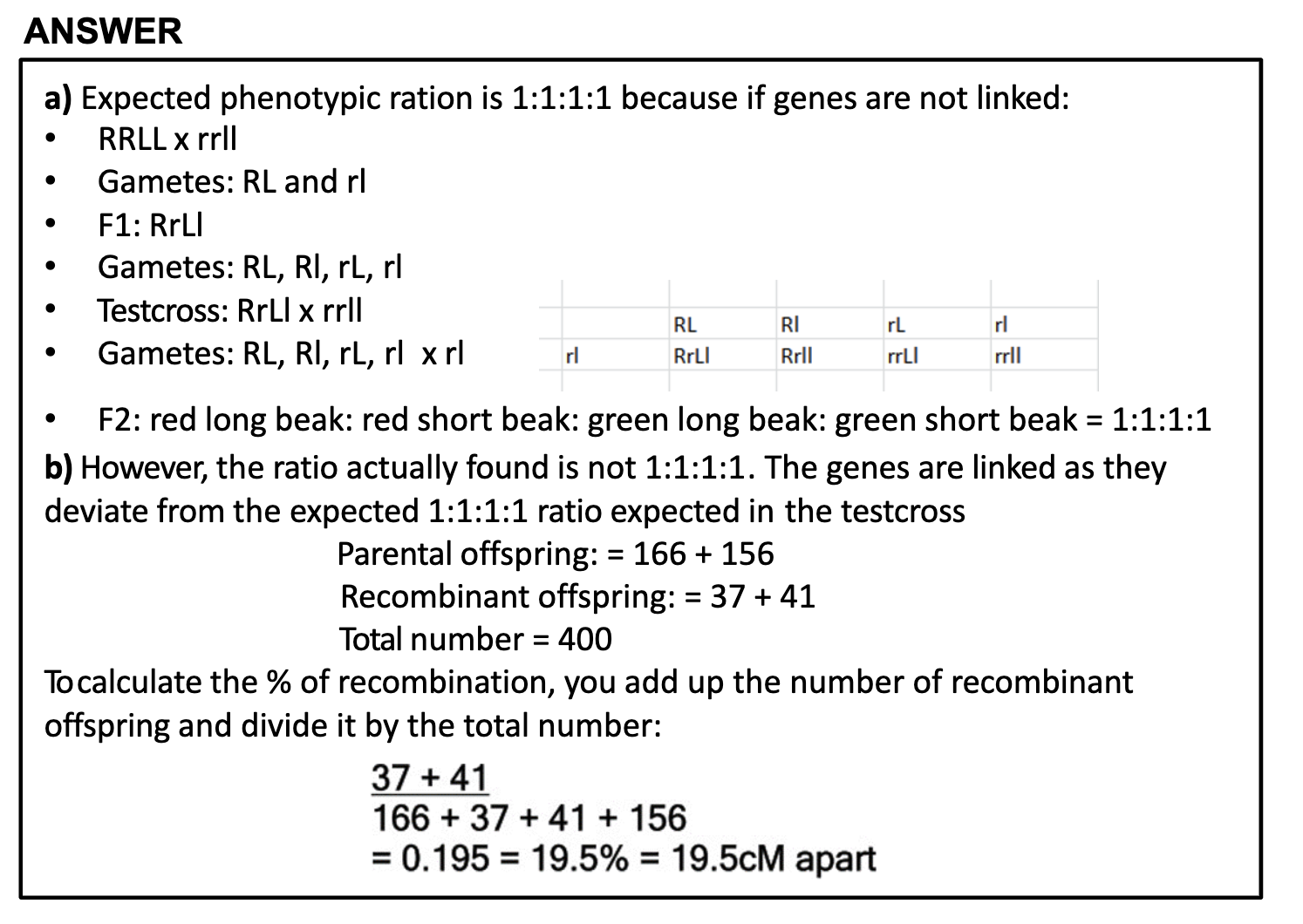
(a) RRLL x rrll -> RL x rl => RrLl (F1)
RrLl x rrll -> RL, Rl, rL, rl x rl => RrLl, Rrll,rrLl, rrll (F2) phenotypic ratio => R-L-: R-ll : rrL-: rrll = 1:1:1:1
(b) RL/RL x rl/rl -> RL x rl => RL/rl (F1)
RL/rl x rl/rl -> RL, rl x rl => RL/rl, rl/rl (parental) + Rl/rl, rL/rl (recombinant by testcross)
-> red long , green short (parental) + red short, green long (recombinant)
-> 166, 156 + 37, 41
37+41/166+156+37+41 = 0.195
19.5% = 19.5 cM
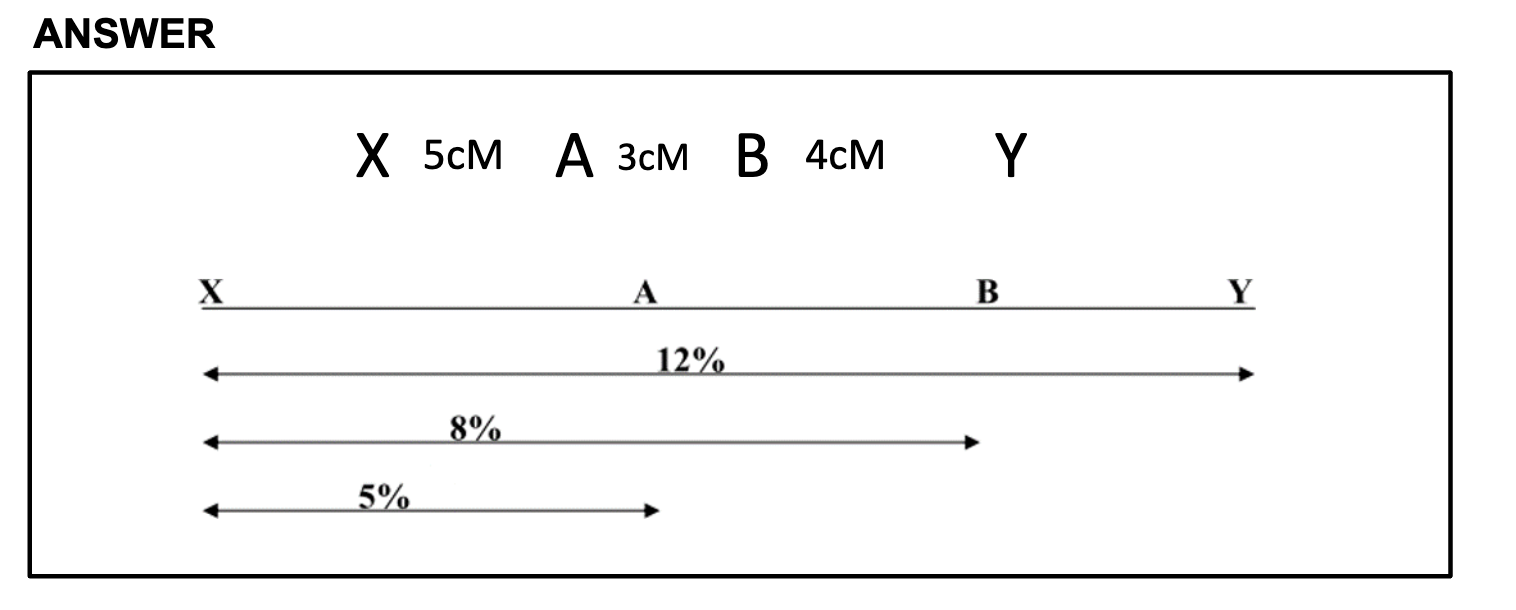




Turner syndrome
-> only affects female, when one of X chromosome is missing
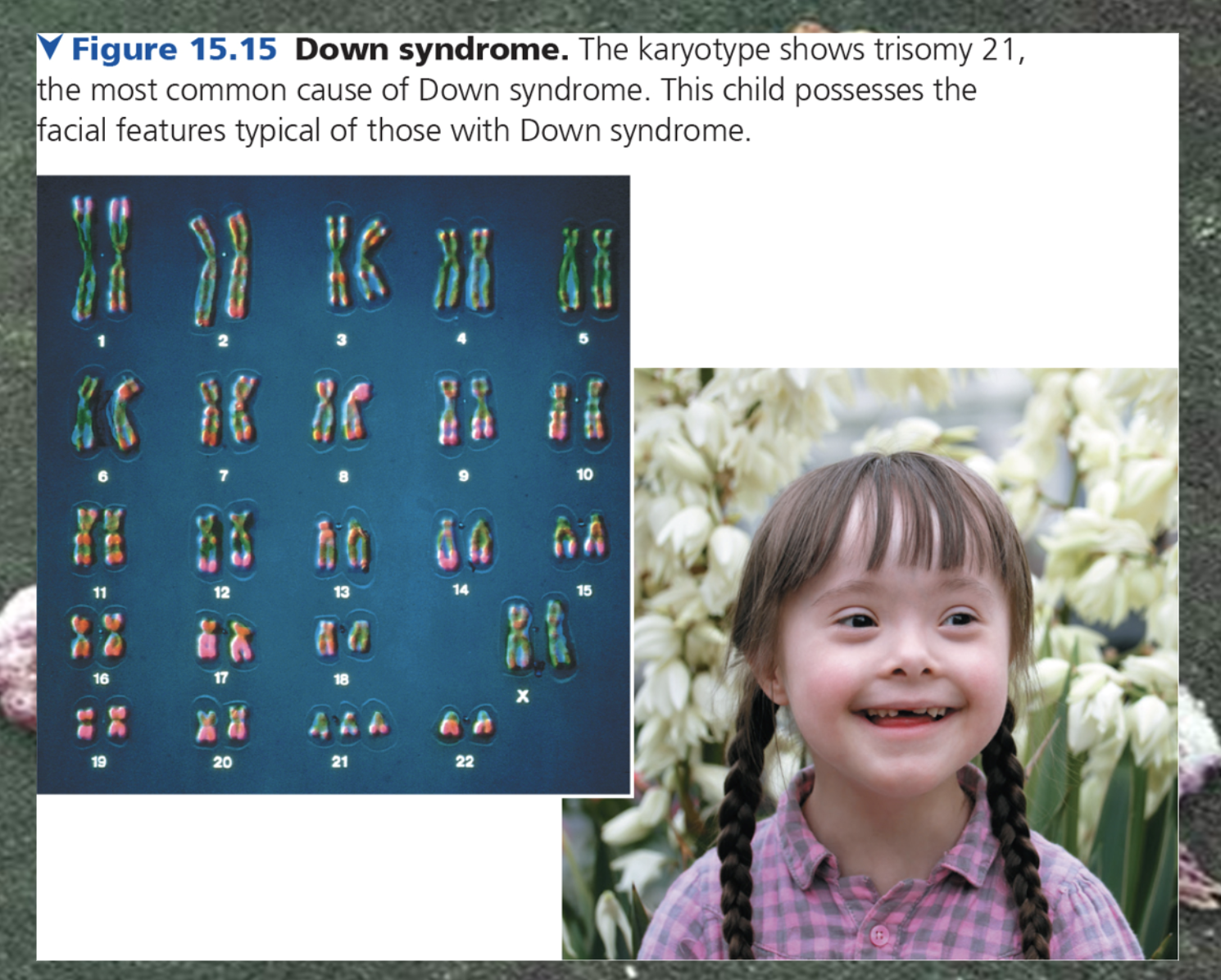
Down syndrome
-> trisomy of chromosome number 21
Duchenne muscular dystropy
-> affects more boys than girls
Cri du chat syndrome
a rare genetic disorder caused by missing pieces on a particular chromosome
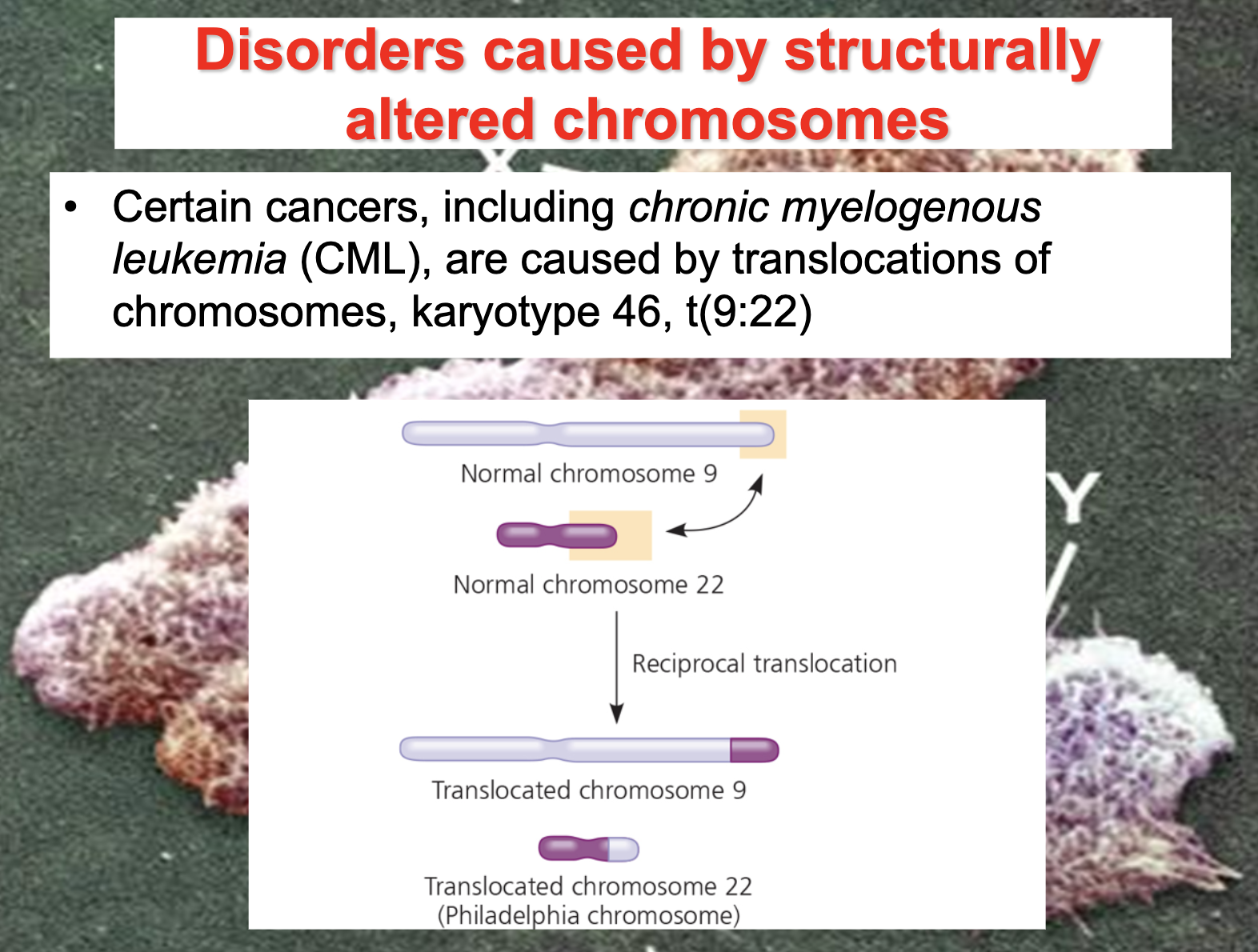
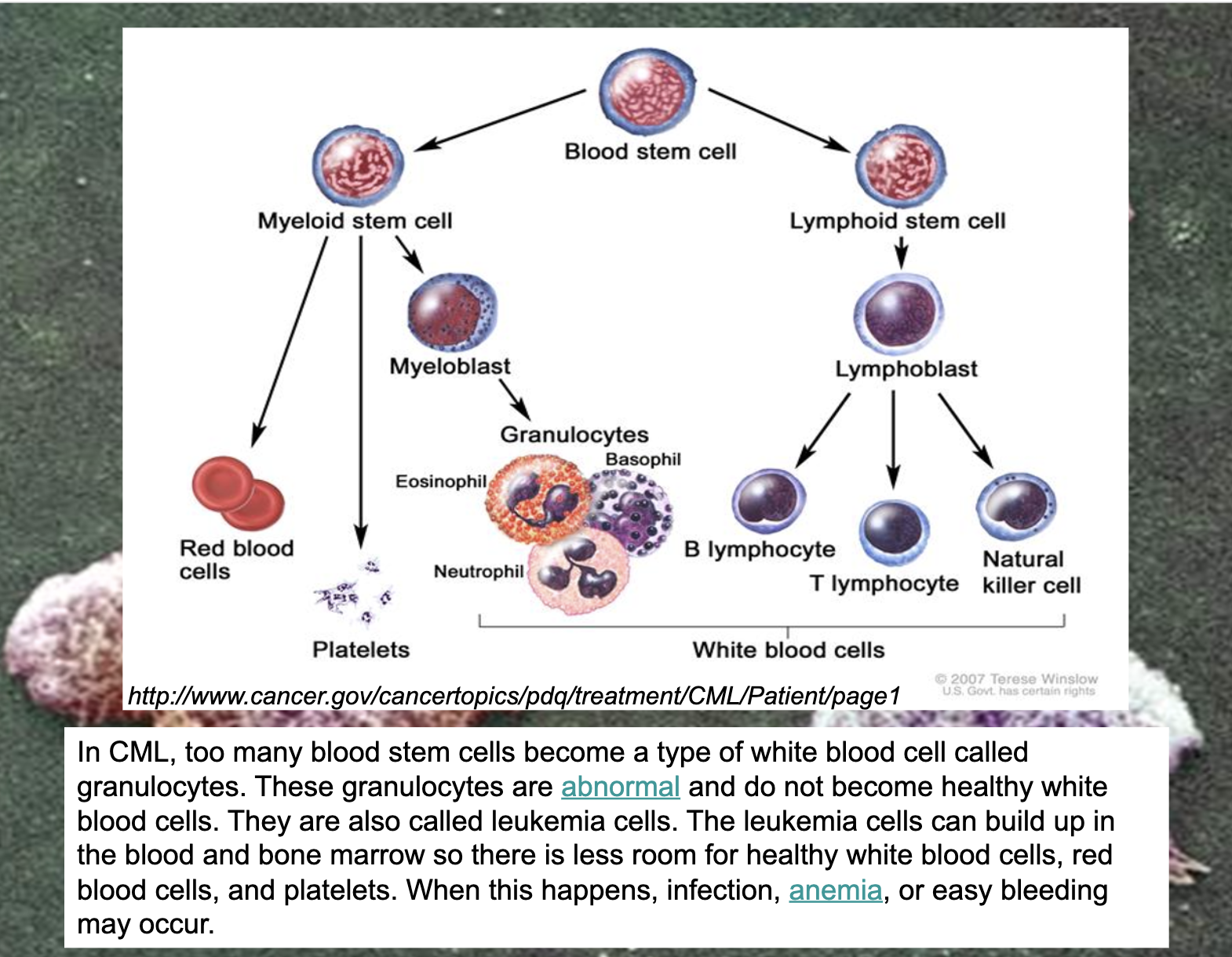
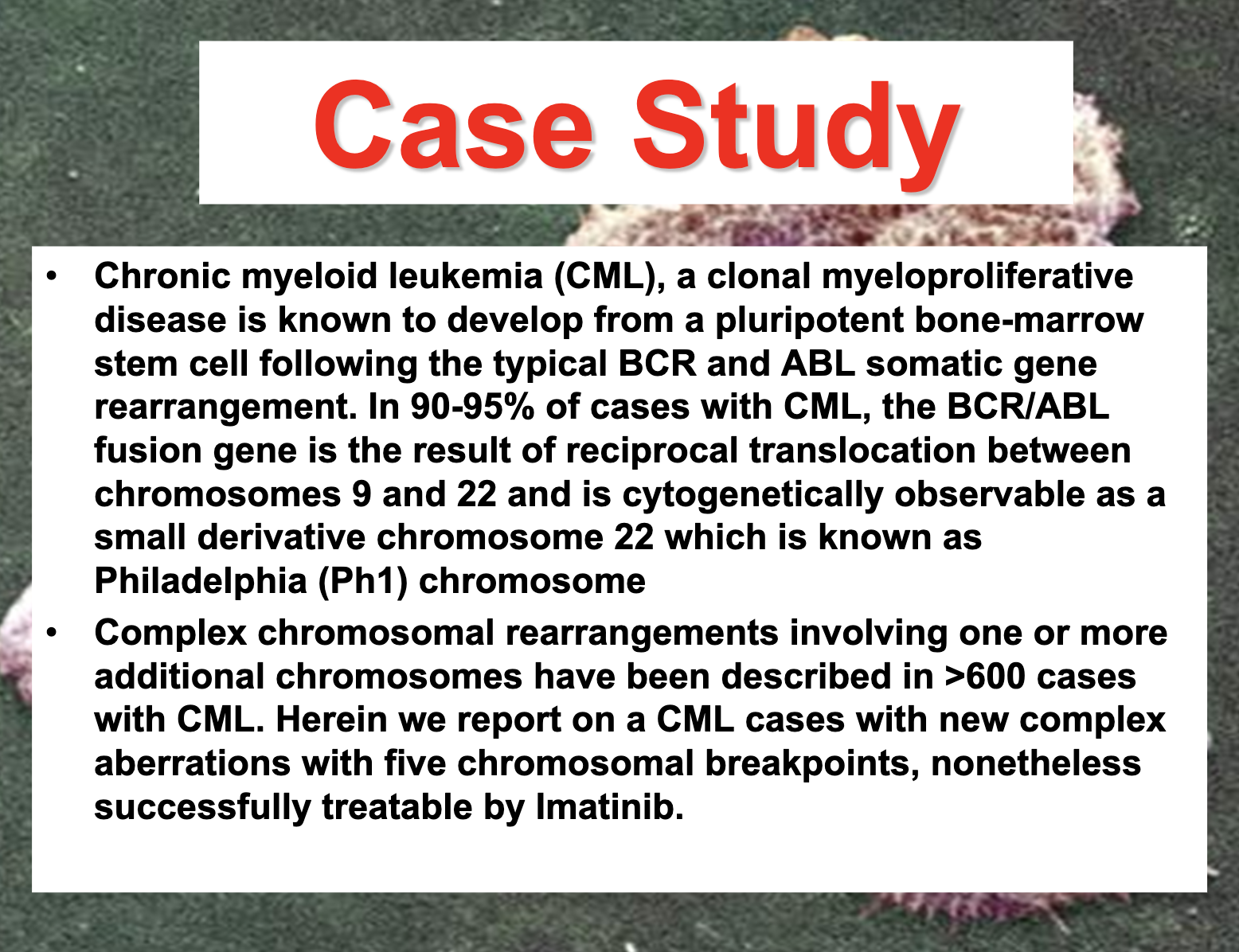
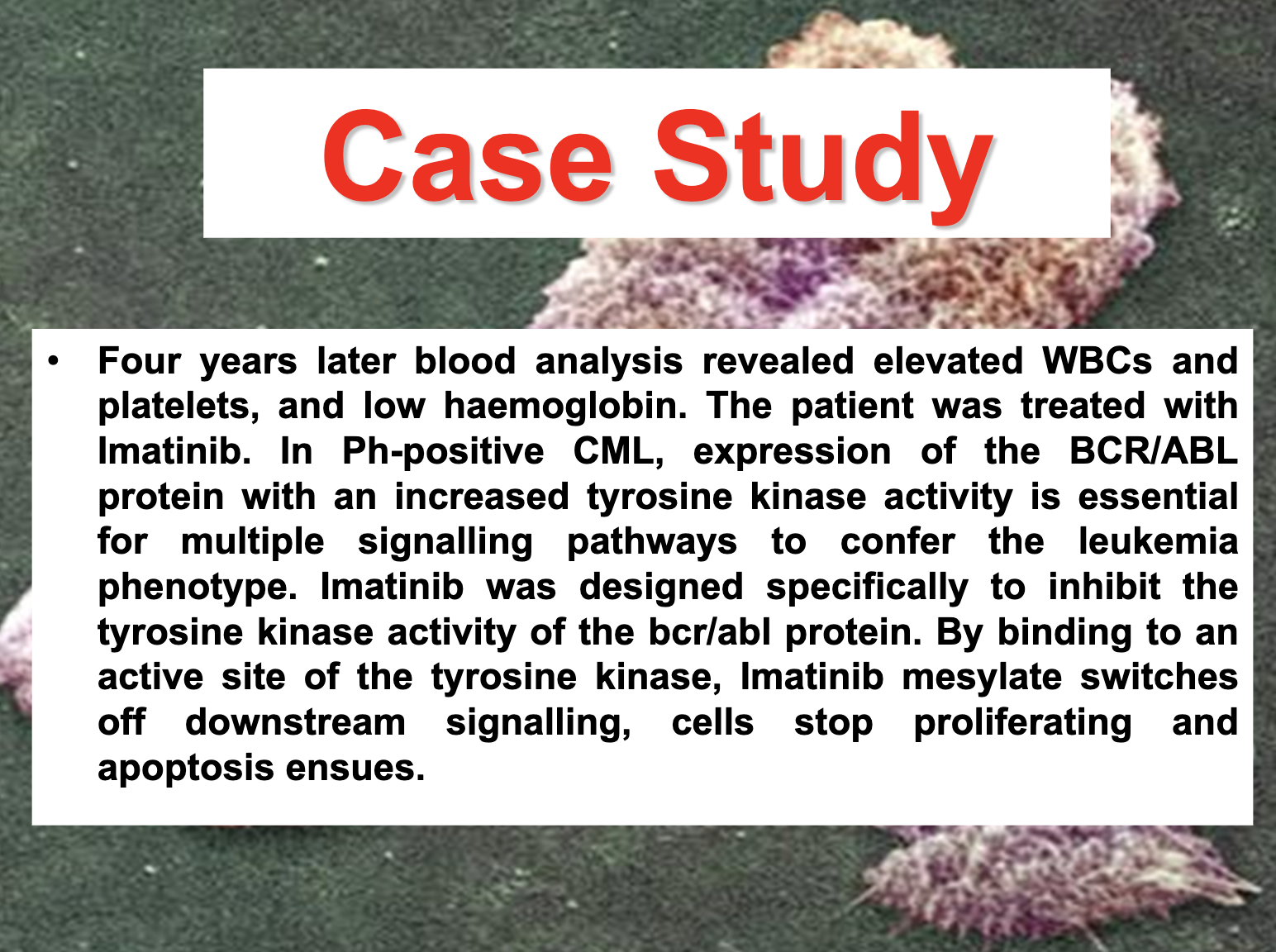
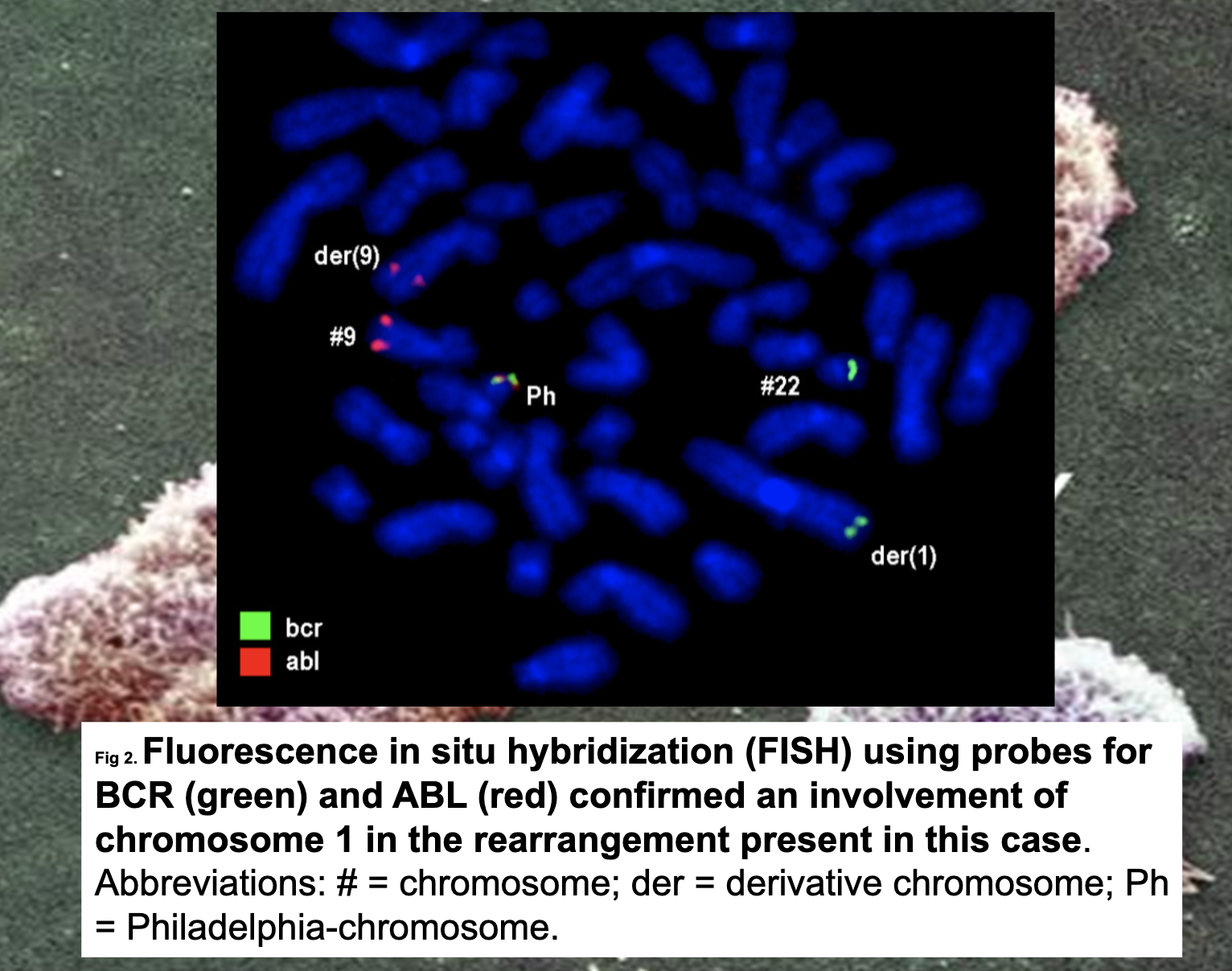
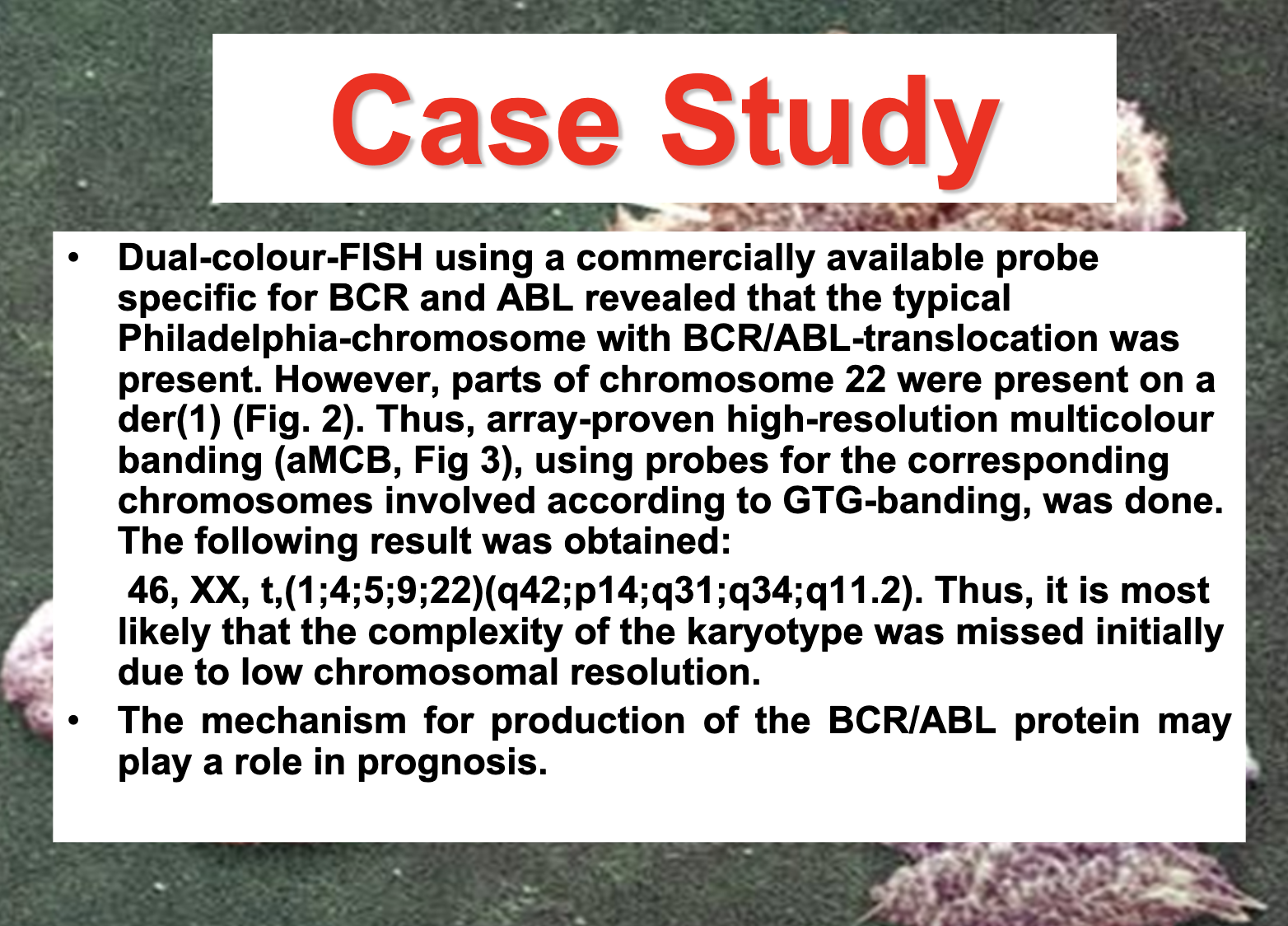
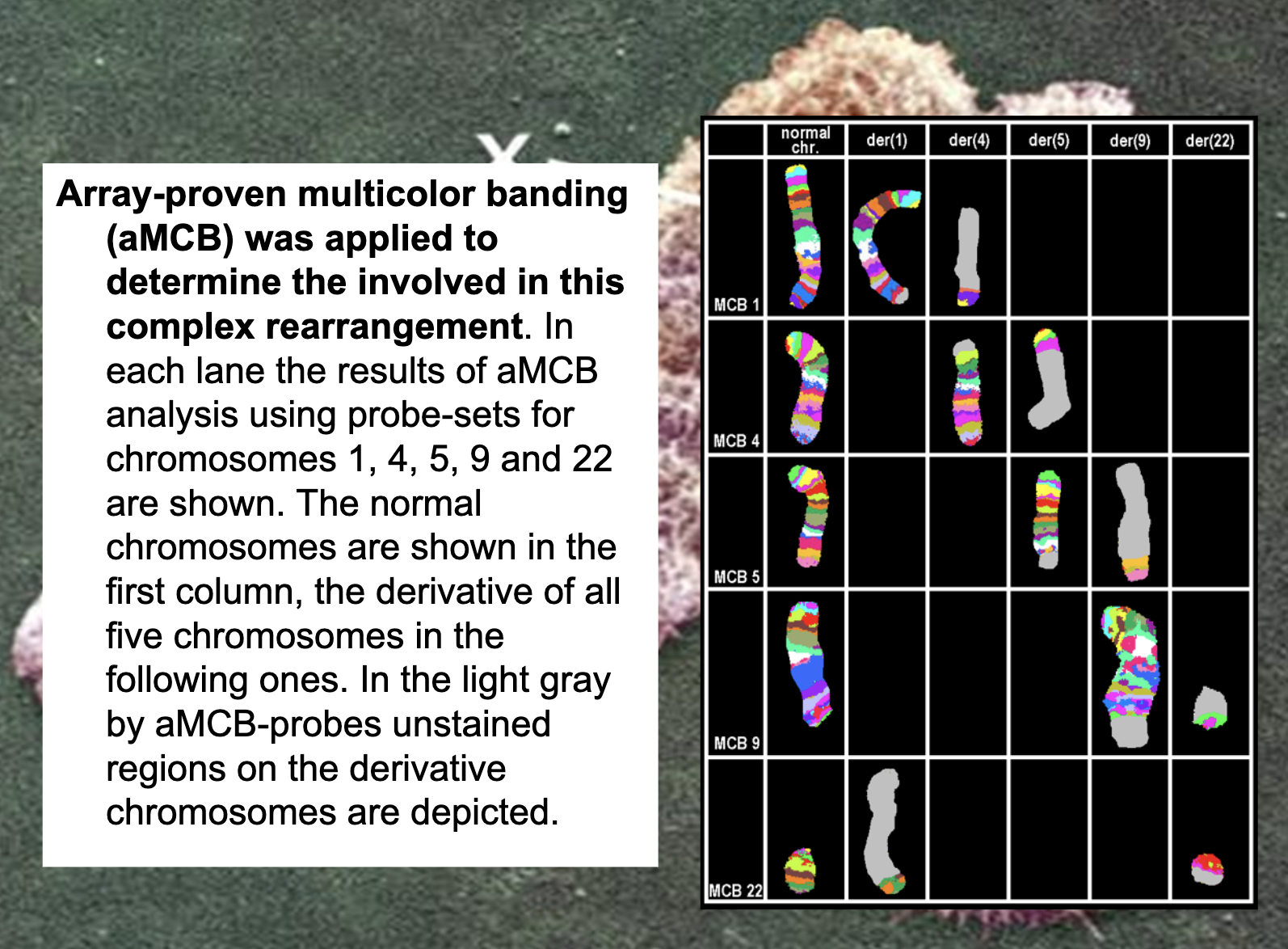
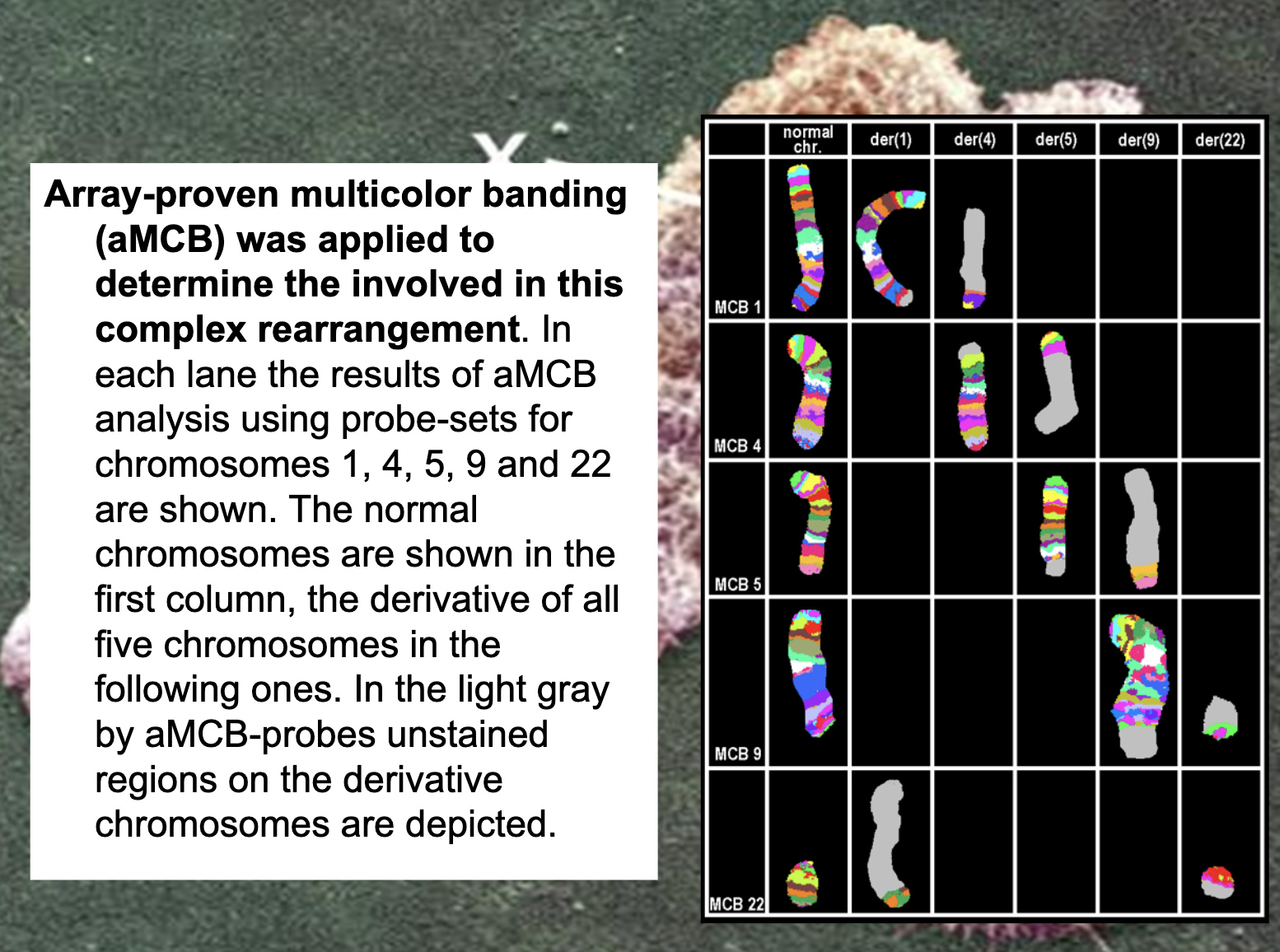
Chronic myelogenous leukemia
translocation between parts of chromosomes 9 and 22 in a single bone marrow cell during cell division.
'Griffith college Tri1 2023 > 1005 QBT (GnD)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [WEEK6] Part 1 Gene Expression (0) | 2023.04.12 |
|---|---|
| [WEEK5] Part 3 Molecular Basis of Inheritance (0) | 2023.04.01 |
| [WEEK3] Part 1 Mendelian Genetics (0) | 2023.03.16 |
| [WEEK2] Part2 Meiosis (0) | 2023.03.15 |
| [WEEK1] Part1 Mitosis (0) | 2023.03.02 |



