PPT


How easy is it to make the molecules required for life?

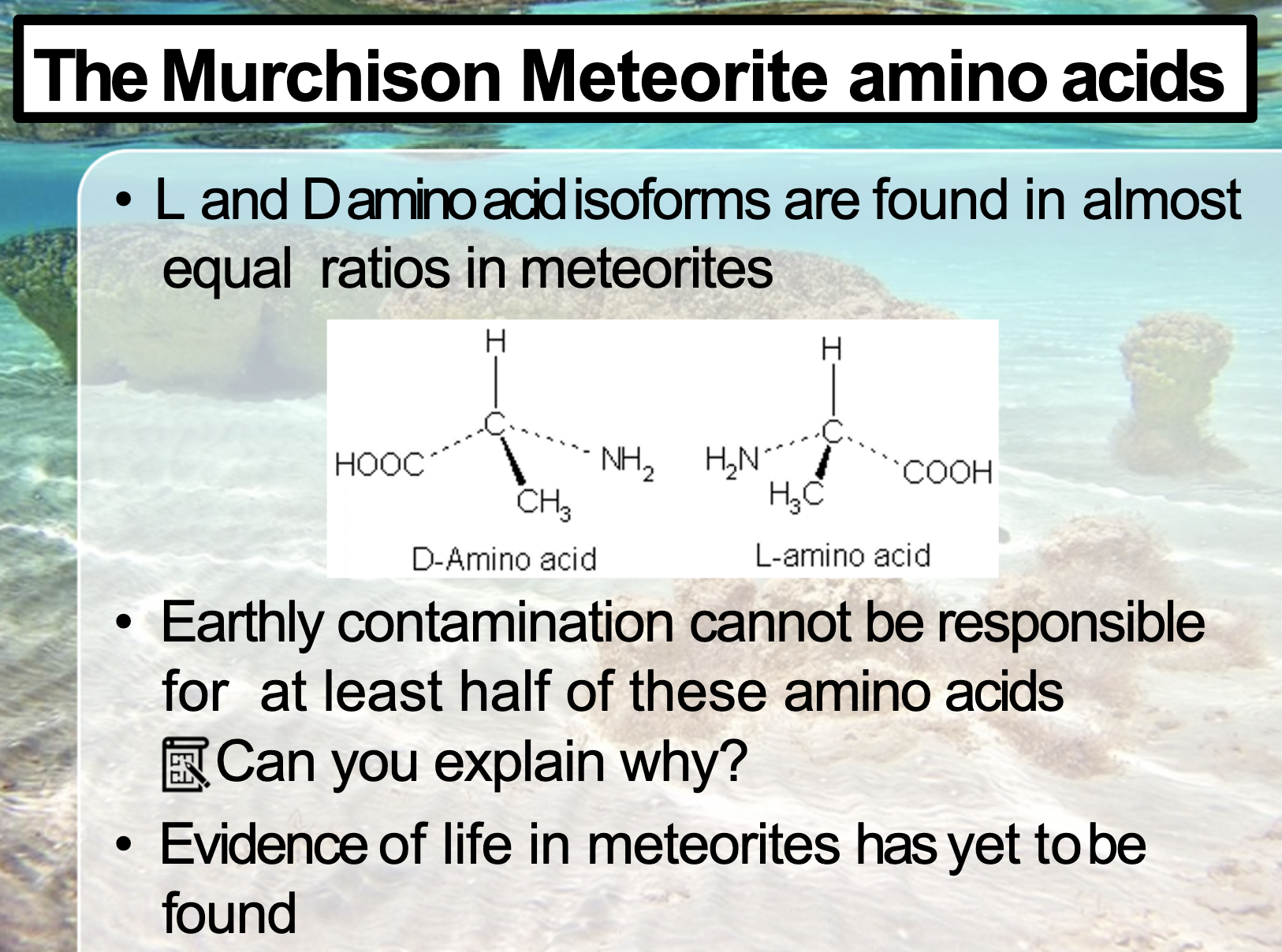
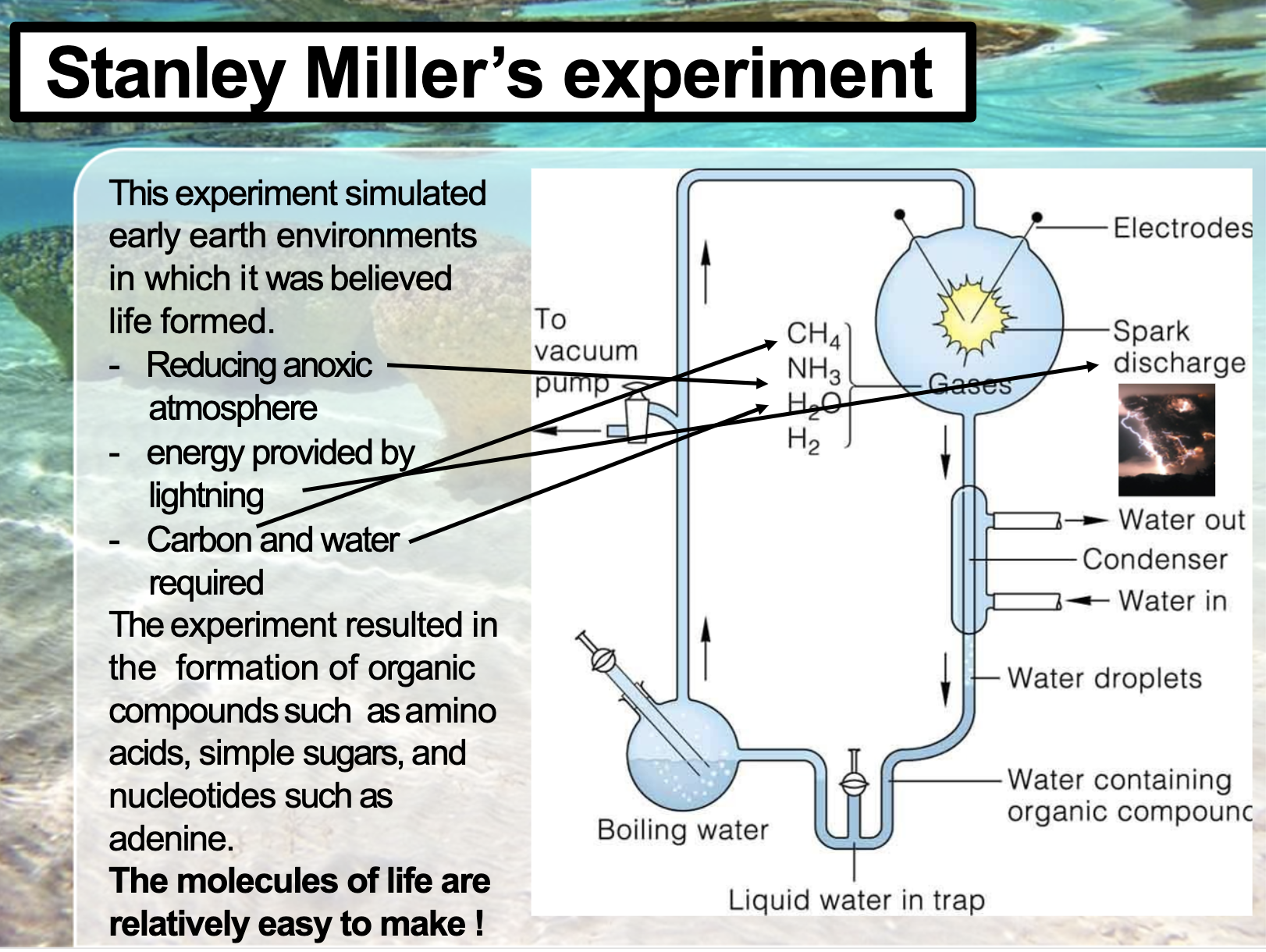

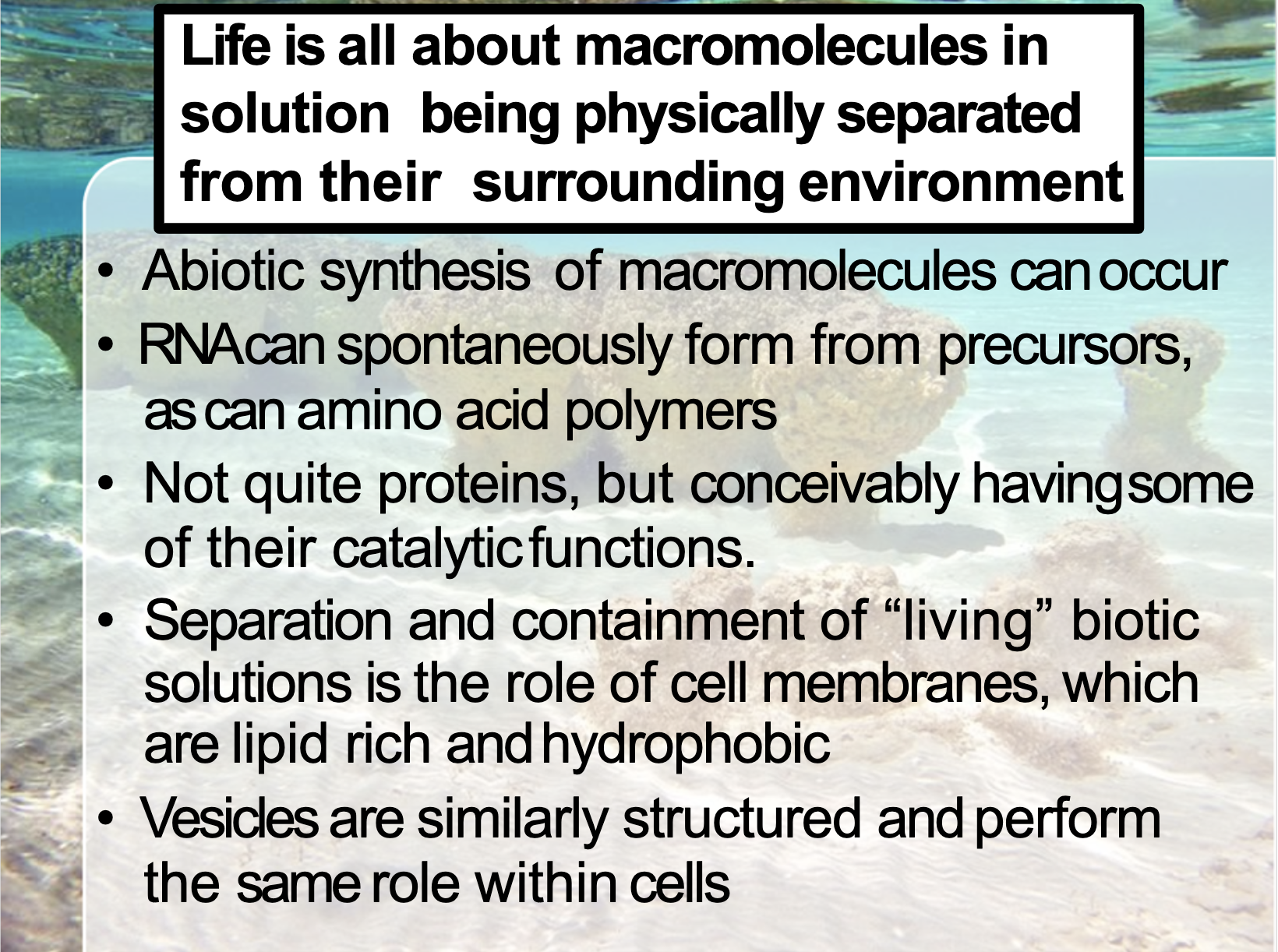
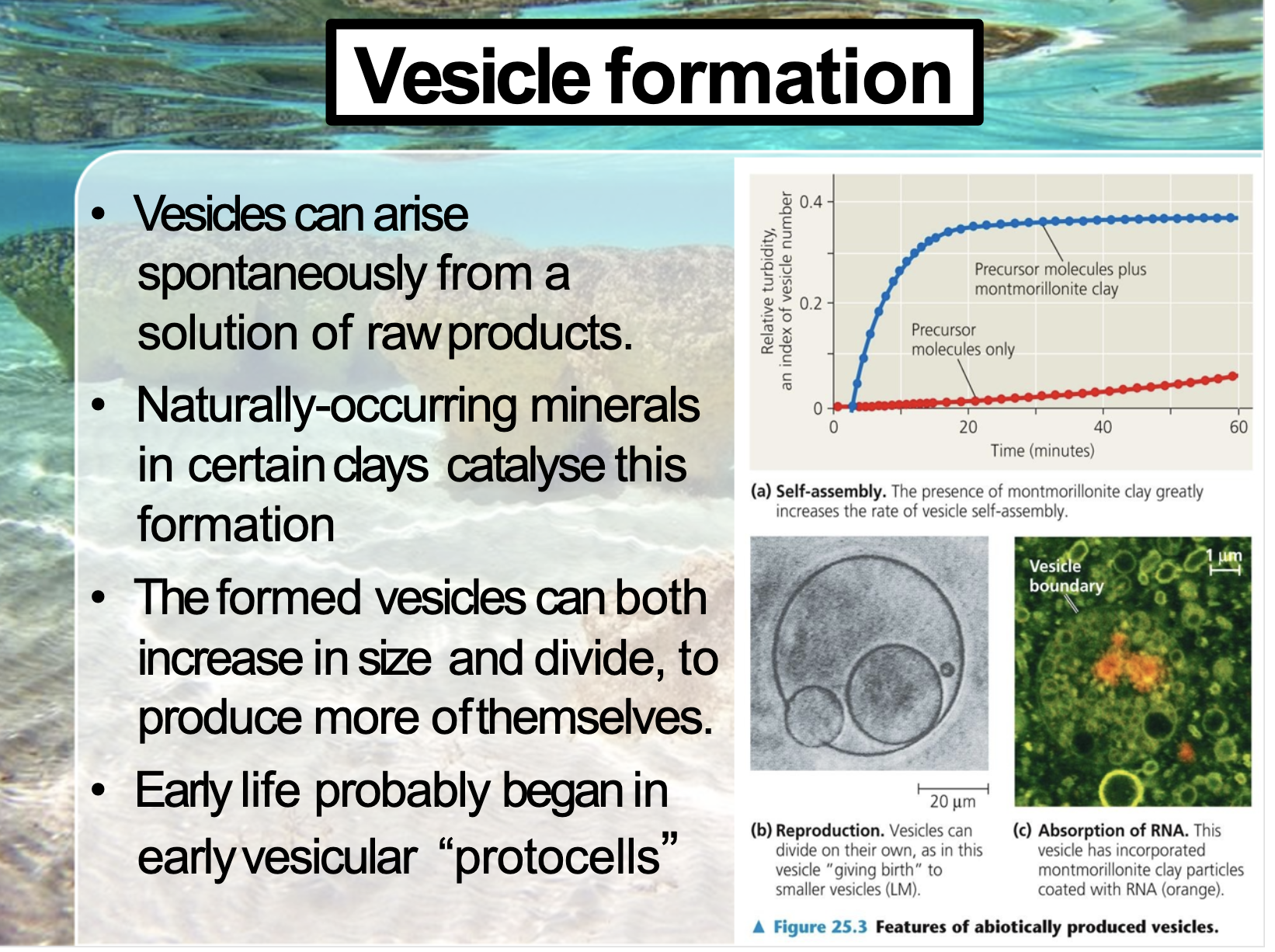
First life on Earth


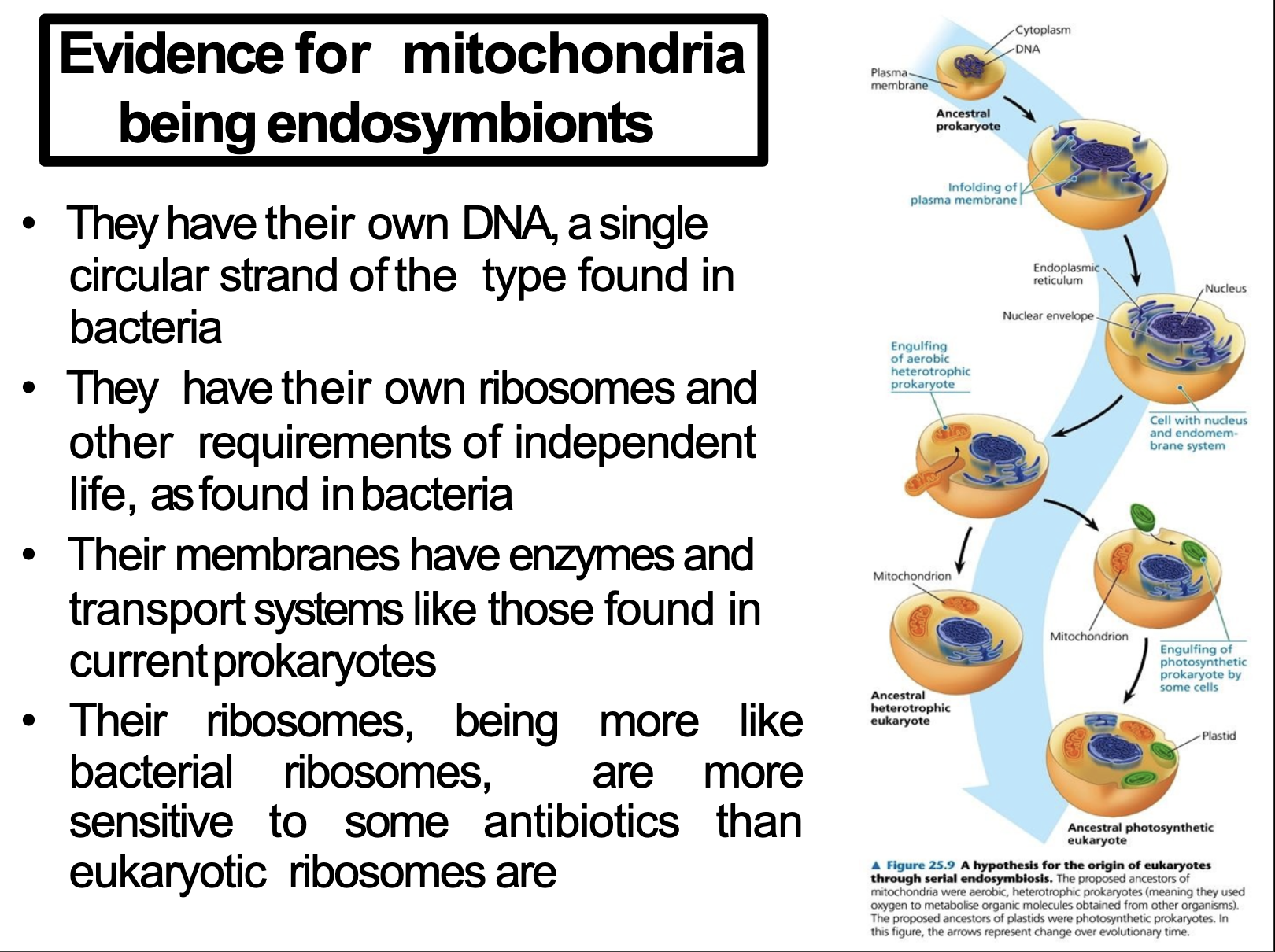
Eukaryote Evolution

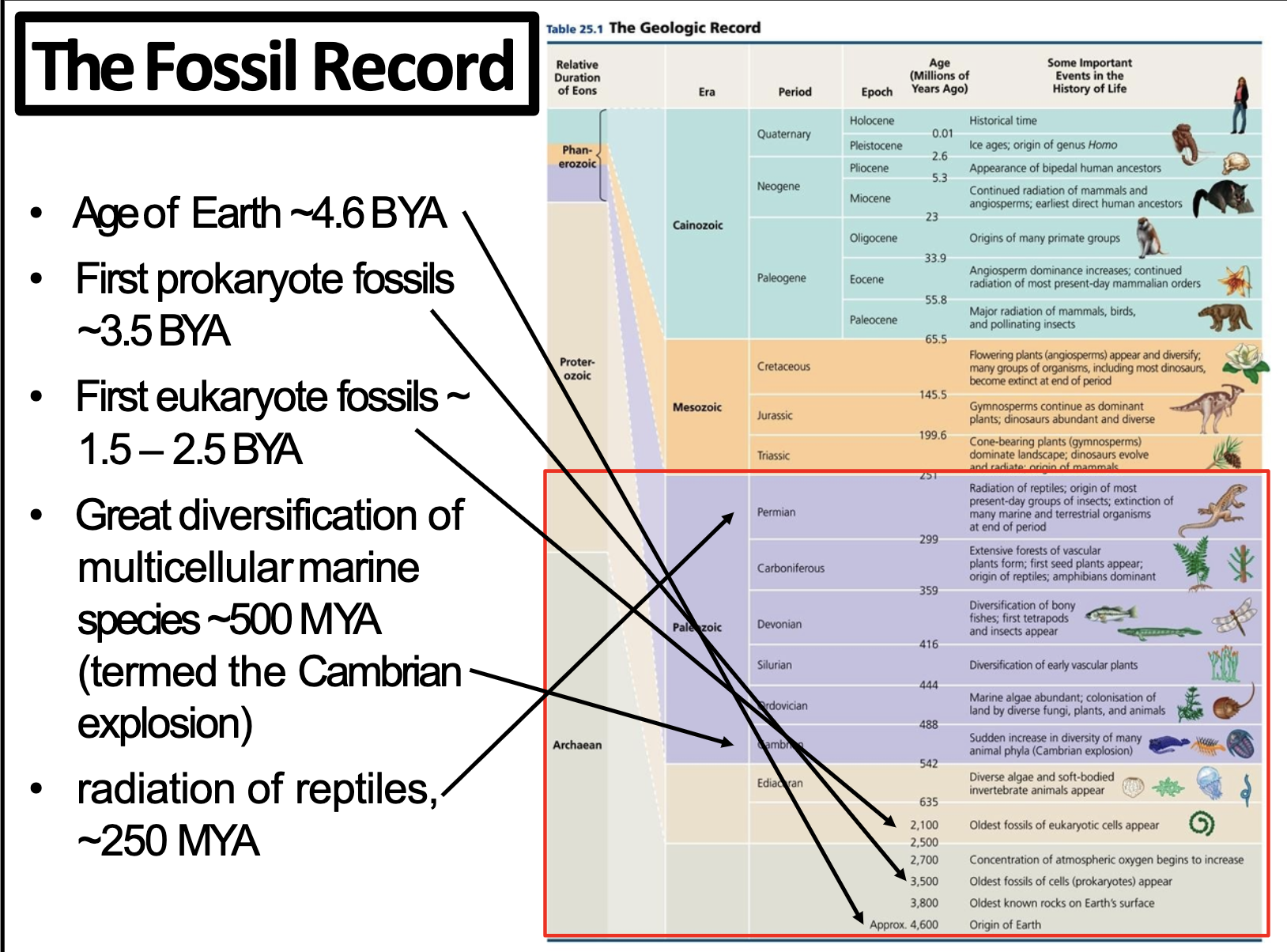
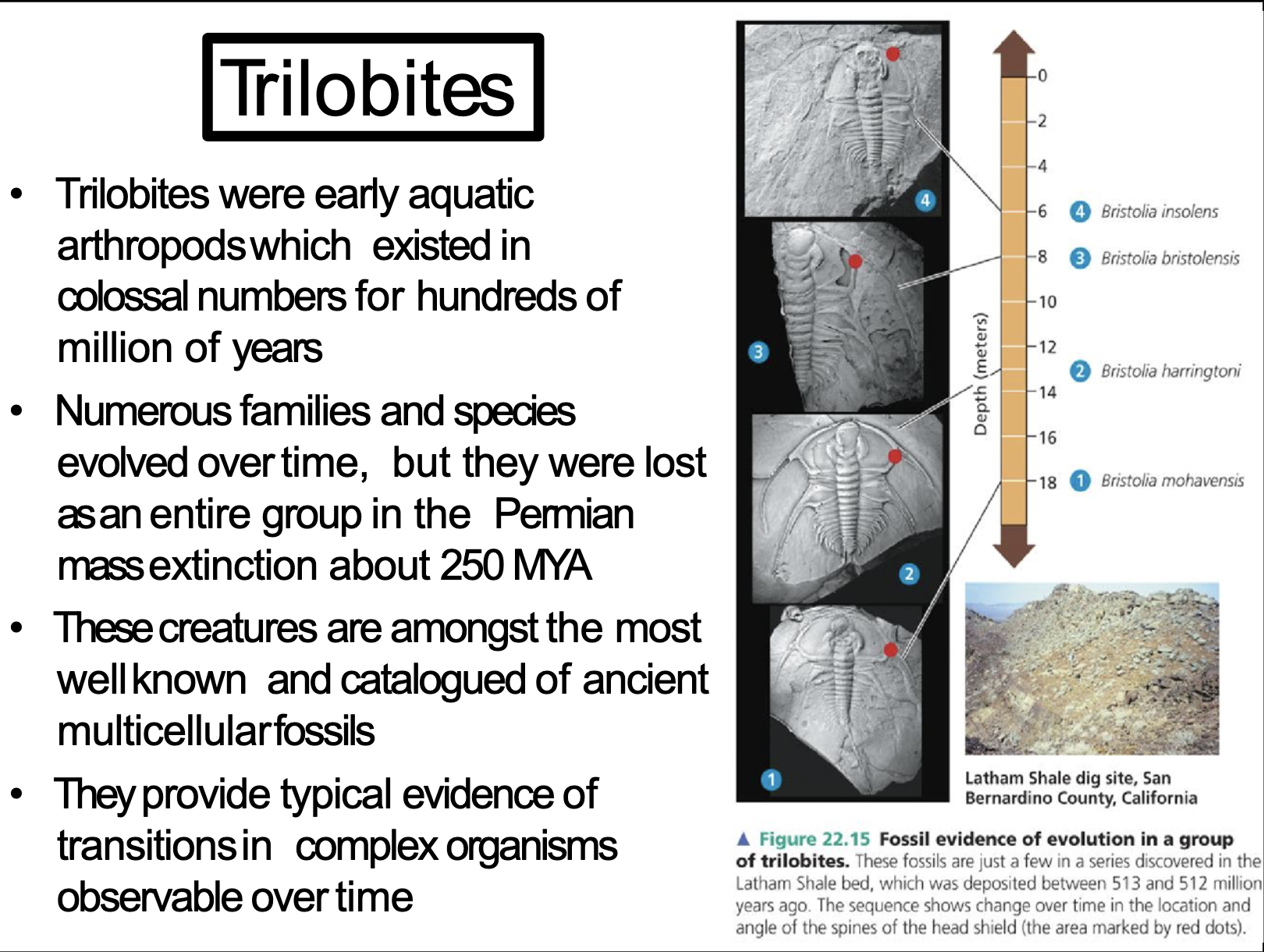
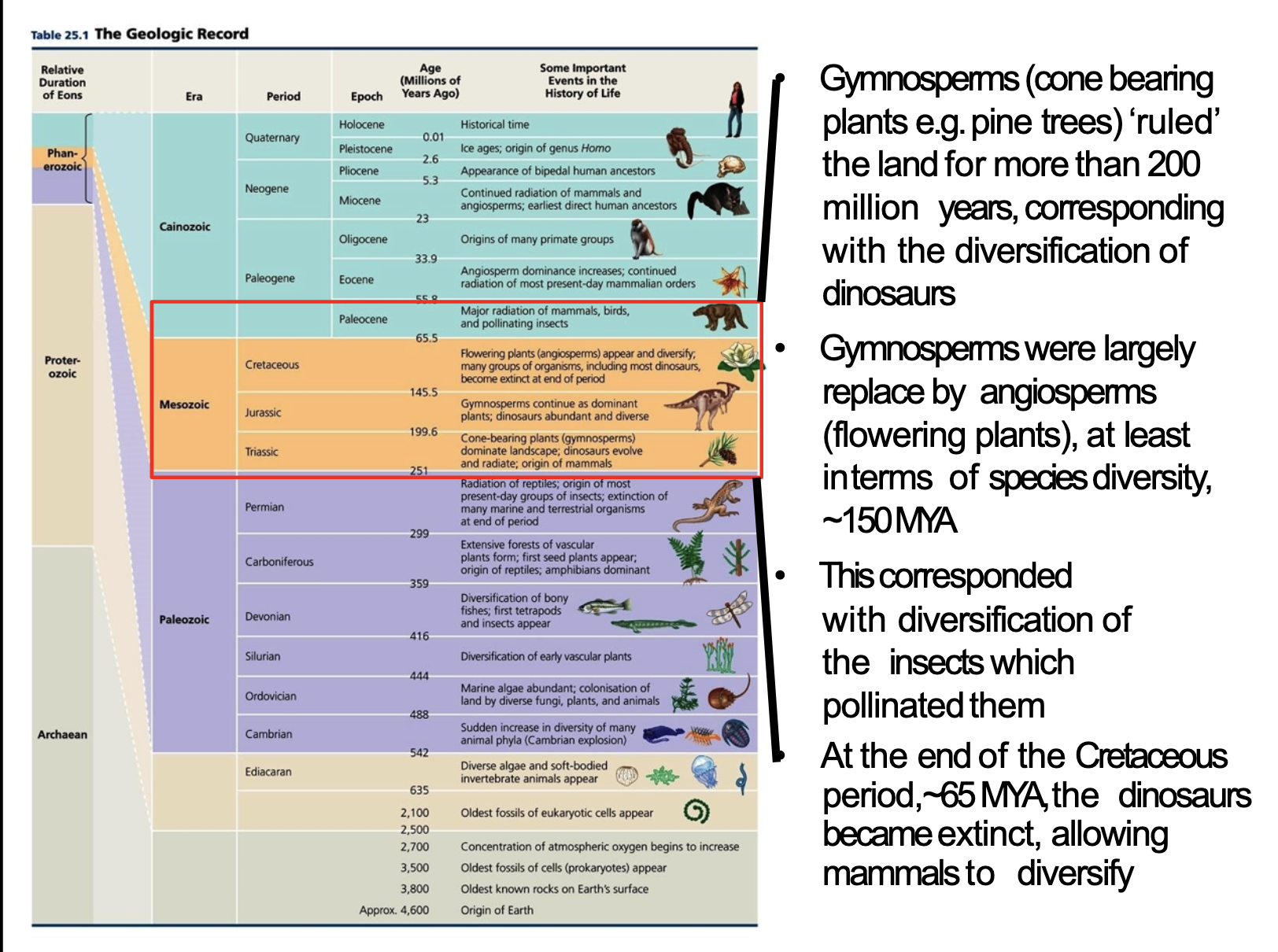
The Fossil Record


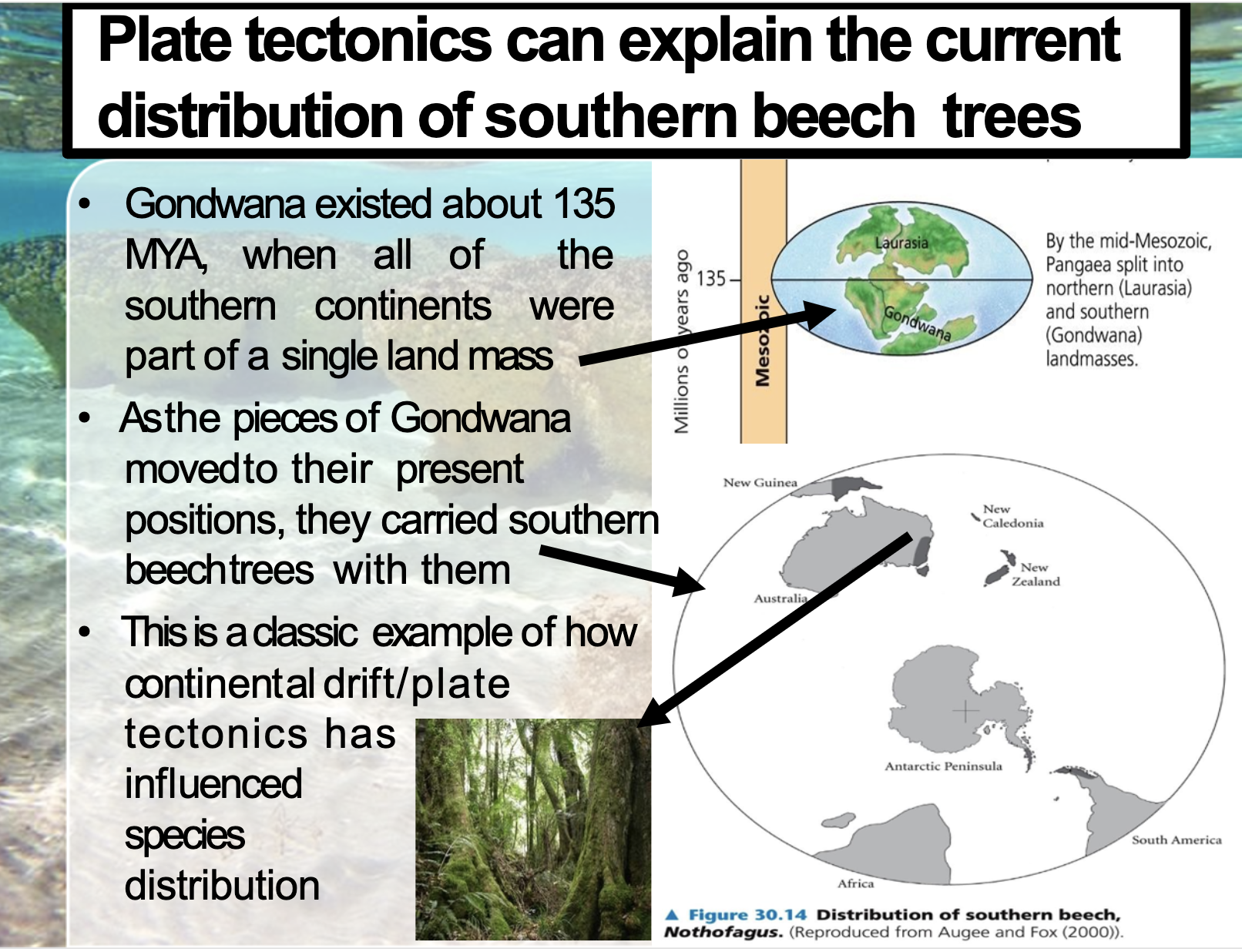
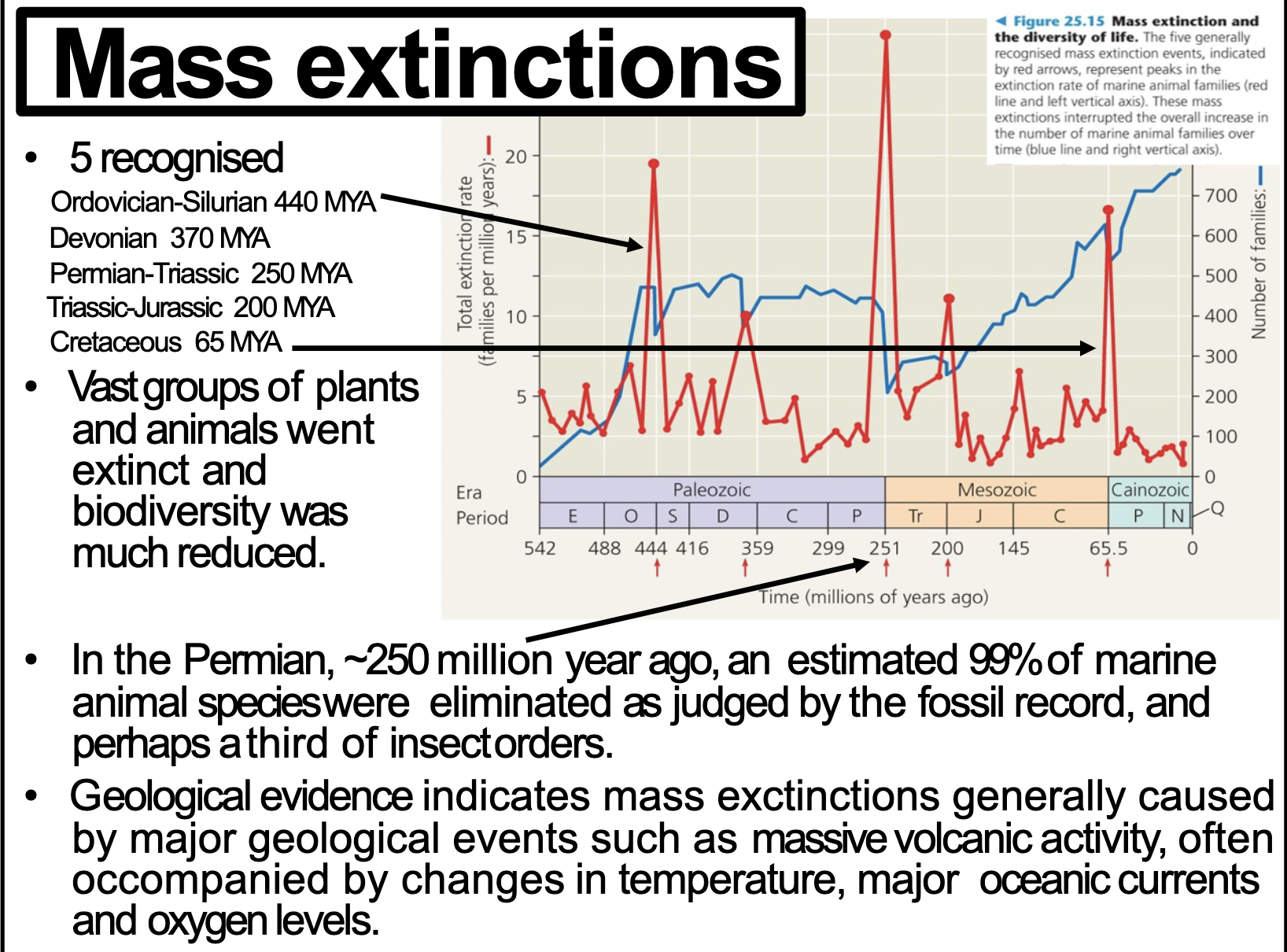
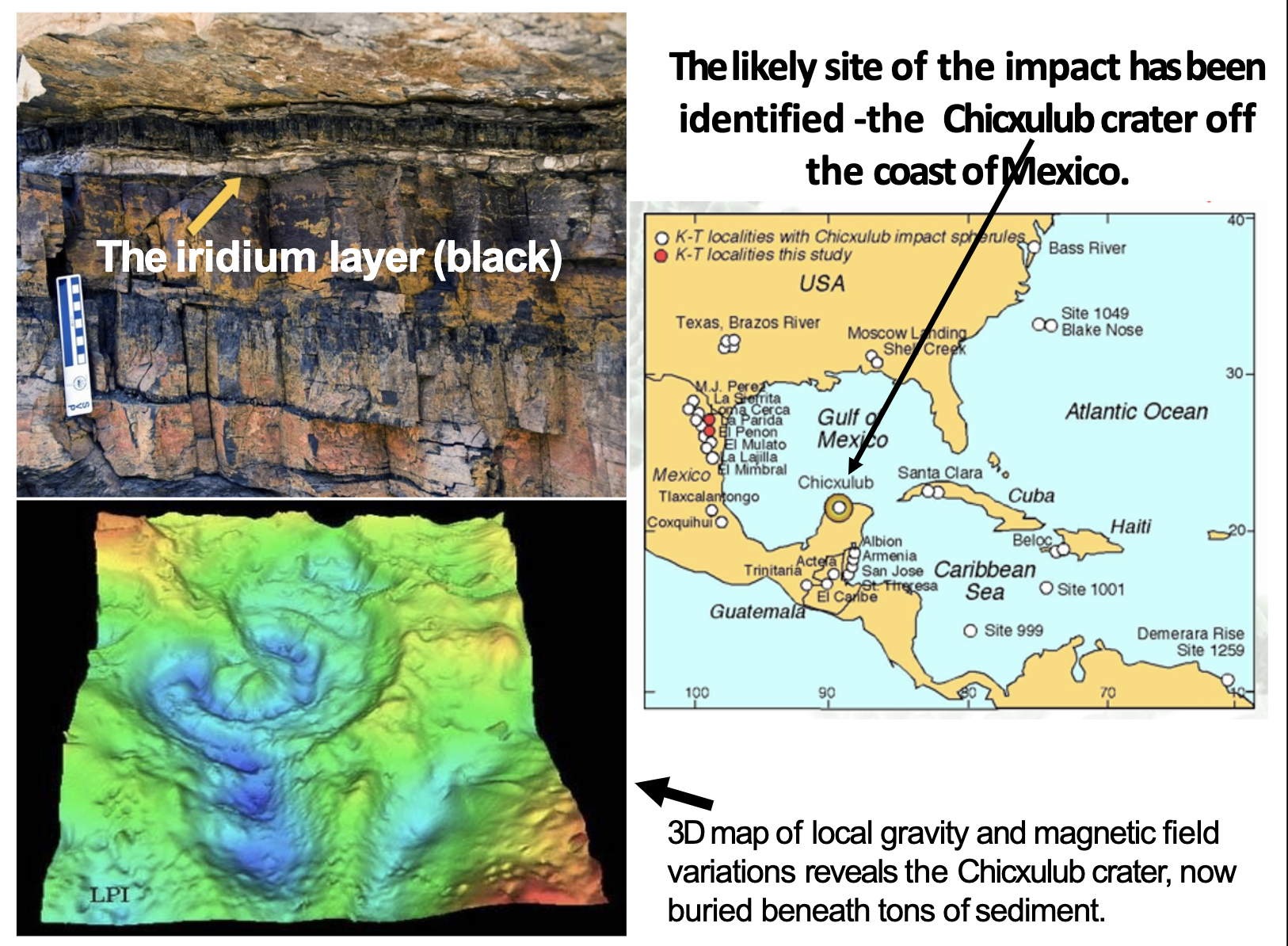
Mass Extinctions



SPQ


1. Darwin finches suggested that the diet differntiate the species. Depending on the finches diet, their beak shaped different.
These different birds are seemed to evolved from a single common finch ancestor but their difference in niches diverged their specoies
(Cactus -> long sharp / Insect -> sharp pointy / Seed -> strong large)
2. Survival of the fittest indicates that depending on the environmental condition, more adaptable individual survive better and have more chance to reproduce so they leave more desecendants




3. Darwin's idea of evolutionary was affected by the fossil and continental changes.
The fossil found closer to the surface had similar appearance to nowdays organism
5.



6.
8.




7.
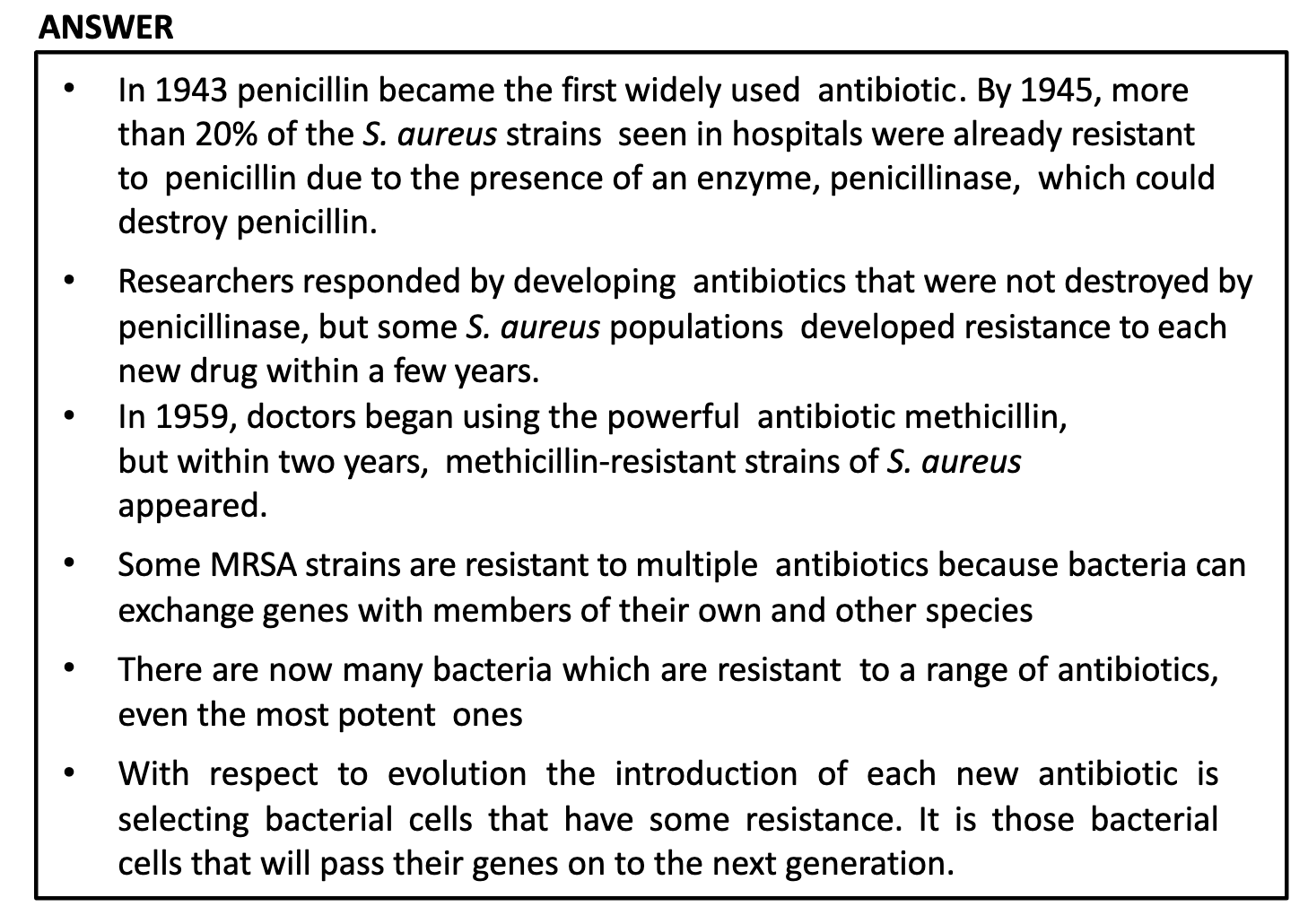
Within six months of effectively using methicillin to treat S, aureus infections in a community, all new infections were caused by MRSA. How can rhis result best be explained?
-> Some drug-resistant bacteria were present at the start of treatment, and natural selection increased their frequency
NOT MAKING WHOLE NEW VERSION
ADAPTION, SURVIVAL,
SIX MONTHS IS NOT ENOUGH TO CHANGE THE GENE/ EXPRESSION / FUNCTION
4.
Natural selection is based on the fact that ...
1) There is heritable variation among individuals
2) Species produce more offspring than the environment can support (so then the competition occurs)
3) Individuals whose characteristics are best suited to the environment generally leave more offspring than those whose characteristics are less well suited
4) Only a fraction of an individual's offspring may survive
HERITABLE VARIATION
MORE OFFSPRING THAN ENVIRONMENT CAN AFFORD -> COMPETITION
MORE FITTED, MORE ADJUSTABLE INDIVIDUAL CAN REPRODUCE MORE OFFSPRING


9.
Natural selection changes allele frequencies because some individuals survive and reproduce more successflly than others
10.
No two people are genetically identical, except for identical twins. The main source of genetic variation among human individual is the reshuffling of alleles in sexual reproduction
Changes the allele frequency in the population
1) mutation
2) natural selection
3) gene drift
4) gene flow
Changes the genetic variation in human
1) random fertilisation between sperm and egg
2) Rule of segregation (homologous choromosome seprate into the gamete randomly)
3) mutation
4) crossing over




11.
From the space we could source CHON, and as the early stage of earth, there were full of energy,
12.
Earth is first formed apprx 4.5 BYA
The first life on earth was unicellular prokaryote, cyanobacteria found in the stromatollite about 3.5BYA


13.
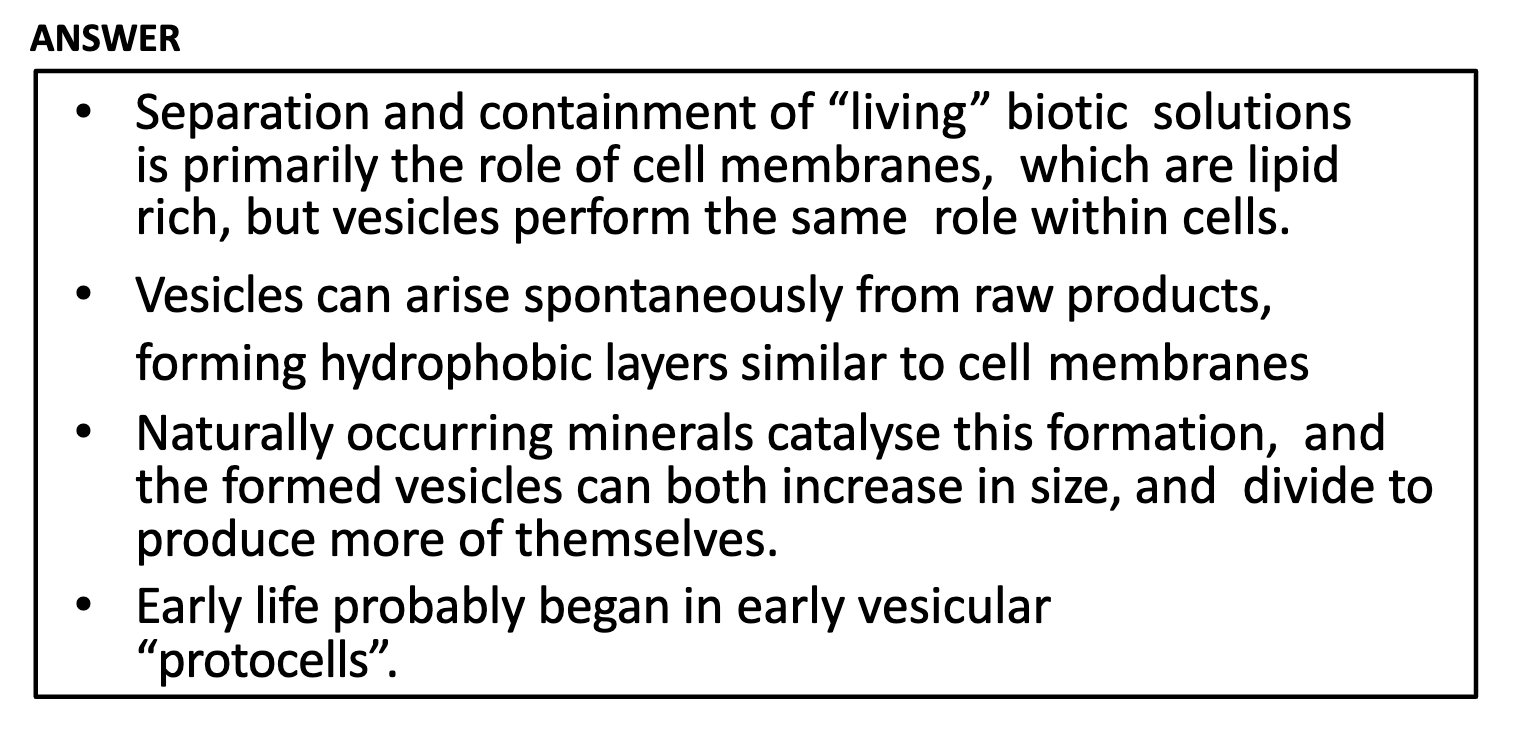
Vesicle seperates the inner mass from the environment.
Proto-cells are composed of vesicles containing DNA inside
As vesicle can arise spontaneously ( catalysed by the clay) + self reproduce + can contain RNA,
It is regarded as having same role as cell membrane
14.
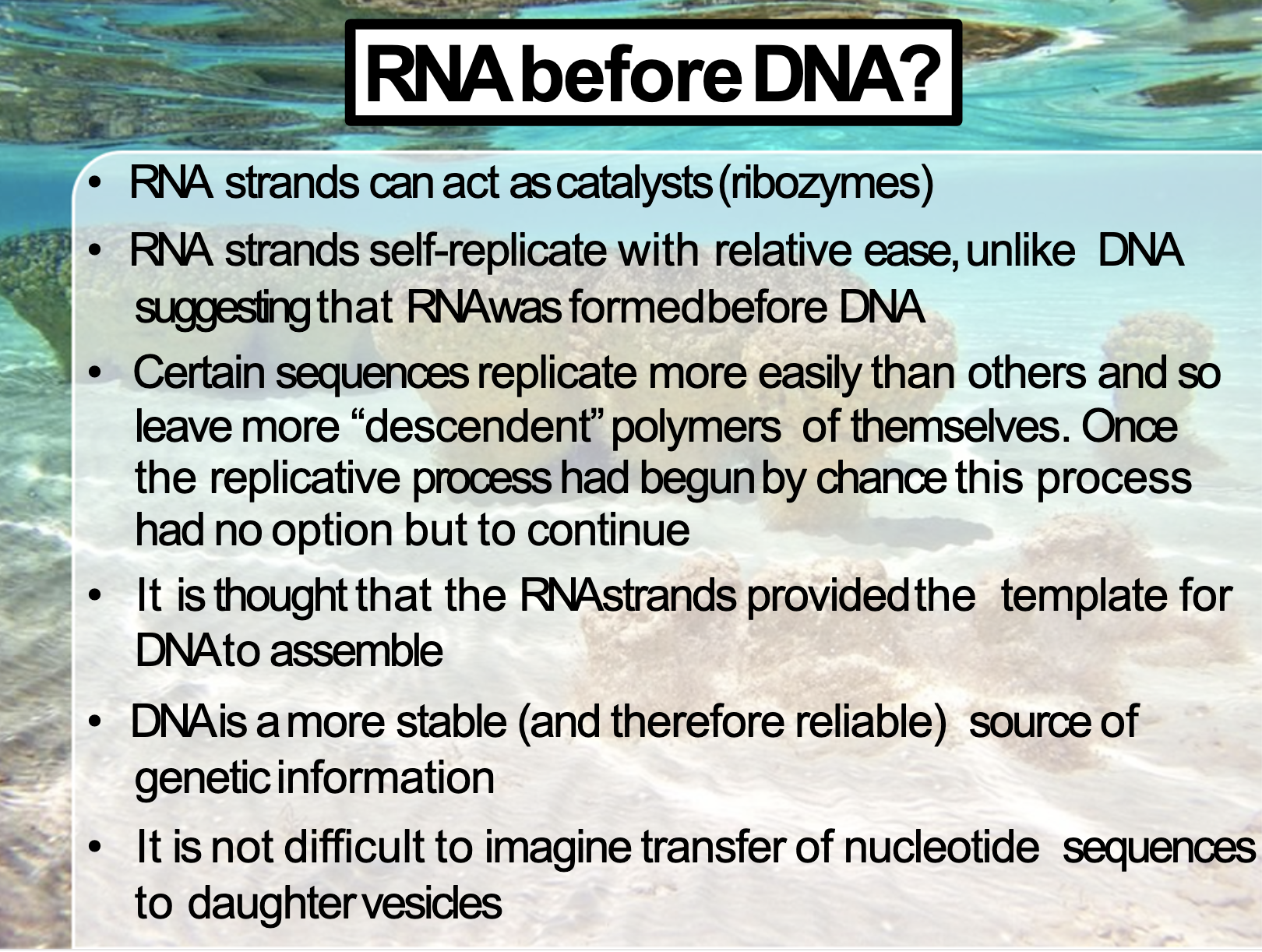
RNA can self replicate (ribosomal RNA produce polypeptides)
RNA act as a catalyst (ribozymes)
DNA is more stable so then it can store genetic information more stable
RNA once the replication process had begun by chance, this process had no option but to assemble



15.
16.




17.
Mammals and life started to diverged
18.



19.


20.
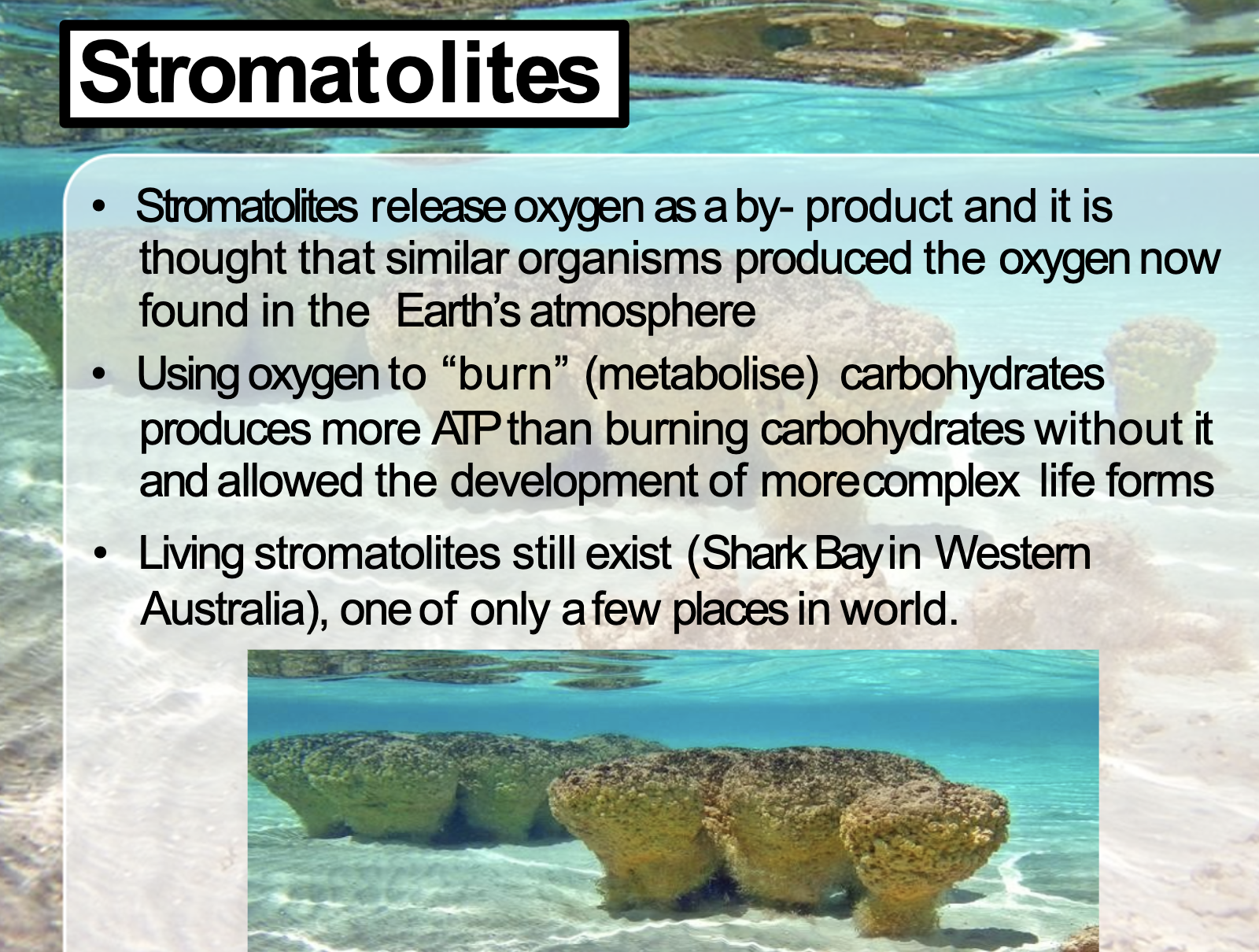
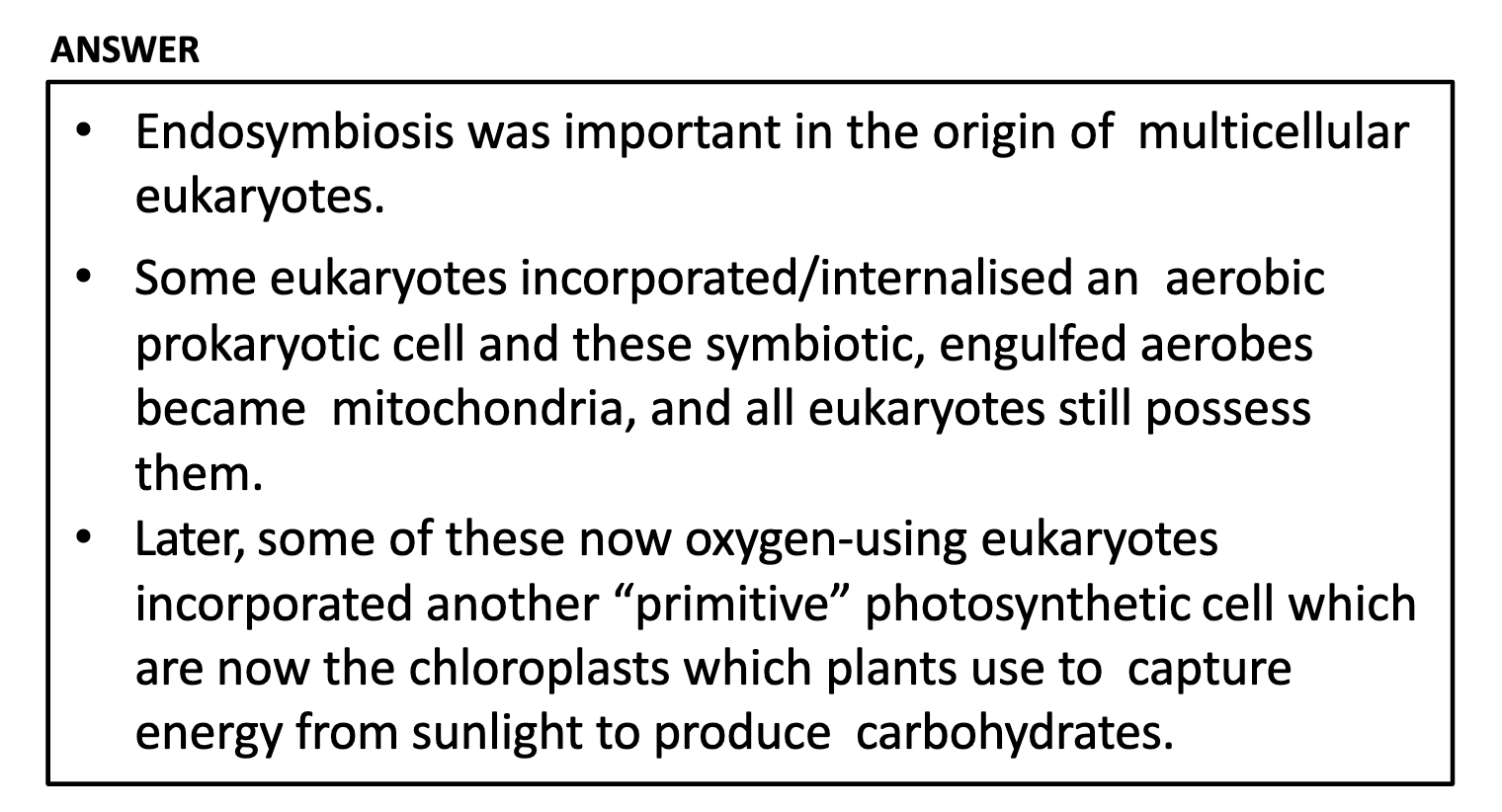
Fossilised stromatolites resemble sturctures formed by bacterial communities that are found today in some warm, shallow, salty bays
Stromatolites release oxygen as a byproduct.
Other organism can use oxygen and produce ATP (aerobic metabolises -> allowed more complex life forms)
21.
The oxygen revolution changed Earth's environment dramatically. Which of the following took advantage of the presence of free oxygen in the oceans and atmosphere?
-> The evolution of cellular respiration, which used oxygen to help harvest energy from organic molecules
'Griffith college Tri1 2023 > 1005 QBT (GnD)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [WEEK12] Vertebrate and Human evolution (0) | 2023.05.28 |
|---|---|
| [WEEK11] Evolution of Populations and Speciation (0) | 2023.05.23 |
| [WEEK10] Charles Darwin and the theory of evolution (0) | 2023.05.13 |
| [WEEK8] Part 3 Developmental Genetics (0) | 2023.04.30 |
| [WEEK6] Part 1 Gene Expression (0) | 2023.04.12 |



