Genetic diversity is dependent on population size; understand how the example of facial tumours in Tasmanian Devils illustrates this.
When the population size is too small, it has less vairability in indiviuals gene, which means that it has less source to be natural selected. Large enough population is required for having a chance for more fitted individual existing.
For example, tasmanian devils has less variation in their immune system gene and they couldn't survive as they don't have more fitted individual to pass their gene to offspring.
Understand what the term “average heterozygosity” within a population means and its relevance for natural selection.
Loci which shows Homozygosity -> 85%
Loci which shows Heterozygosity -> 15%
Heterozygosity often refers to the gene variability.
It is important for natural selection as it sources the natural selection to happen.
Less variability means less sources to be favoured by the environment, less chances to have individual fitted to selection
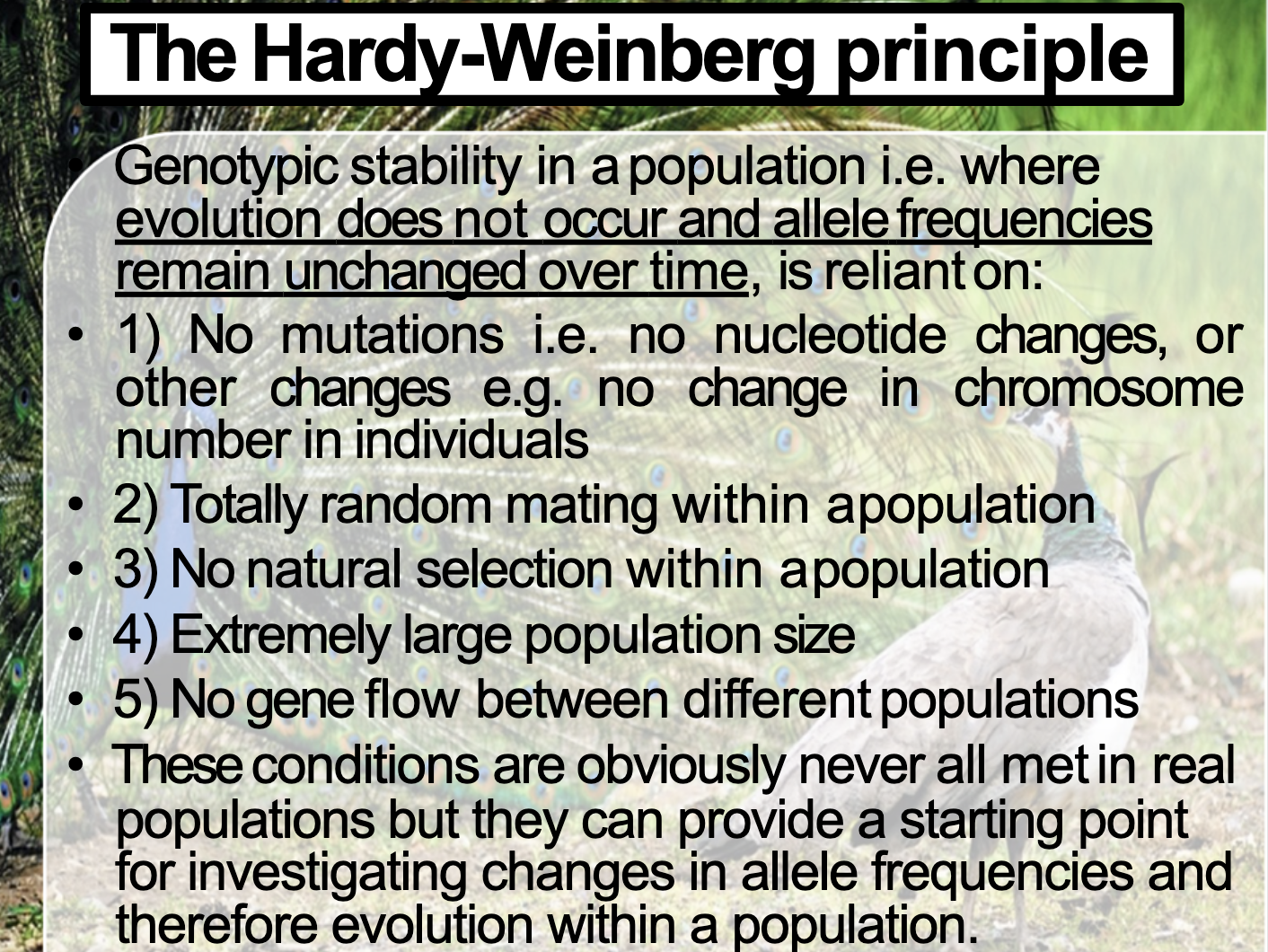
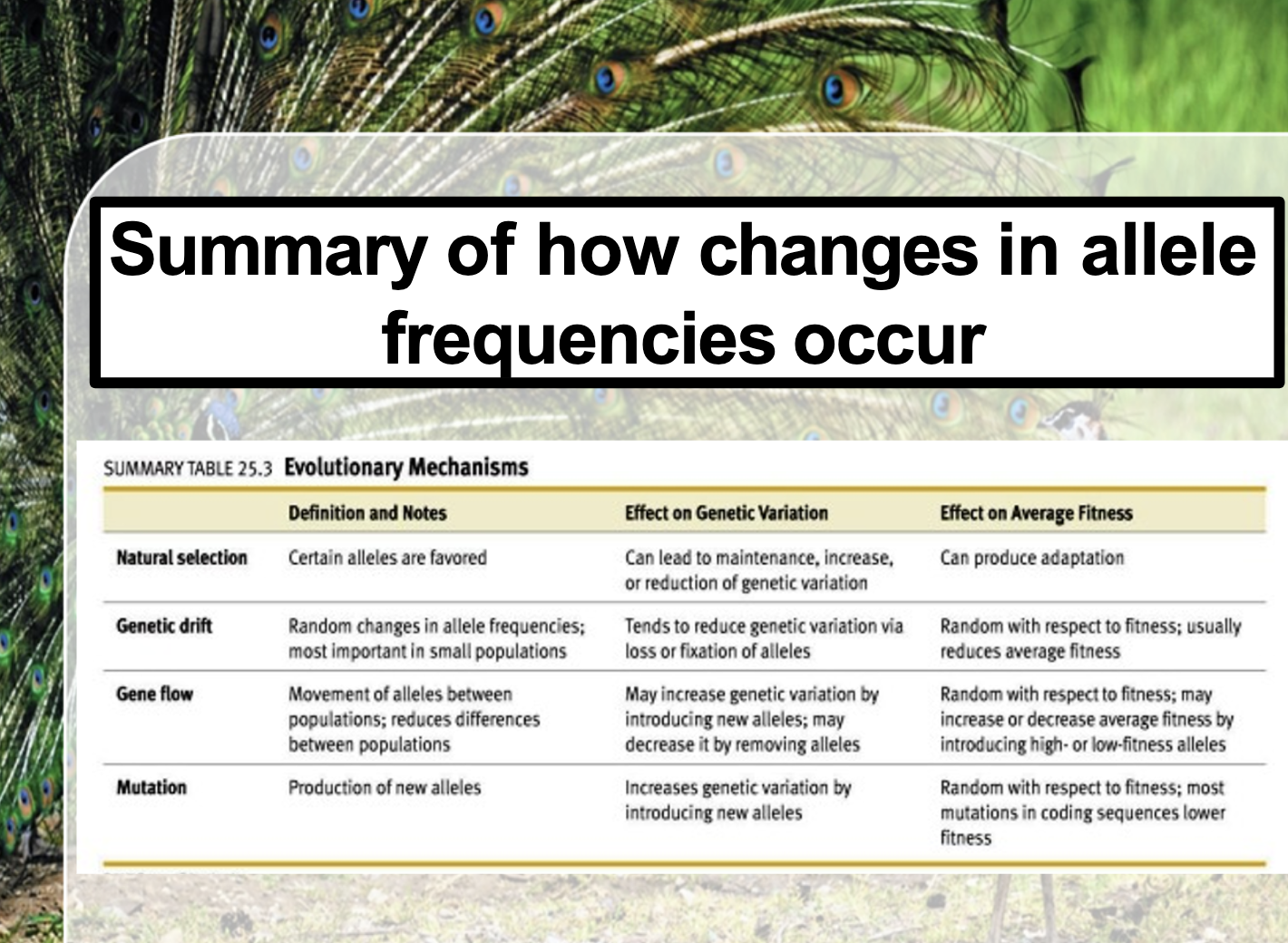
Understand the conditions (described by the Hardy-Weinburg Principle) that will prevent a population from undergoing changes to form or function, i.e. where there is genotype stability over the generations, with no evolutionary changes possible.
1) Too large population
2) no mutation
3) no natural selection
4) no gene flow
5) Totally random mating
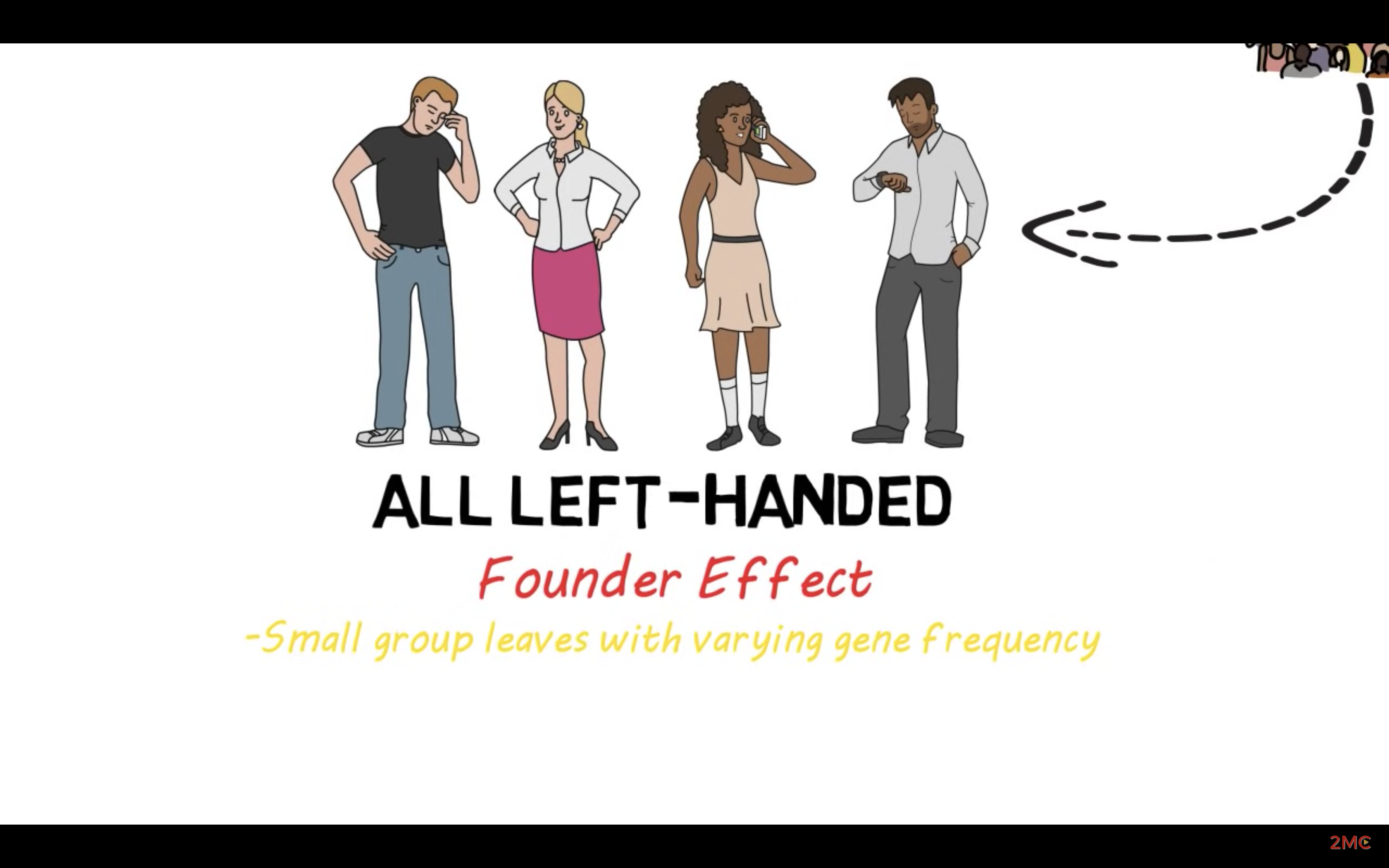
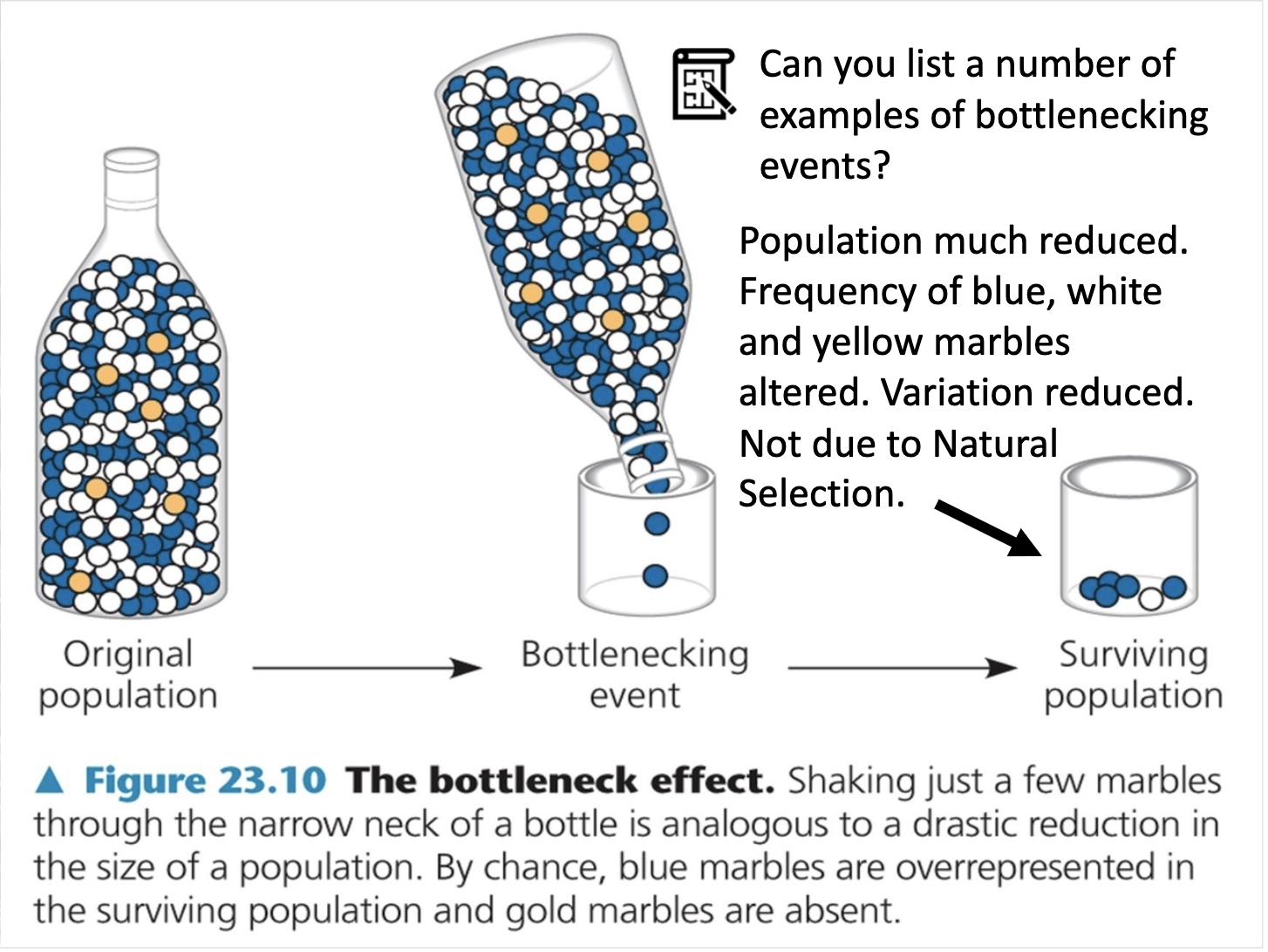
Understand how marked genotypic changes can occur inadvertently in small populations, independent of natural selection, and relate this issue to the bottleneck and founder effects, with examples of the latter.
When the population is so small, natural selection less occur as there is not enough source to be selected. Howver, instead of natural selection, gene drift occurs effectively to the smaller population. It is not selective as natural selection. It is random process. Gene drift has two different type. Bottle neck effect and founder effect. Bottle neck effect occurs when the catastrophic disaster decreases the population extensively and the gene pool of the population changes. Founder effect is when the small group of population fall apart from the original population and compose its own group, it creates its own gene pool.
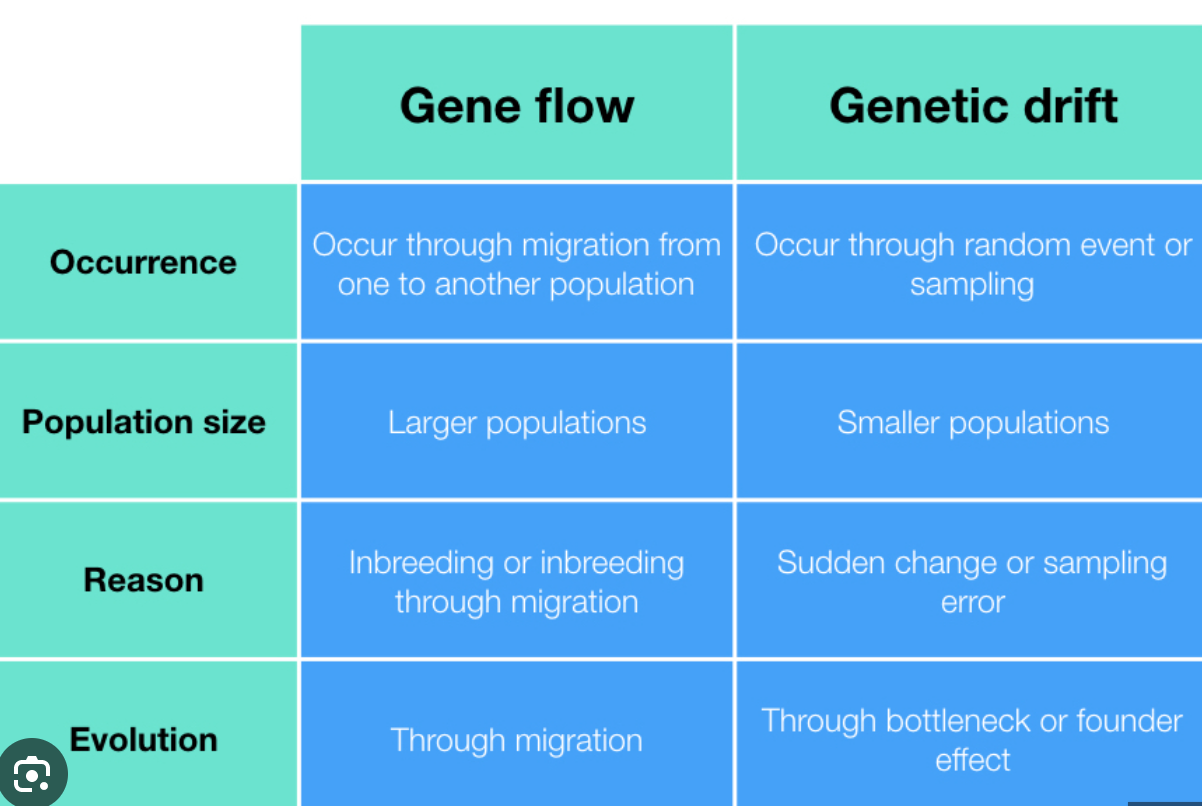
Understand that gene flow between populations does not necessarily confer an evolutionary advantage.
Gene flow means when the gene is introduced in one population group, and changes its gene pool.
Gene that introduced can be not advantageous gene. For example hunington disease is introduced in population group, and as it is autosomal dominant disease, it spreads trhough the population and changed the gene pool. However the disease is not regarded as evolutionary advantageous gene.
Be able to describe sexual selection, both inter-sexual and intra-sexual, and examples of each.
Sexual selection occurs within the species.
Intersexual selection occurs between male and female. For an example, male peacok with larger tail feather is favoured and selected by female, reproducing more offspring. Intrasexual selection occurs in same sex, for example male moose fight to mate with female.
Be able to describe what the term “balancing selection” means, using sickle anaemia as an example.
Although homozygous is more favoured than heterozygous, heterozygotic advantages leave the gene in certain population. (balancing selection)
Sickle cell anemia is homozygous recessive. When individual has heterozygous(carrier) for the gene, they can survive better against malaria. Homozyous dominant individual doesn;t suffer from sickle cell anemia but in disadvantage of surviving from malaria.
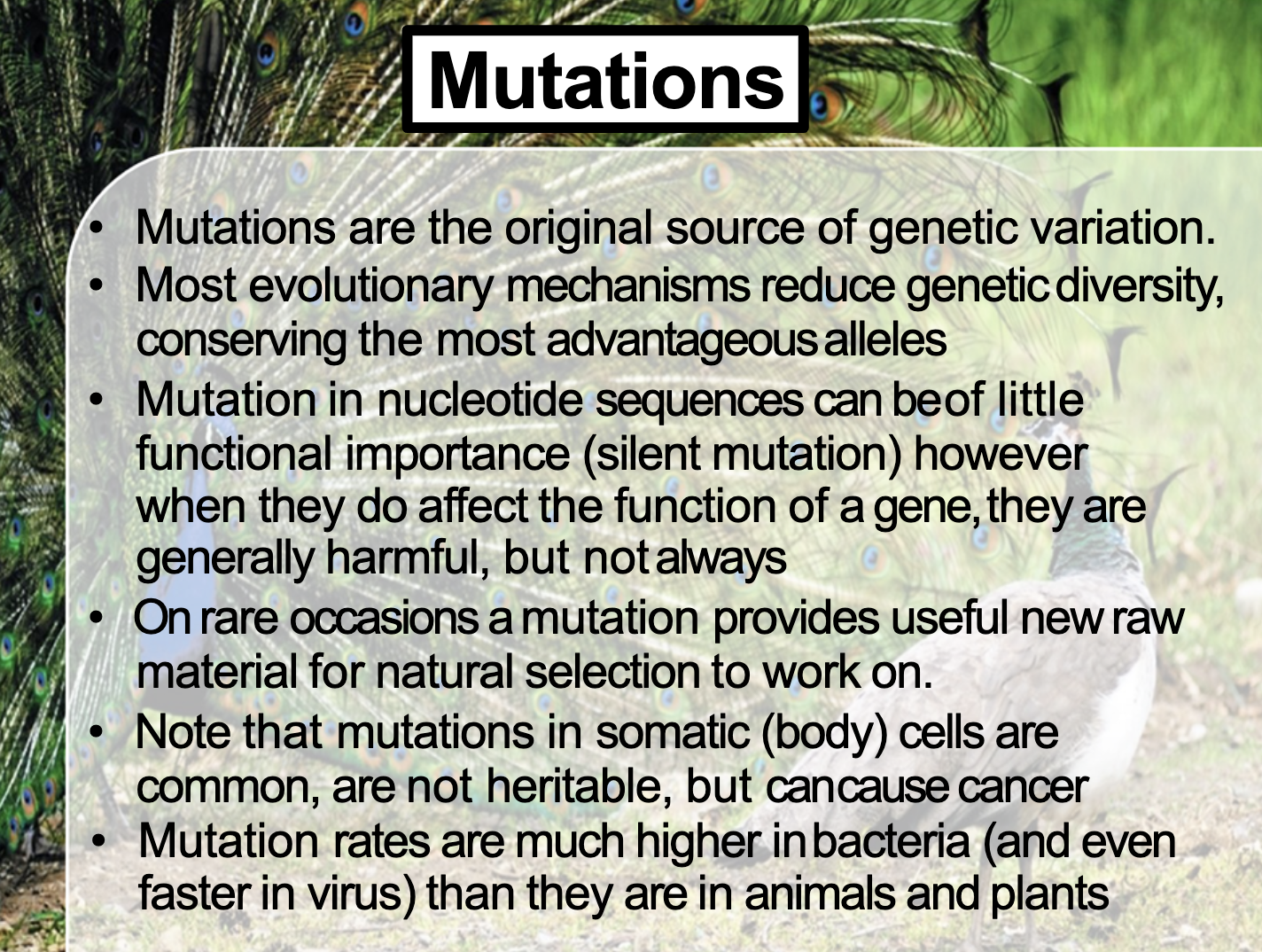
Understand the crucial role mutations play in increasing genetic diversity.
Genetic diversity can be obtained by 1) mutation 2) gene drift 3) gene flow 4) natural selection
Mutation is a production of new alleles. It increases the genetic variation by introducing new alleles
It is different from mutation that it occurs randomly, not related to fitness
Most mutations in coding sequences results in lower fitness level.
Understand what constitutes a species, while appreciating that definitions vary.
If they are same species, they can interbreed, their offspring is fertile.
Howver the definition can be ambigous as the interbreeding can happen between different species, making hybrid.
For the exemption, grizzly and polar bear are expected to be different species but they can interbreed and their offspring is fertile. It shows the gene flow between different species.
Be able to discuss the speciation of polar and grizzly bears, and the effects of climate change on these species.
If their habitat become less distinct by the climate change, it is worried that both species might disappear
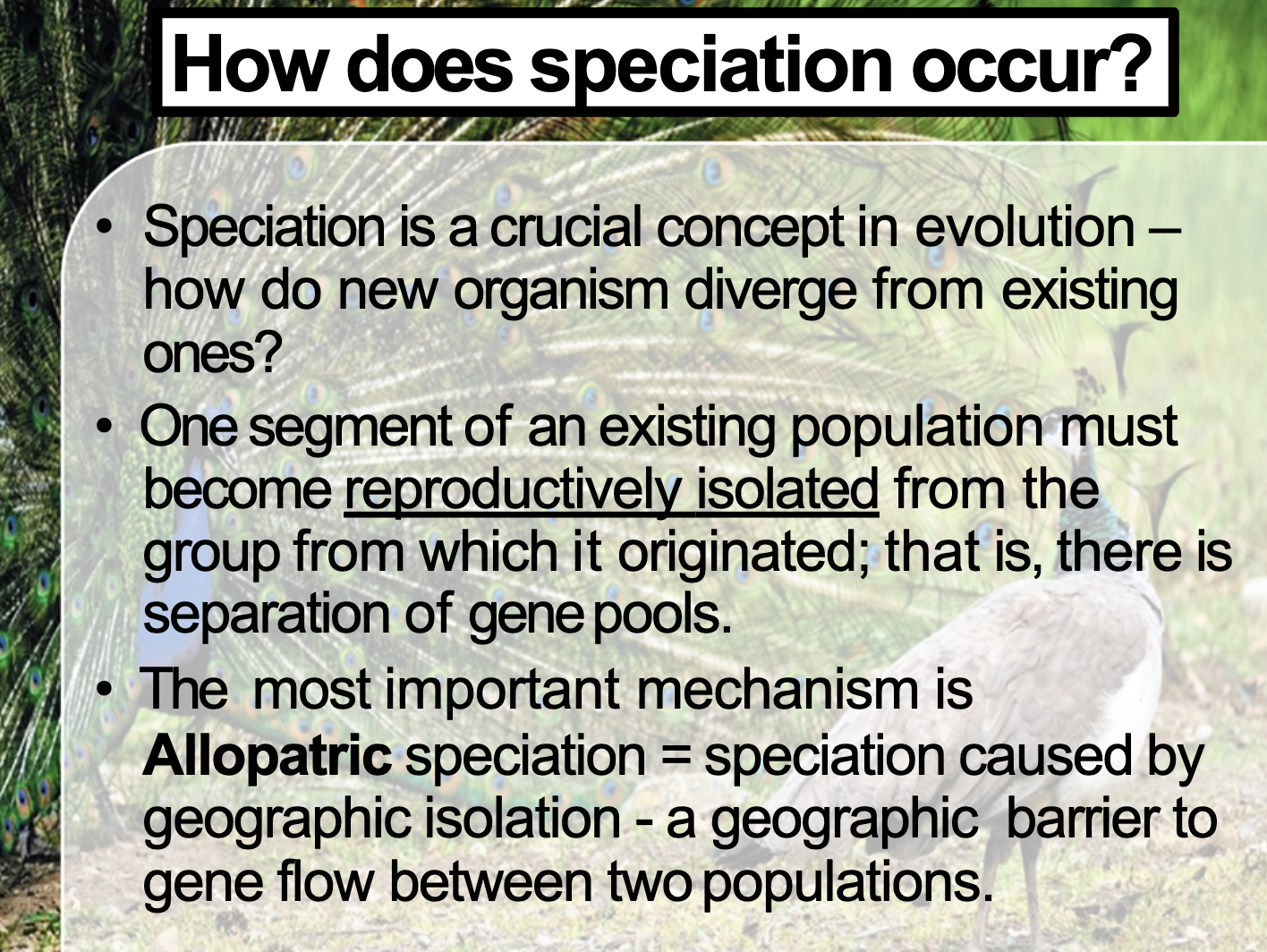
Understand that geographical isolation is almost always required for speciation to be initiated.
Speciation occurs when the population is isolated, and the mechanism of differentiating allele frequency operate to each population independently, resulting in the gene pool changes. If the isolation doesn't occur, it allows gene flow between two population and makes no difference between two population group
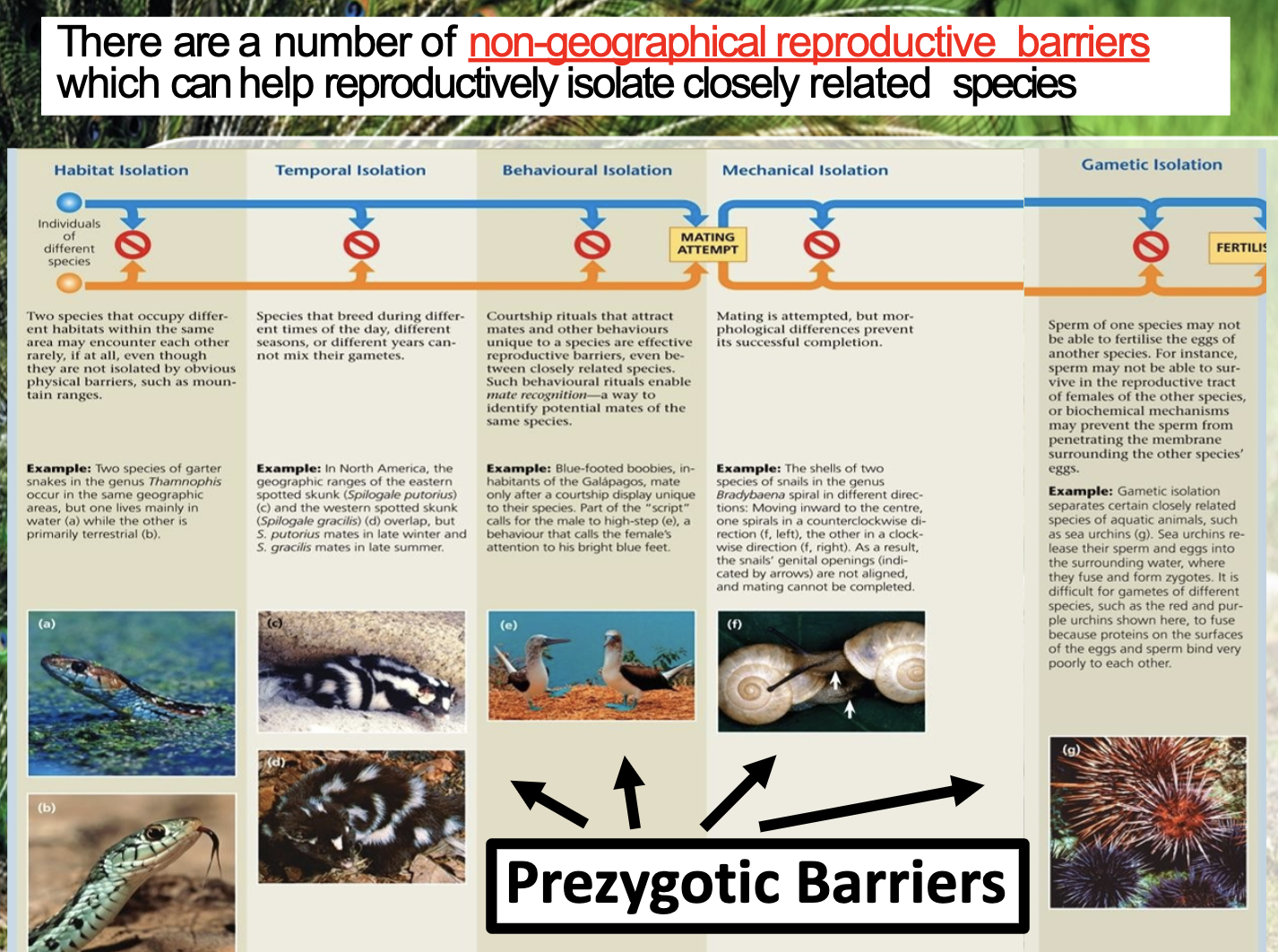
Appreciate that once divergence has occurred, various barriers can prevent or lessen the chance of closely related species interbreeding, and be able to list a number of these.
(Prezygotic)
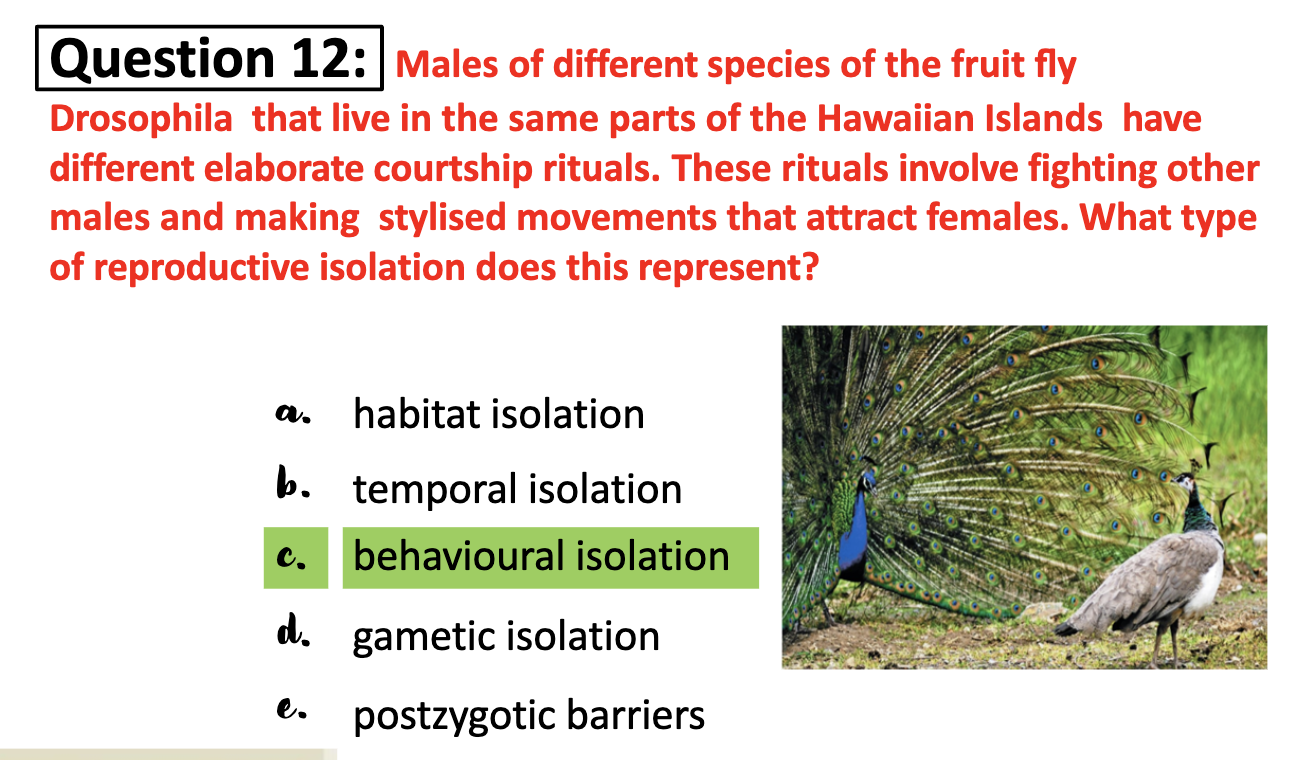
-behavioral
-temporal
-habitual
-mechanical
-gamete formation
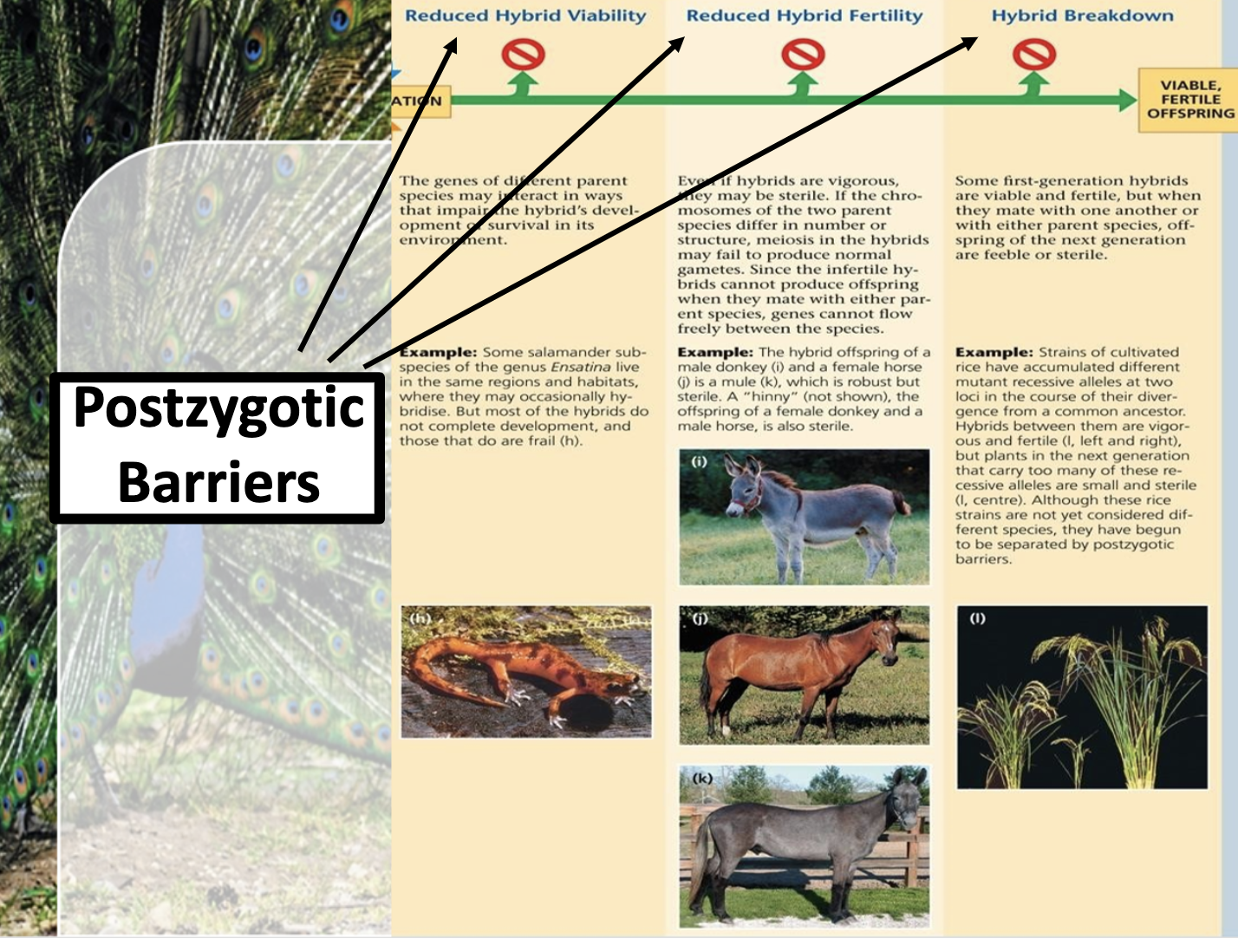
(Postzygotic)
-when hybrid cannot reproduce, or fail to grow
(hybrid breakdown is when the first generation is fertile and reproduce, but the offspring of them is sterile)
Gene flow occurs when the individual migrate from one to another population and breeding in the different group. It occurs in larger population. As the individual migrated is random, not selected or advantage in fitness level, it can be advantageous or disadvantageous in changes of gene pool
Gene flow is when the exchange of gene happens by migrating individuals from one population group to another. Normally they occur in large population. Unlike natural selection, it is random, which means the migrating individual might be advantageous or disadvantageous in fitness level. By migrated individual interbreeding within the population
Understand that hybrids of closely related species may be more, but are often less, viable.
Appreciate that the rate of speciation, i.e. divergence of a species into another, can vary widely from between tens of thousands of years to tens of millions of years.
Speciation can be extremely raid by evolutionary standards once divergence starts to occur (within 4,000 years)
The average speciation time is estimated to be ~6.5 million years which indicates how long it takes to have a widely diverse biosphere after a mass extinction
Punctuated equilibrium describes that the new species can varied rapidly, maintain for so long.
PPT




The smaller population, less possible variation
Tasmanian devils has less variation in immune system gene, so it has been decimated over recent years
-> it represents that less variation/ less raw material to make natural selection happen is disastrous to a powerful aselective force such as disease.
MEASURING GENETIC DIVERSITY/VARIABILITY

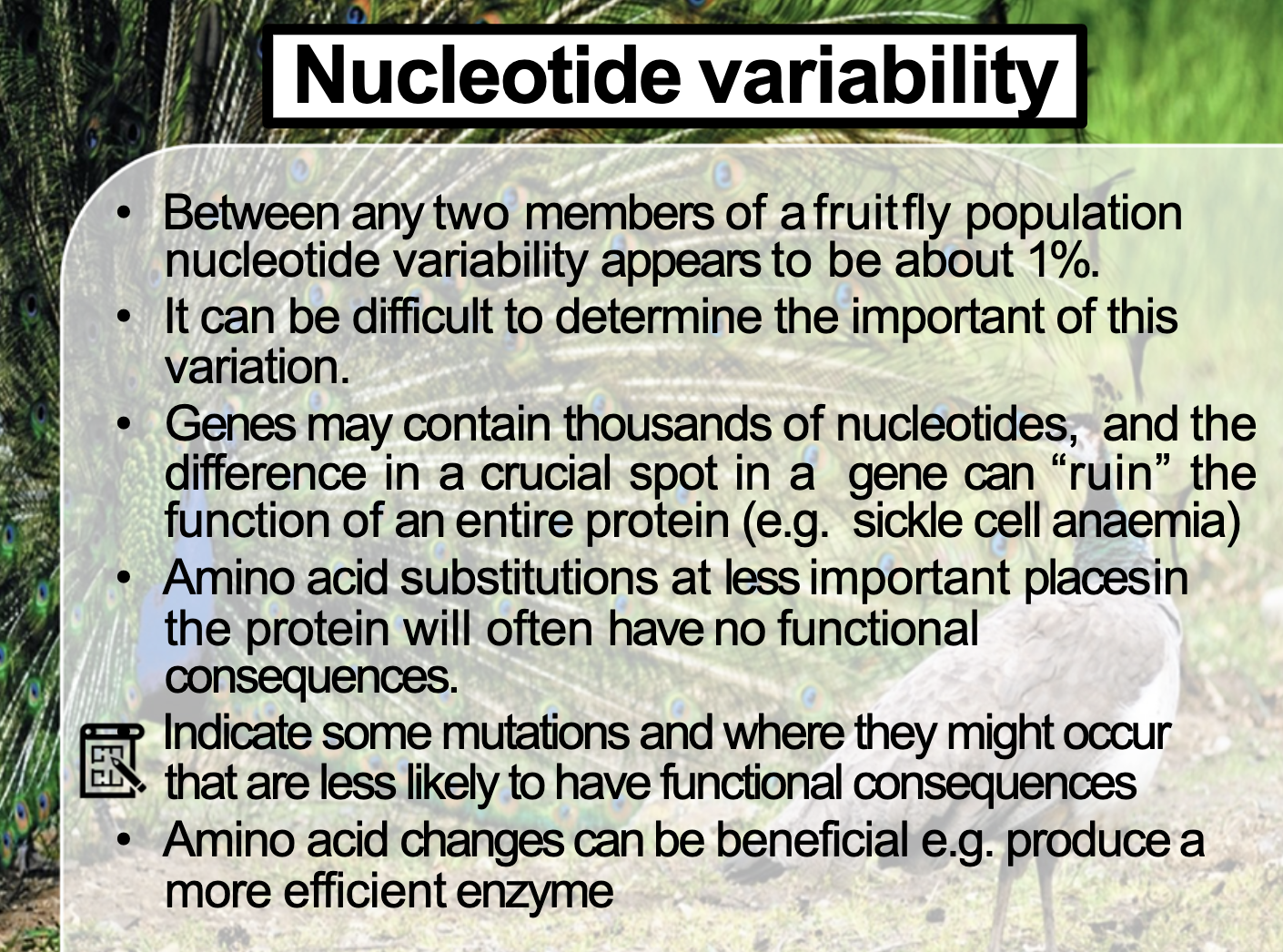
Nucleotide variability -> JUST COMPARING DNA SEQUENCE
Homozygous -> 85%
Heterozygous -> 15%
Heterozygotic variability provides ample raw material for natural selection to operate
WHAT ALTERS ALLE FREQUENCIES?
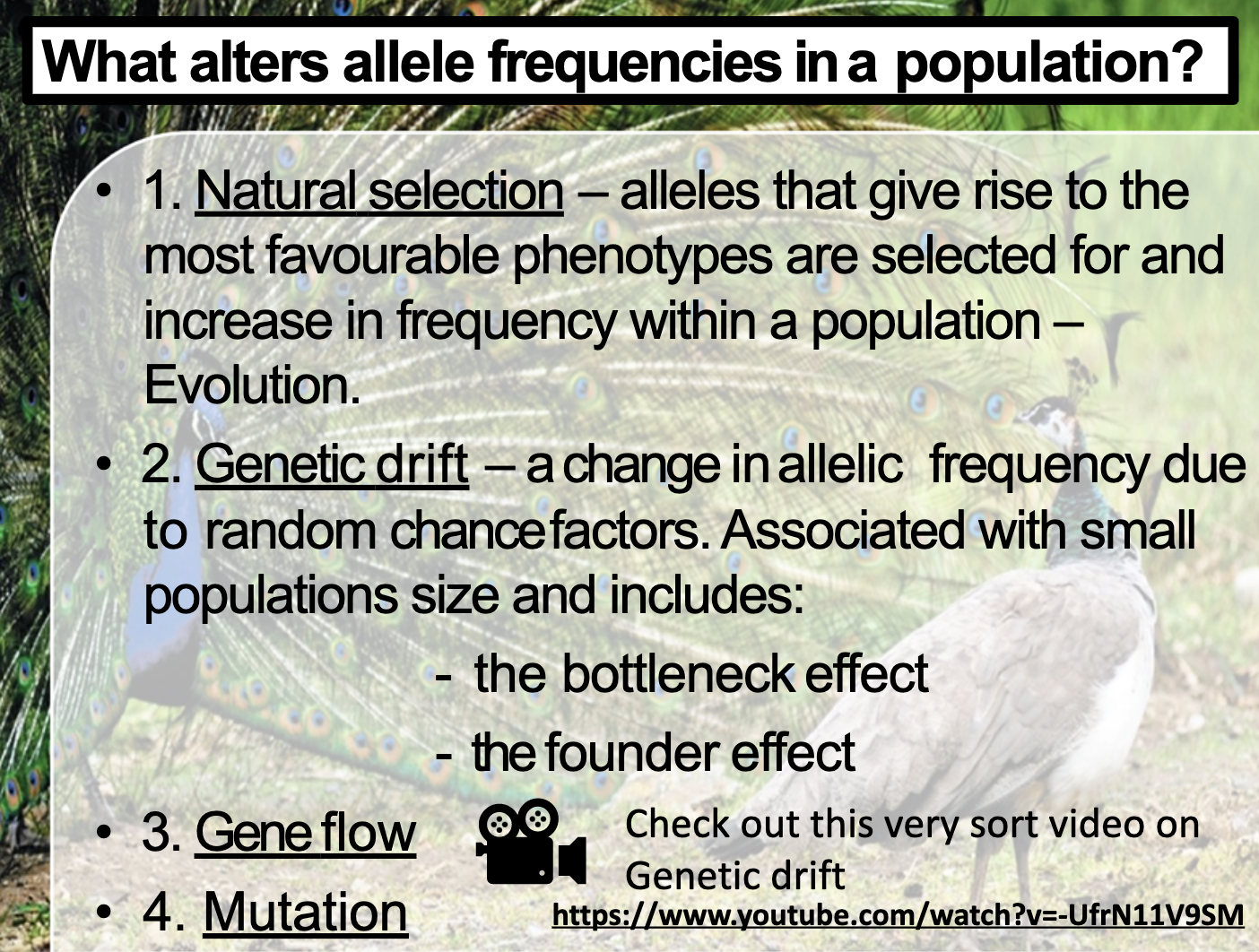


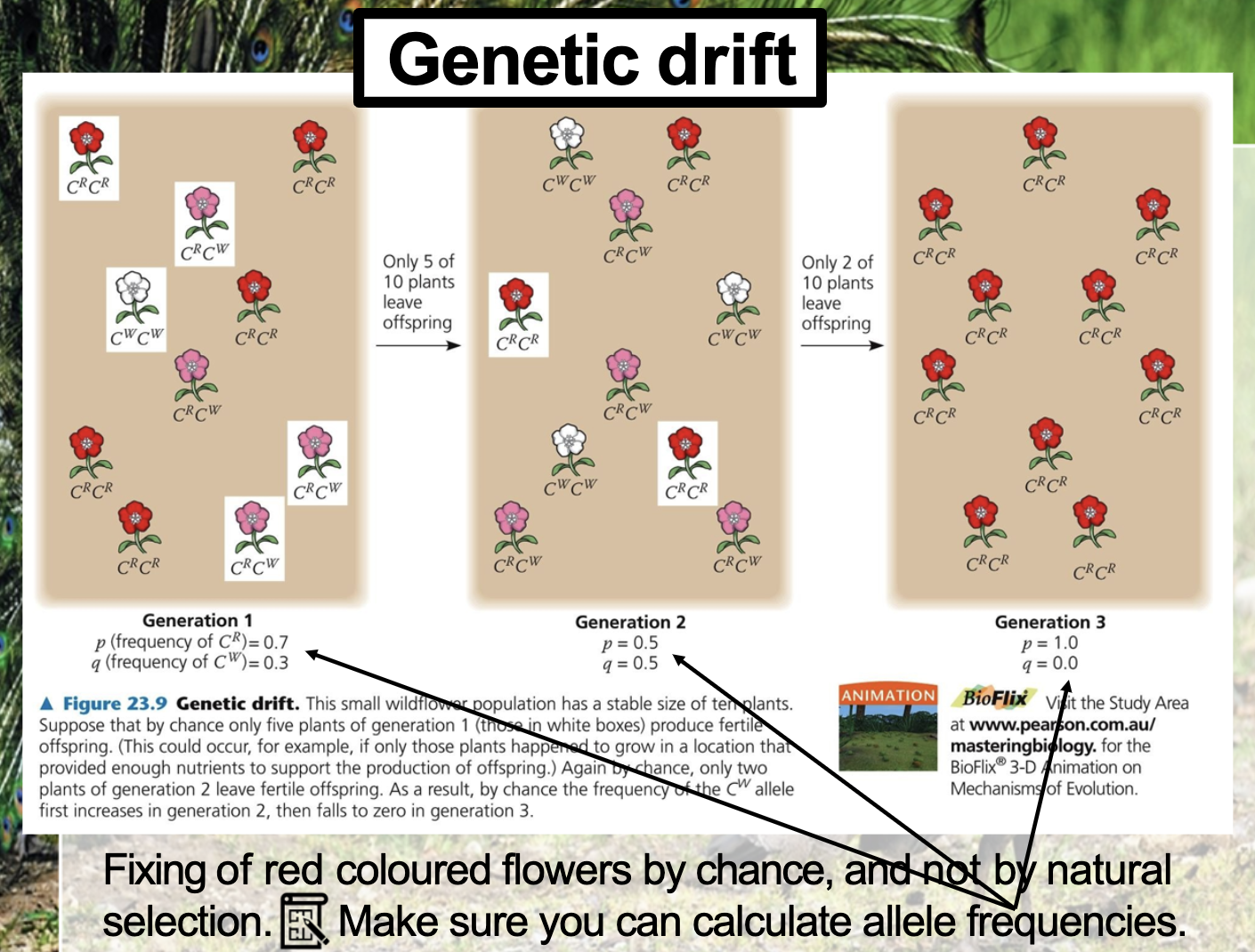
From the bottle neck effect, the ratio between phenotype of population before the bottlenecking events is proportional to the survival population after the event


Genetic reduction is relevant to
number of alleles per locus indicates variation of gene (gene variability)
When the population decreases, the gene variability also decreases
Control -> bottom two examples

BALANCING SELECTION
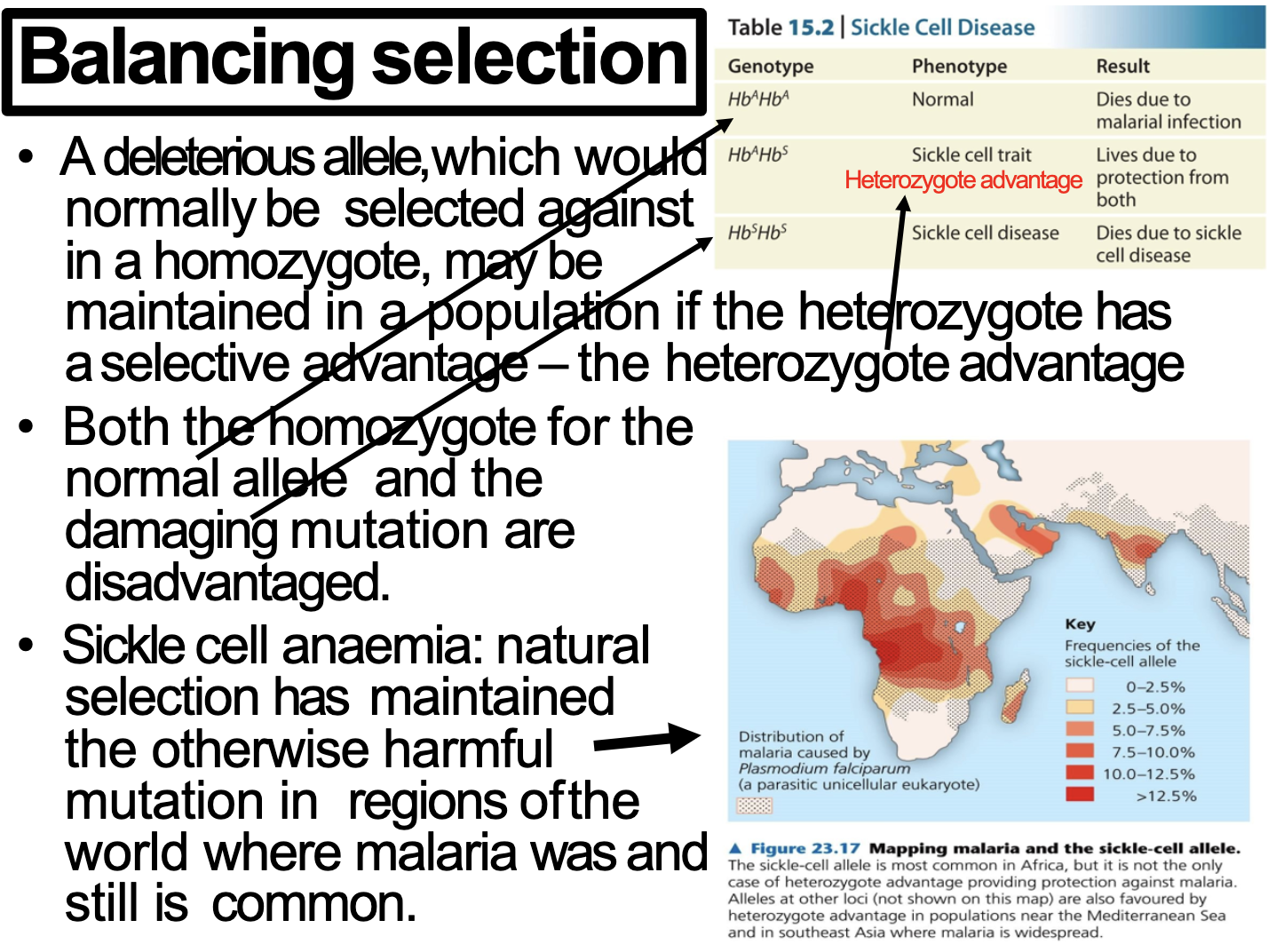
Variation is preserved
What is balancing selection
Because of the benefits to have the gene, even having the gene as homozygous brings disease, the gene doesn't disappear.
SEXUAL SELECTION



It leads sexual dimorphism


INTER SEXUAL SELECTION
We can add the result that showing the female gray frog prefer to mate with LC males
1) result showing that LC gene performance better than SC gene in survival
2) result showing that female gray frog favor LC males in mating
-> Female gray frog prefer mating with the male with better performance gene
Even if they have longer call (attract predators), they can survive better (they are fitter)
in larval growth, larval survival, time to metamorphosis
number, graph, should be added to make the conclusion better
SPECIATION


They havent completely diverged so that they can interbreed
-> their speciation was pretty recent


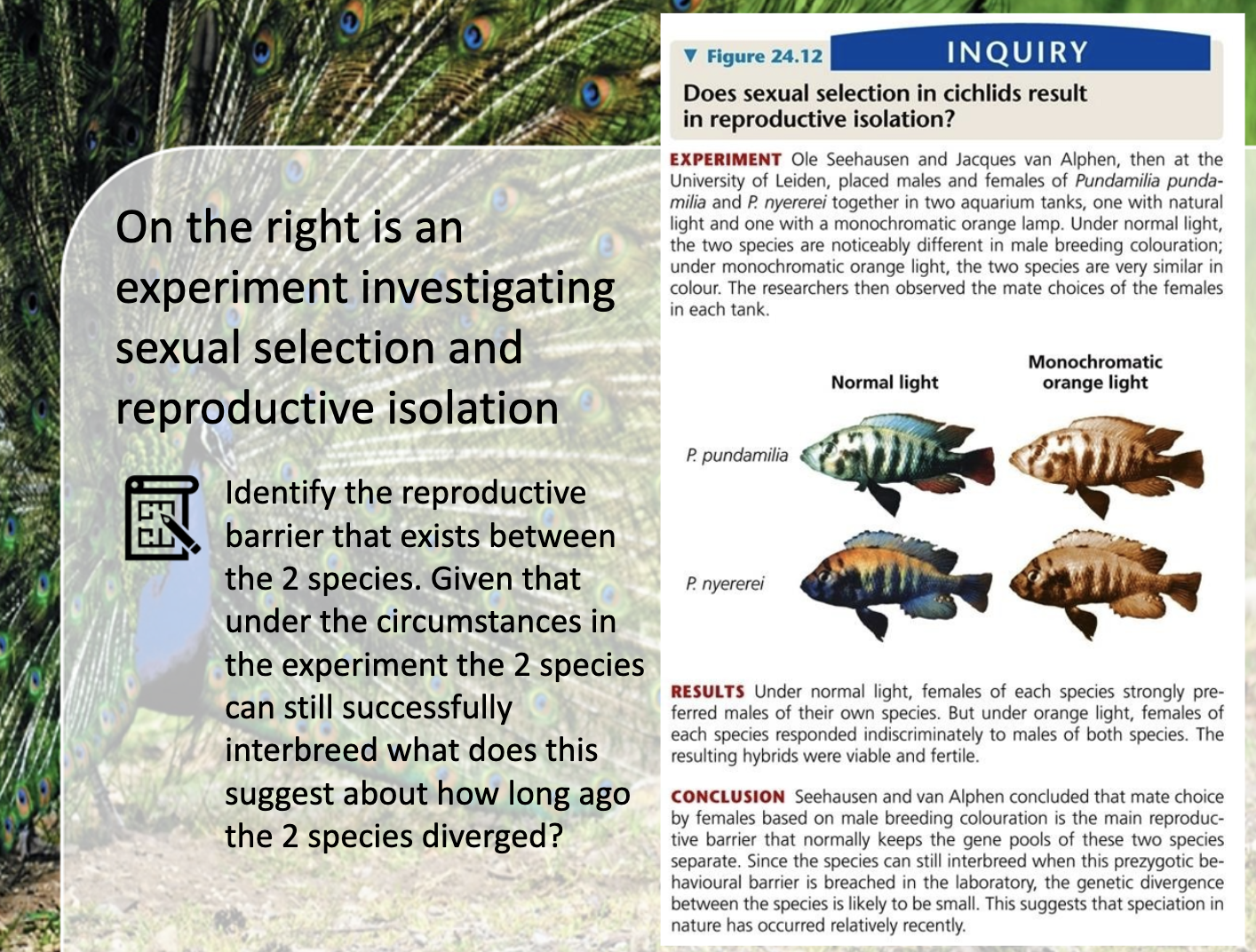
-Intersexual selection
-Behavior barriers
-Females are selecting males by color
-Color is manipulated
-As they can interbreed -> their speciation was pretty recent




SPQ


1.
Speciation is a formation of a new species by reproductively isolating the species.
Allopatric speciation occurs when the species is isolated by the geographical barrier, each of the gene pool experiencing evolution mechanism independently, and as a result speciation occurs.
Sympatric speciation occurs not because of the physical barrier.
There are two different barriers, pre-zygotic (temporal, behavioural, habital, ..) and post-zygotic (if the offspring is sterile, or the individual cannot grow normally) barrier.



2.
Natural selection in an aquatic environment resulted in significant changes to whale forelimb anatomy (=> natural selection reflect the environmental conditions)
3.
Allele frequencies can changed by -Mutations/ gene flow/ gene drift/ natural selection
Small population inevitably has less gene variability than the large population. Less gene variation means there is less chance to have individuals with different characteristics that is favoured by environment between individuals
In this small population, other mechanism occurs to exhibit changes. For example, genetic drift, such as bottle neck effect and founder effect are most efficient in smaller population. They occur by chance so it is not natural selection. Bottle next effect is when the catastrophic disaster decreases the population excessively, and the gene pool changes. Survival population is proportional to the previous population. Founder effect is when the small group leaves the original population and create the seperate group, their gene pool differs from the original group.
Gene flow is when the separated group exchange the gene and it changes allele frequencies.


4.
Huntington is an autosomal dominant disease. It is an example of gene drift, the founder effect. The population introduced with Huntington disease grew with the individuals with the disease and the gene pool of the population changes because of the introduction of the disease is so powerful
답지 : The founder effect probably accounts for the relatively high frequency of certain inherited disorders among isolated human populations.
Disease-causing mutations can become fixed in small, isolated populations with arrival of mutation in a single carrier (hence term ‘founder’)
Initial descendants with disease are immediately disproportionately represented in that small population, and the proportion of sufferers in the population may subsequently be maintained at higher frequencies, even as the population grows


5.
To not to evolve, there must be certain conditions to be met.
Conditions that contribute to gene stability
1) Too large population size
2) No mutations
3) Totally random mating within a population
4) No natural selection within a population
5) No gene flow between different population


6.
Probably the sexual selection might occur. For intersexual selection, if the female whip bird prefer the male whip bird with long tail more than normal one, the population of long tail whip bird grows because they are more selected by females


7.
The differentiation in species due to reproductive isolation is called speciation.
Speciation has two different types.
Allopatric, if they are reproductively isolated due to the geographical barrier.
Sympatric, if they are reproductively isolated due to the factors other than geographical barrier.
Sympatric speciation has prezygotic, post zygotic barriers.
Prezygotic barriers prevent them from making zygote. It includes..
-behavioral: when their mating behaviour doesn’t appeal to other sex in one species
-temoral : when their mating season is different (summer/winter, daytime/night time)
-habitual : they live in geographically same place but one preference in habitat is different (aquatic/ground)
-mechanical: their physical appearance doesn’t fit each other to mate and reproduce
-gametic : sperm of one species unable to fertilise the eggs of another species (sperm cannot survive in reproductive tract or biochemical factors prevent sperm penetration of egg)
Post zygotic barriers refers to the situation when the offsprings are sterile, or they cannot grow completely(fail to grow) For example, mating between different species can produce hybrid, but they are sterile so they cannot have offspring.


8.
Grizzly and polar bears are different species. So they remain as seperate species. Originally different species cannot interbreed and their offspring is sterile. However, for the exemption for this case is these bears. They can interbreed and their offsprings are fertile. It can indicate that these two species are distinct by their appearance, habitat and geographically, gene flow can happen.


9.
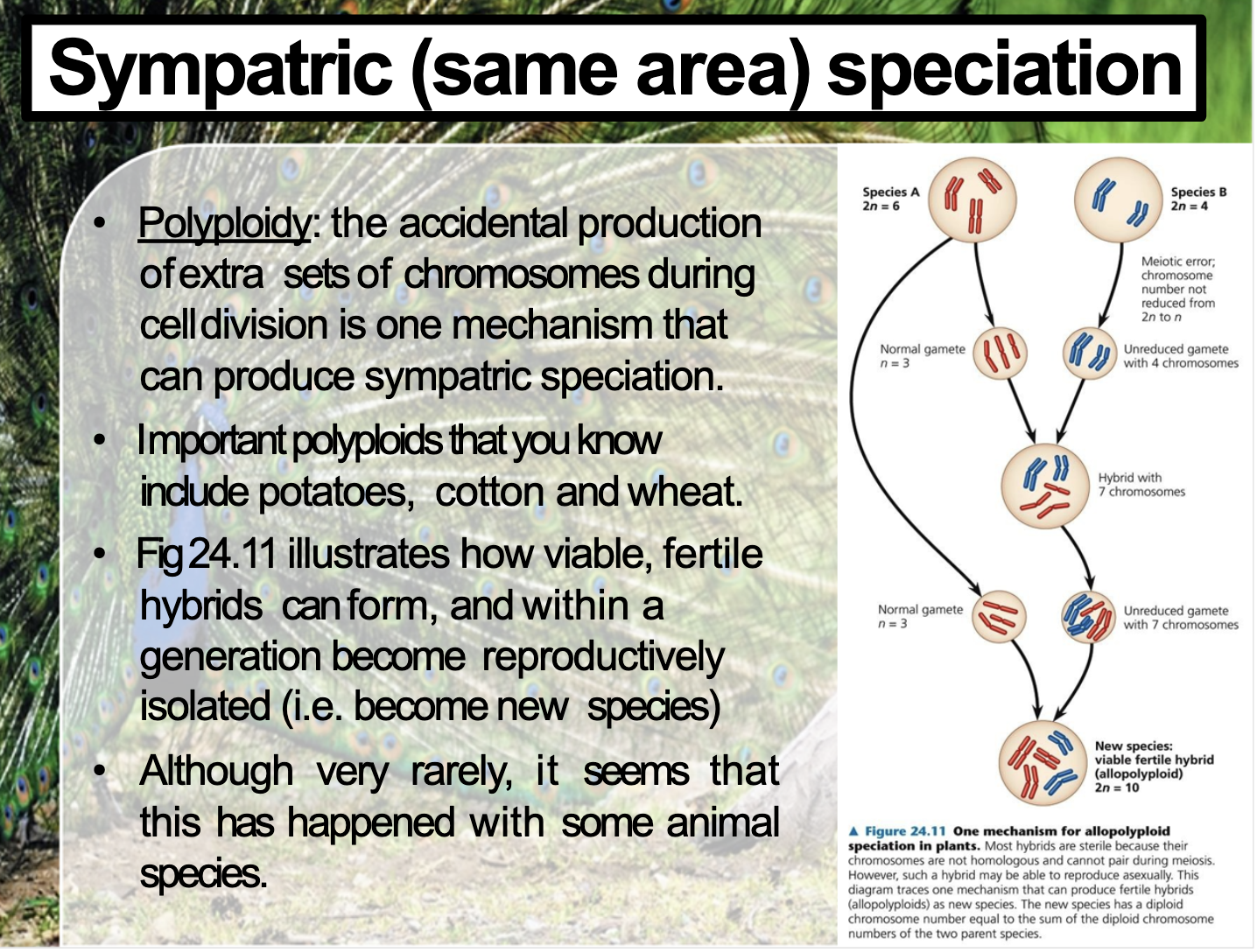
When cell division doesn’t occur during the gamete formation, polyploidy might occur.
Most hybrids are sterile as their chromosomes are not homologous. But still they can reproduce asexually.
A lot of Plants are used in experiments to produce polypoid to make the hybrid.
When hybrid is made by using unreduced plants’ gametes, after several fertilisation, they matches the chromosome numbers equal to the sum of the diploid chromosome number, new species are made.
답지 :
A species may originate from an accident during cell division that results in extra sets of chromosomes, a condition called polyploidy. Polyploid speciation occasionally occurs in animals. (The grey tree frog Rhyl versicoloured but is far more common in plants (oats, cotton, potatoes, tobacco, and wheat)) Plant genetics generate new polyploids in the lab by using chemicals that induce meiotic and mitotic errors

10.
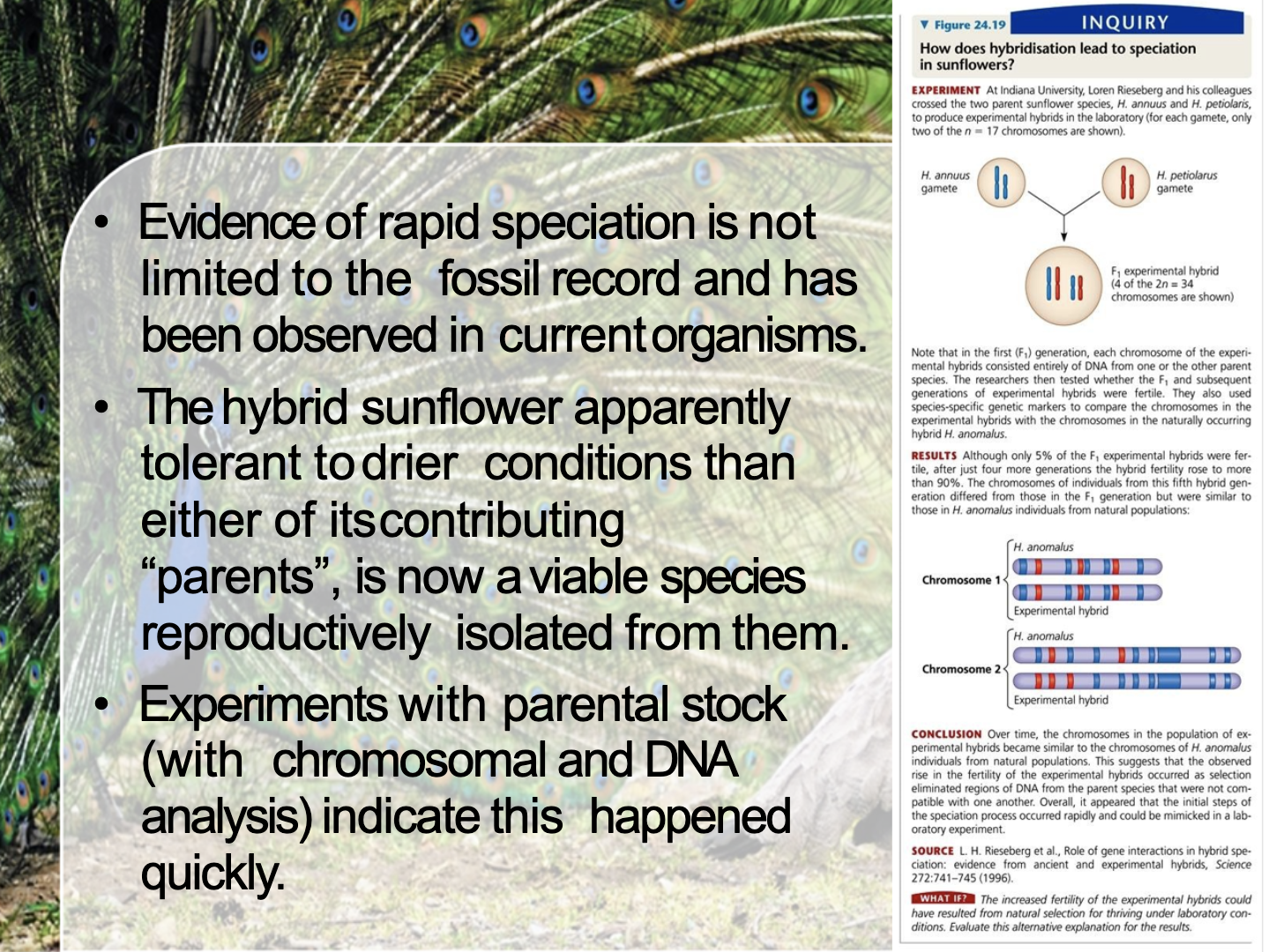
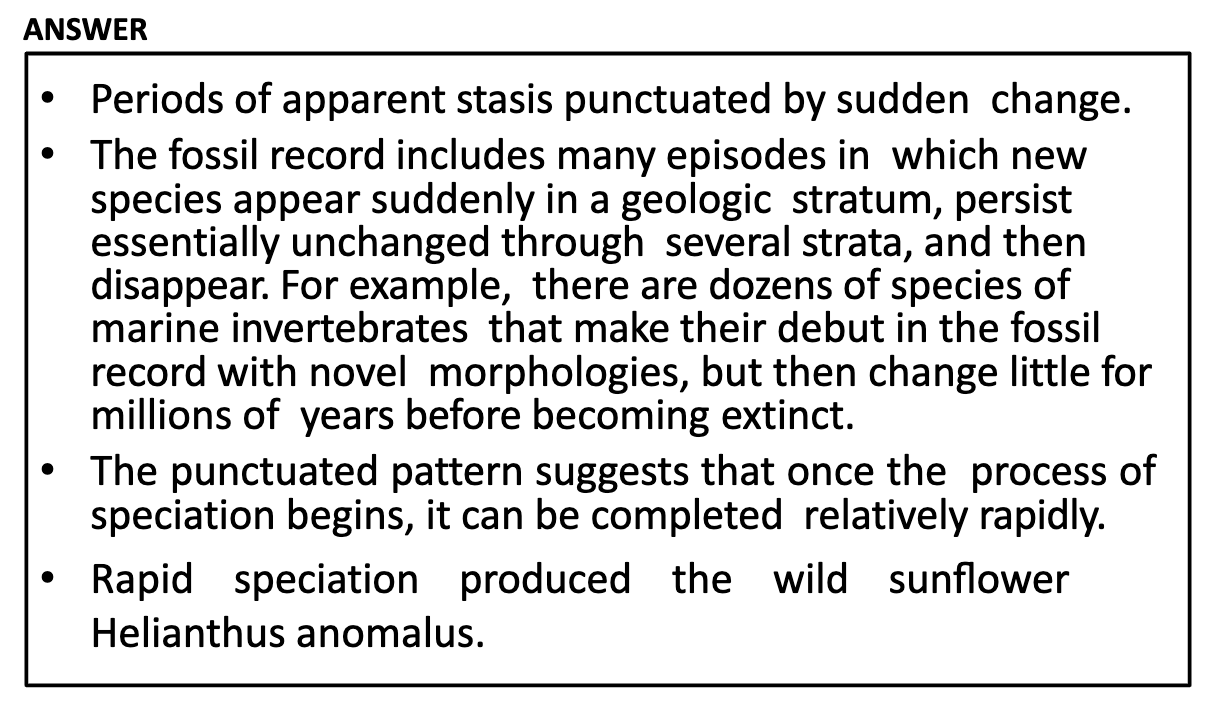
Punctuated equilibrium refers to the phenomenon that once the change in species appears (new species appear suddenly), the stability of that species maintain for so long period without any changes.
Hybrid Sunflower which is tolerant to drier conditions than parents appeared suddenly and it remained as a new species.

11.
The largest unit within which gene flow can readily occur is a species……
12.
According to the punctuated equilibrium model, most new species accumulate their unique features relatively rapidly as they come into existence, then change little for the rest of their duration as a species
(CHANGE RAPIDLY AND MAINTAIN FOR SO LONG)



13.
The standard that makes it same species is that the two forms interbreed often in nature and their offspring have good survival and reproduction
15.
A population becomes geographically isolated from the parent population => allopatric speciation occurs
The separated population is small and genetic drift occurs => allopatric speciation occurs
The isolated population is exposed to different selection pressures than the ancestral population => allopatric speciation occurs
Different mutations begin to distinguish the gene pools of the separated populations => allopatric speciation occurs
Gene flow between the two populations is extensive => LESS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TWO POPULATION -> BECOME ONE GROUP
The mechanism that changes allele frequencies within a group -> mutation/gene drift/gene flow/natural selection
When the group is too large/ no mutation/ no natural selection/ no gene flow/ total random mating -> genetic stability is formed


17.
Given the fact that marsupials appeared to have first evolved in the Northern hemisphere, how do plate tectonics explain why marsupials reigned in Australia in recent times, but are almost entirely extinct elsewhere?
답지:
With the breakup of Pangea, South America and Australia became island continents, and their marsupials diversified in isolation from the eutherians that began an adaptive radiation on the northern continents
Australia has not been in contact with another continent for about 65 million years, In contrast southern America once had a diverse marsupial fauna, it has experienced several migration of eutherians. One of the most important migrations occurred about 3 million years ago. When north and South America joined at the Panamanian isthmus and extensive two-way traffic of animals took place over the land bridge
Today, only three families of marsupials live outside the Australian region, and the only marsupials found in the wild in North America are a few species of opossum


18.
Explain how the mutant allele that causes sickle cell anaemia persists in some populations throughout the world.
BALANCING selection
Sickle cell anaemia is a gene mutation that inherited as autosomal recessive. In some population throughout the world (near the equation), individuals who are the carrier for this gene is in benefit to survive from malaria. It causes this sickle cell gene to survive until now.
(In this regions, heterozygous is more favoured than homozygous dominant)
답지:
Heterozygotes for the sickle cell allele are protected against the most severe effects of malaria, a disease caused by a parasite which infects red blood cells
This partial protection occurs because the parasite is unable to enter red blood cells
Protection against malaria is important in tropical regions where the disease is a major killer
In such regions, selection favours heterozygotes over homozygous dominant individuals, who are more vulnerable to the effects of malaria, and also over homozygous recessive individuals, who develop sickle-cell disease
'Griffith college Tri1 2023 > 1005 QBT (GnD)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [WEEK12] Vertebrate and Human evolution (0) | 2023.05.28 |
|---|---|
| [WEEK10] How did life start on Earth? (0) | 2023.05.13 |
| [WEEK10] Charles Darwin and the theory of evolution (0) | 2023.05.13 |
| [WEEK8] Part 3 Developmental Genetics (0) | 2023.04.30 |
| [WEEK6] Part 1 Gene Expression (0) | 2023.04.12 |



