
Contents
3.1 What is academic writing?
3.2 Introduction Paragraphs
3.3 Body Paragraphs
3.4 Effective Presentations
3.5 Evaluating Presentational Speaking
3.1 What is academic writing?
How do you write academically?
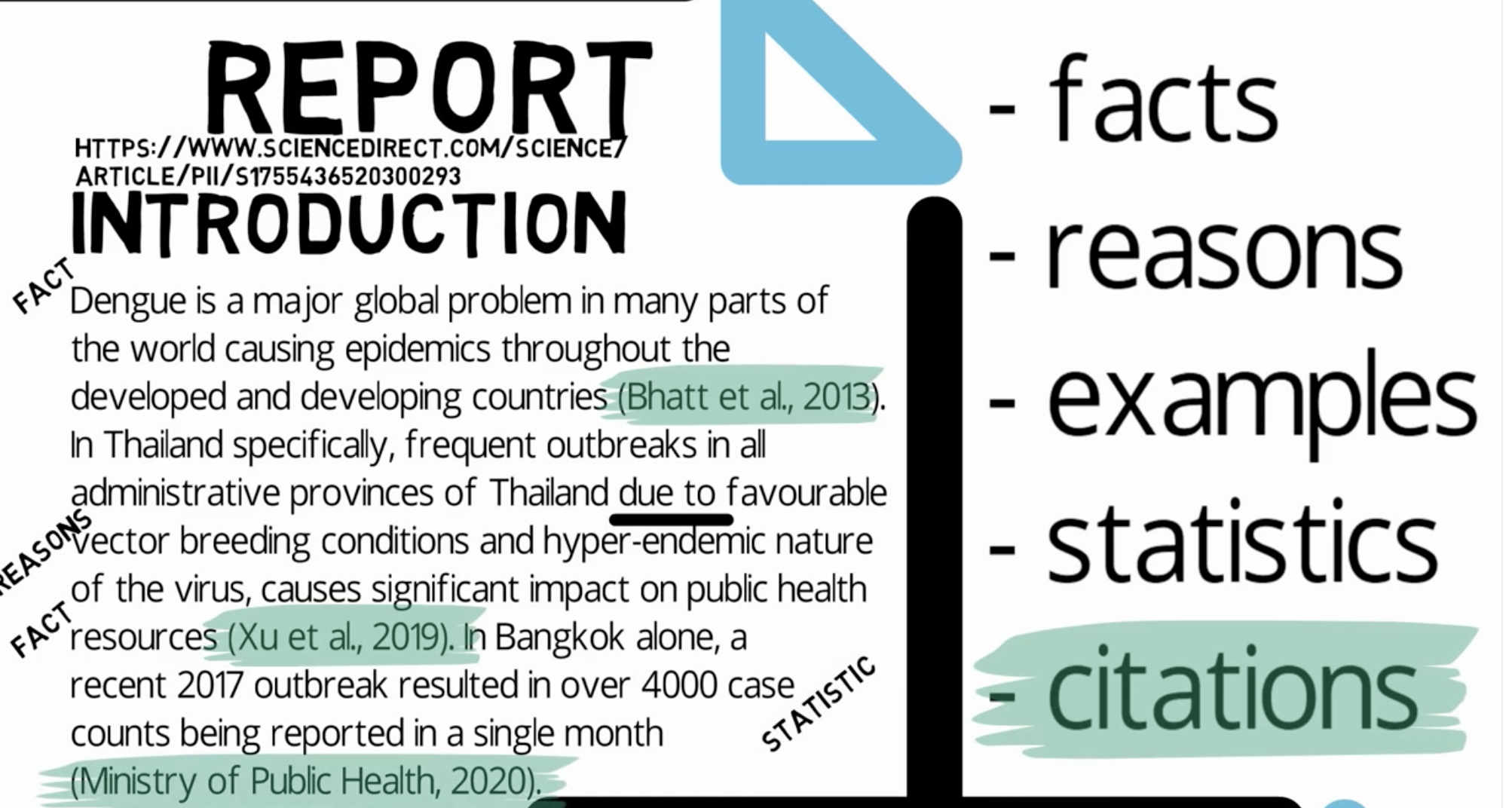
-
CLEAR and FOCUSED
At the outset, you should be clear on what you are writing. Planning is an essential part of the process and will make sure you stay focussed on your purpose. If you are responding to an essay question, your writing should answer the question and demonstrate an understanding of the subject. For a report, you should consider the focus of the report.ADDRESSED TO YOUR AUDIENCE
It is important to identify who you are writing for and how you need to communicate your ideas. Consider, for example, whether you need to explain technical terms or summarise key concepts for readers less familiar with the subject than you.
STRUCTURED
Academic writing needs to be coherent, written in a logical order, and bring together related points and material.
EVIDENCED
You should demonstrate knowledge of the subject area, support any opinions or arguments with evidence and ensure you have referenced accurately.
FORMAL IN TONE AND STYLE
At university, you will need to use appropriate language and the correct tense. Your tone and style should be clear, concise, and balanced.Academic writing is writing which communicates ideas, information and research to the wider academic community. Academic writing should be: structured, evidenced, critical, precise, balanced, objective, and formal. Academic writing can be divided into two types: student academic writing, which is used as a form of assessment at university; and expert academic writing, which is writing that is intended for publication in an academic journal or book. Both types of academic writing (student and expert) are expected to adhere to the same standards, which can be difficult for students to master.








https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Cq4J8bPBcck&t=449s
3.2 Introduction Paragraphs
This essay examines how relevant Grit motivation, time management strategies are to self-regulated learning and students’ academic success at university. It appears that these are important influences on student’s ability to succeed academically at university. Wolters and Hussain (2015) argued that university learners inclination to organise and manage their time in order to avoid needless interruptions to finishing academic work as well as to control the environment in which they study is an important link between personal character and qualities and learners academic success (p. 306). However, while many students are motivated and determined to do well in their academic studies, they may not regulate their study approach and learning environments in such a way to support their academic success. This essay argues that in general, students who are motivated to study and manage their learning environment are more likely to be successful in their studies. Furthermore, it is argued that developing Grit that is the determination and perseverance to succeed also influences students’ academic success. However, while it is recognised that motivation and time management strategies play important roles in supporting students to achieve their academic goals, this essay argues that unless students are also able to self-regulate their study approach and learning environment, they risk academic failure.
Topic statement
Background sentence
Linking sentence
Argument/thesis/position statement
3.3 Body Paragraphs
Research tasks are used as assessment tools at university to assist students to demonstrate a thorough understanding of course content. University assessments are designed to test students’ learning in key skills specific to course content and general academic skills. As developing a deep understanding of course material is important, it seems that research should be considered a mandatory skill required by students at university. White (2011) stated that research tasks tend to enhance understanding of subject matter, as students are able to read widely and deeply on a set topic (p. 67). In other words, students are encouraged to compare and evaluate information from a range of sources before presenting an argument. Wills and Stoker (as cited in Jones, 2012, p. 20) agree with White, claiming, "it is essential for students to extend their understanding of their discipline areas through being actively engaged in research activities.” In addition, research tasks could be considered one of the fundamental ways that deep learning occurs at university. Furthermore, through carrying out primary research, students are able to contribute to ongoing knowledge in the discipline.

Topic sentence -> a general idea + a comment
3.4 Effective presentations
- Organisation and Structure. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qFLL-XB56UU
- Engaging the Audience http:// https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lo9xOV6WUqM
- Signposting Language https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T_dkl-6zSMY
- Body Language and Voice https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tXzkpIrmhQw
- Purposeful Practice https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R5SYFiPvXzc
- Voice https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FnOvASURr7A
- Visuals and PPT https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O-D9fZN01yk
- Anxiety https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ryXOW1QS0ZM
- Soft skills , presentations https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ADJAcyTq1us




'Griffith college Tri3 2022 > Headstart' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Headstart] Learning & Technology (0) | 2022.10.14 |
|---|---|
| [Headstart] Citizenship & Employability (0) | 2022.10.03 |
| [Headstart] Teamwork and participation (0) | 2022.09.23 |


