Learning objectives
- Be able to list and describe the functions of the various structures that make up the integumentary system
- Your integumentary system is your body's outer layer. It consists of your skin, hair, nails and glands. These organs and structures are your first line of defense against bacteria and help protect you from injury and sunlight. Your integumentary system works with other systems in your body to keep it in balance.
- Describe the structure and function of the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis
- Skin has three layers: The epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. The dermis, beneath the epidermis, contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands. The deeper subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) is made of fat and connective tissue.
- Describe the structure and functions of the sub-layers of the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis

- What are the different appendages of the skin?
- The skin appendages include sweat glands, nails, and the pilosebaceous unit of the skin, comprised of the hair shaft, hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and arrector pili muscle
- Describe the structure, function and distribution of hair
- Hair serves a variety of functions, including protection, sensory input, thermoregulation, and communication. For example, hair on the head protects the skull from the sun.

- Describe the structure, function and distribution of sweat glands and the differences between eccrine and apocrine sweat glands, and of sebaceous (oil) glands
- 땀은 신체의 체온조절 체계의 중요한 요소로서 교감성신경의 지배를 받아 체온증가시 분비된다. 땀샘은 크게 에크린샘(eccrine gland)과 아포크린샘(apocrine gland)으로 나눌 수 있다. 에크린샘에서는 샘세포는 그대로 있으면서 세포외유출(exocytosis)에 의해 땀을 분비하는 샘으로서 신체 전부위에서 발견되며 손바닥, 발바닥, 이마, 겨드랑이에 가장 풍부함. 아포크린샘에서는 샘의 세포의 일부가 떨어져 나가 땀이 분비되는 샘으로서 겨드랑이, 젖꽃판, 항문생식기 부위의 몇군데에서만 분비됨.
- Merocrine glands: Merocrine glands release their substances through a process called exocytosis. ...
- Apocrine glands: Apocrine glands make buds of the cell membranes, which break off into the duct. ...
- Holocrine glands: With holocrine glands, the cell membrane bursts to release its substance.
PPT
Function of the integumentary system
1. Protection 2. Cutaneous sensation 3. Body temperature regulation 4. Metabolic functions 5. Blood reservoir
6. Excretions


*What is the main metabolic function of the skin and what is excreted by the skin?
Vitamin D precursor is synthesized with the cholesterol in epidermis by the sun.
*acid mantle
The acid mantle is a thin film on the skin's surface composed of lipids from the oil glands mixed with amino acids from sweat.
*defensin
Defensins are small (29–35 amino acids) proteins produced by circulating white blood cells and tissue cells.
*plant oleoresin
Oleoresins are semi-solid extracts composed of resin and essential or fatty oil, obtained by evaporation of the solvents used for their production.
*dentritic cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) represent a heterogeneous family of immune cells that link innate and adaptive immunity
*pacinian corpuscle 파치니소체
sensory receptors for vibration and deep pressure and are essential for proprioception고유감각
*Dermal papillae
모유두 세포(dermal papilla cell)는 모발의 성장을 담당하는 핵심세포입니다. 머리카락은 피부 내부와 외부에 걸쳐 있습니다. 피부 밖에 있는 게 모발줄기이고, 피하에 있는 뿌리가 모근입니다. 모근은 털주머니인 모낭의 보호를 받습니다
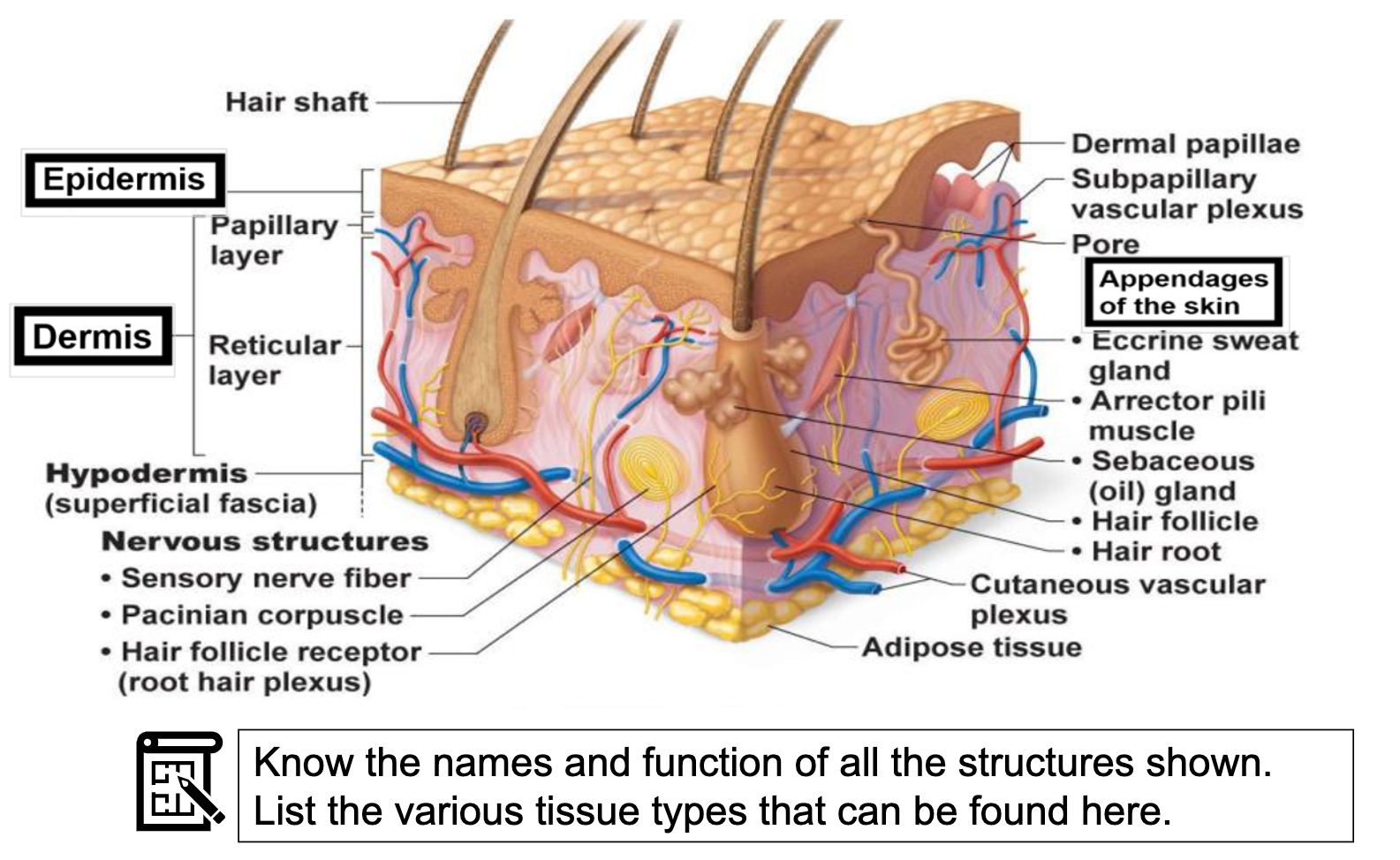
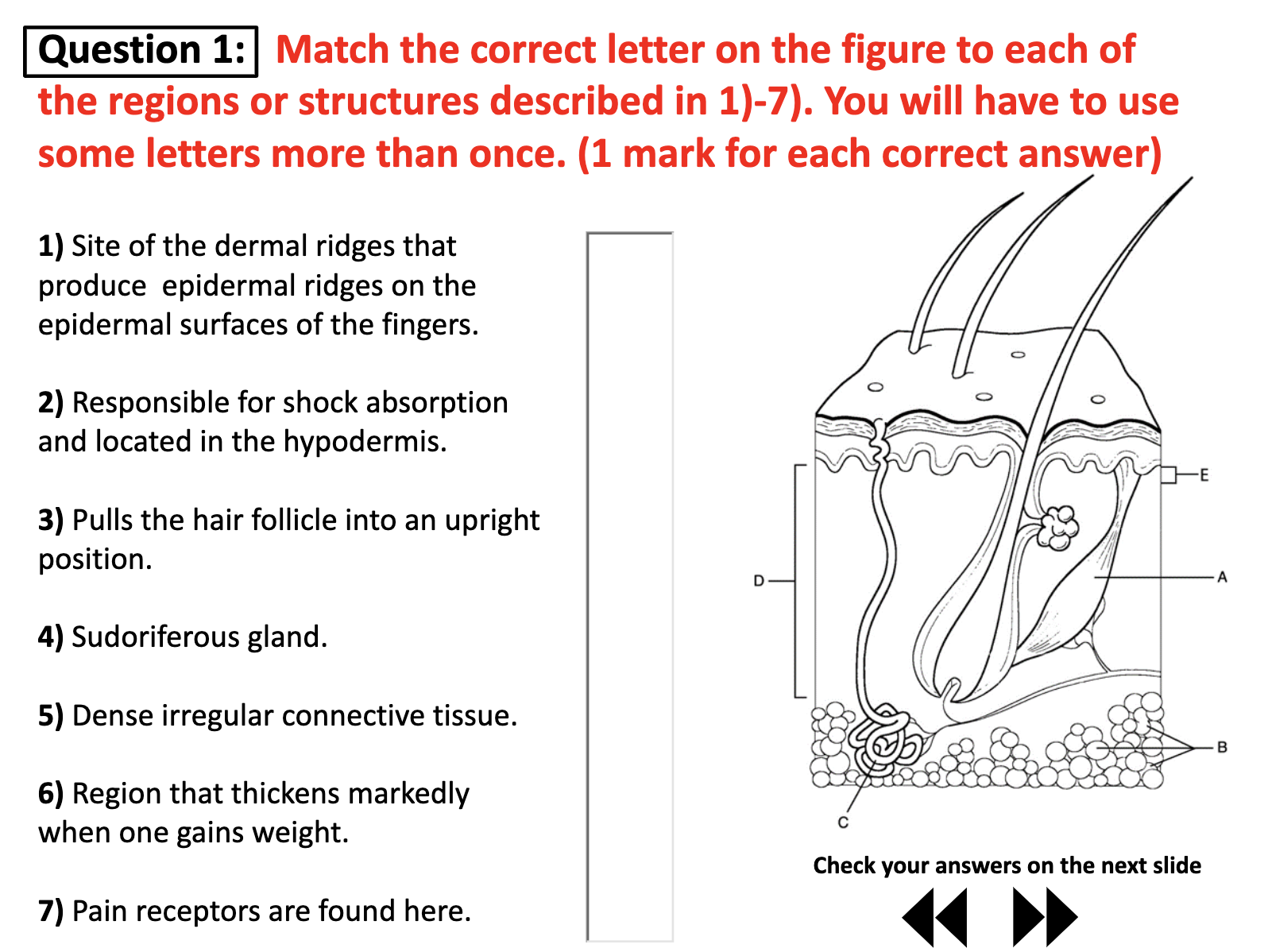
*Know the names and function of all the structures below. List the various tissue types that can be found here.
Hair(shaft, follicle,root), Pore, Dermal papillae subpapillary
Ecrine sweat gland, sebaceous gland,
Cutaneous vascular plexus, subpillary vascular plexus,
Adipose tissue
Hair follicle receptor(root hair plexus)
Pacinial corpuscle, Sensory nerve fiber,
Epidermis
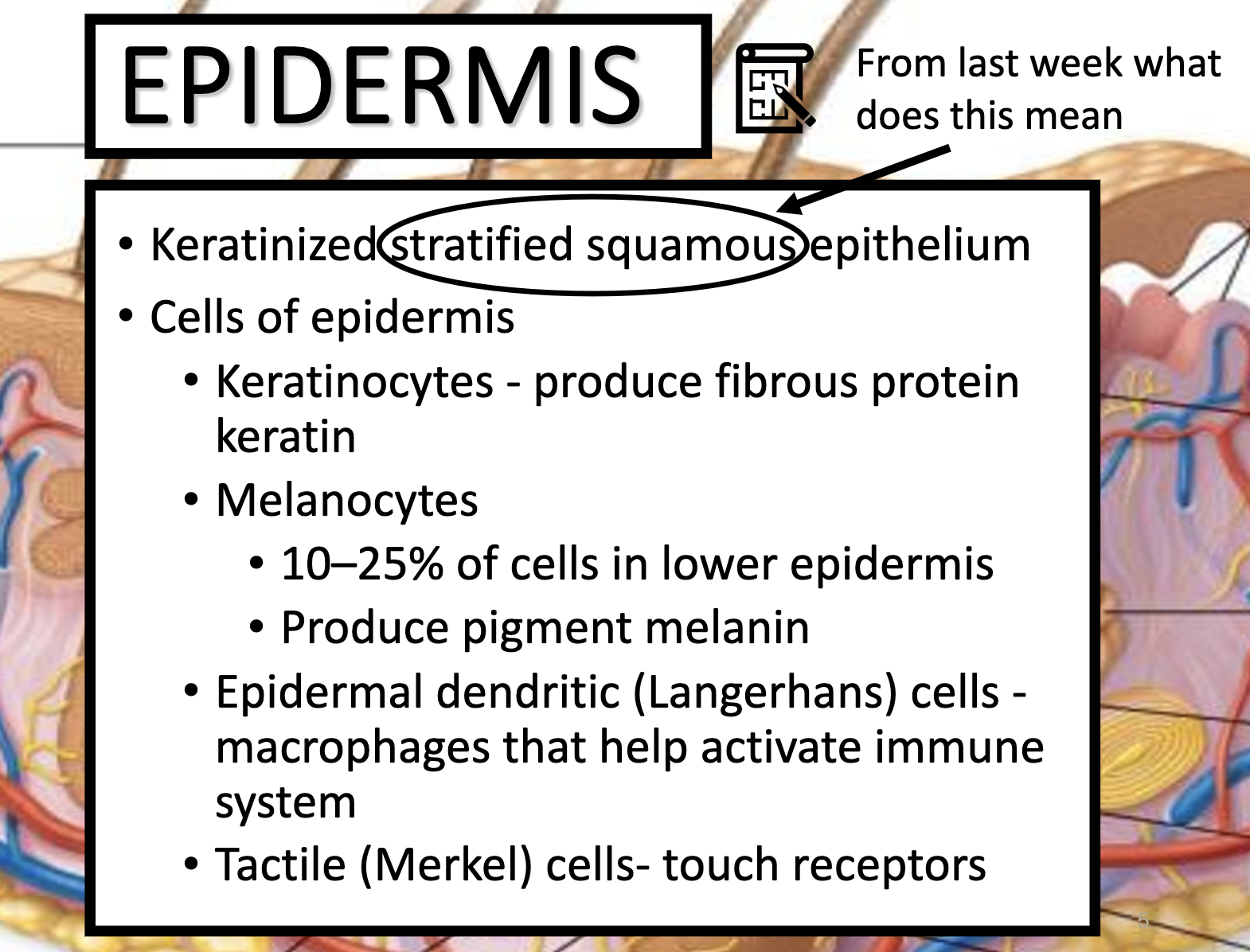
*Stratified squamous : flat, multi layered
*Epidermis
-Keratinocytes : produce fibrous protein (keratin)
-Melanocytes : produce pigment melanin
-Epidermal dendritic (Langerhans) cells : macrophages that help activate immune system
-Tactile (Merkel) cells : touch receptors
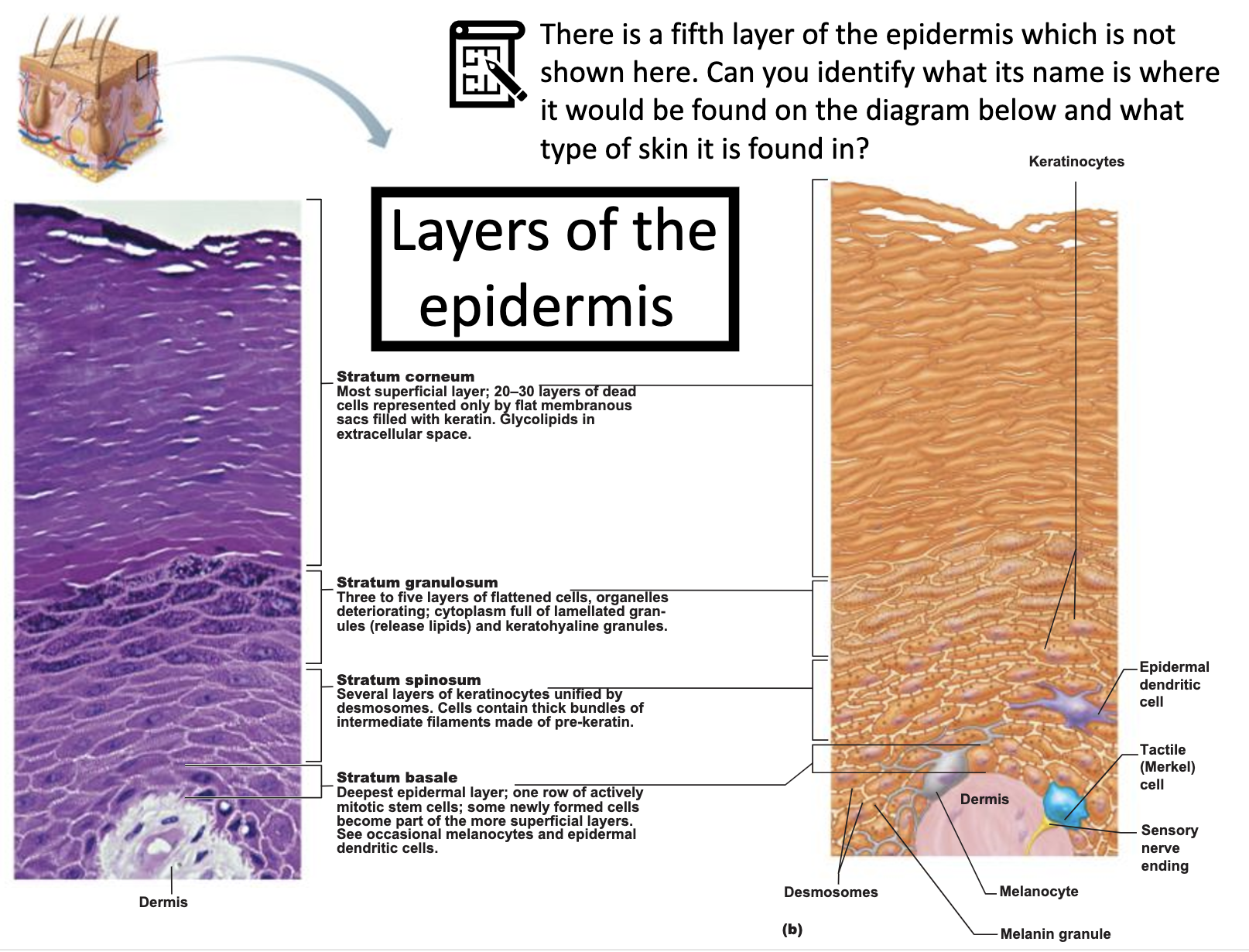
*There is a fifth layer of the epidermis which is not shown here. Can you identify what its name is where it would be found on the diagram below and what type of skin it is found in ?
stratum corneum : Most superficial layer, 20~30 layers of dead cells represented only by flat membranous sacs filled with keratin. glycolipids in extracellular space
stratum lucidum : It regulates the temperature and the amount of water released in the environment.
Stratum lucidum is a thin, clear layer of dead skin cells in the epidermis of the skin. It is composed of five layers of dead flattened keratinocytes.
stratum granulosum : Three to five layers of flattened cells, organells deterioatting, cytoplasm full of lamellated granules (release lipids) and keratohyaline granules
stratum spinosum : several layers of keratinocytes unified by desmosomes. cells contain thick bundles of intermediate filaments made of pre-keratin
stratum basale : deepest epidermal layer, one row of actively mitotic stem cells, some newly formed cells become part of the more superficial layers. See occasional melanocytes and epidermal dendritic cells
*Melanin is a substance in your body that produces hair, eye and skin pigmentation. The more melanin you produce, the darker your eyes, hair and skin will be.
*Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells that capture, process, and present antigens to lymphocytes to initiate and regulate the adaptive immune response.
(랑게르한스 세포(Langerhans cells, LC)는 피부 조직에 상주하는 대식세포이다)
*Merkel cells/ Tactile cells are very close to the nerve endings that receive the sensation of touch and may be involved in touch. The cells also contain substances that may act as hormones.
Dermis

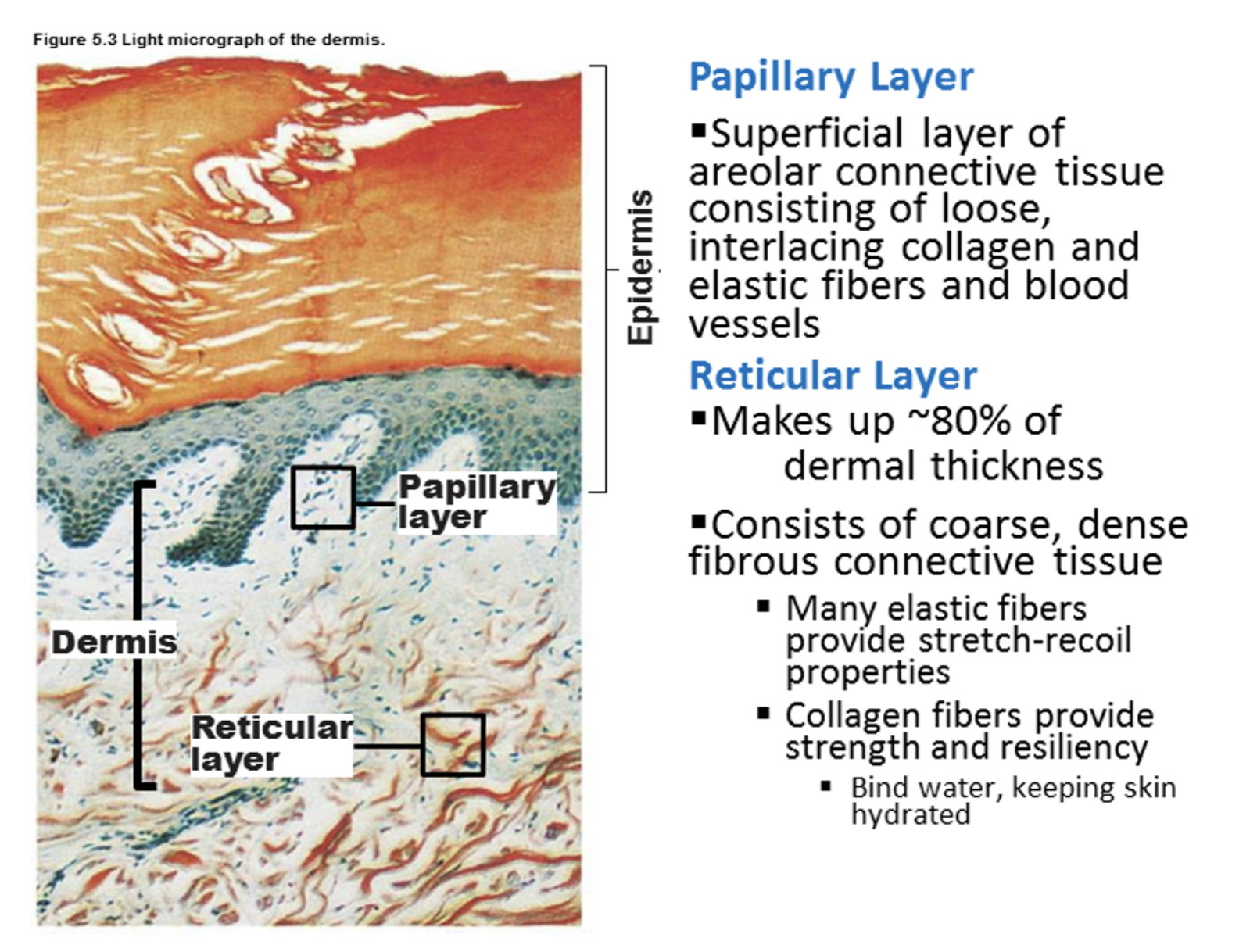
-Dermis -> Fibroblasts, macrophages, and occasionally mast cells and WBC
contains nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels, epidermal hair follicles, oil glands, and sweat glands
-papillary (areolar connective tissue consisting of loose interlacing collagen and elastic fibers and blood vessels)
The papillary layer of dermis is made up of areolar ct which is loose ct and it allows immune cells to wander through it.
-reticular (consists of coarse, dense irregular connective tissue)
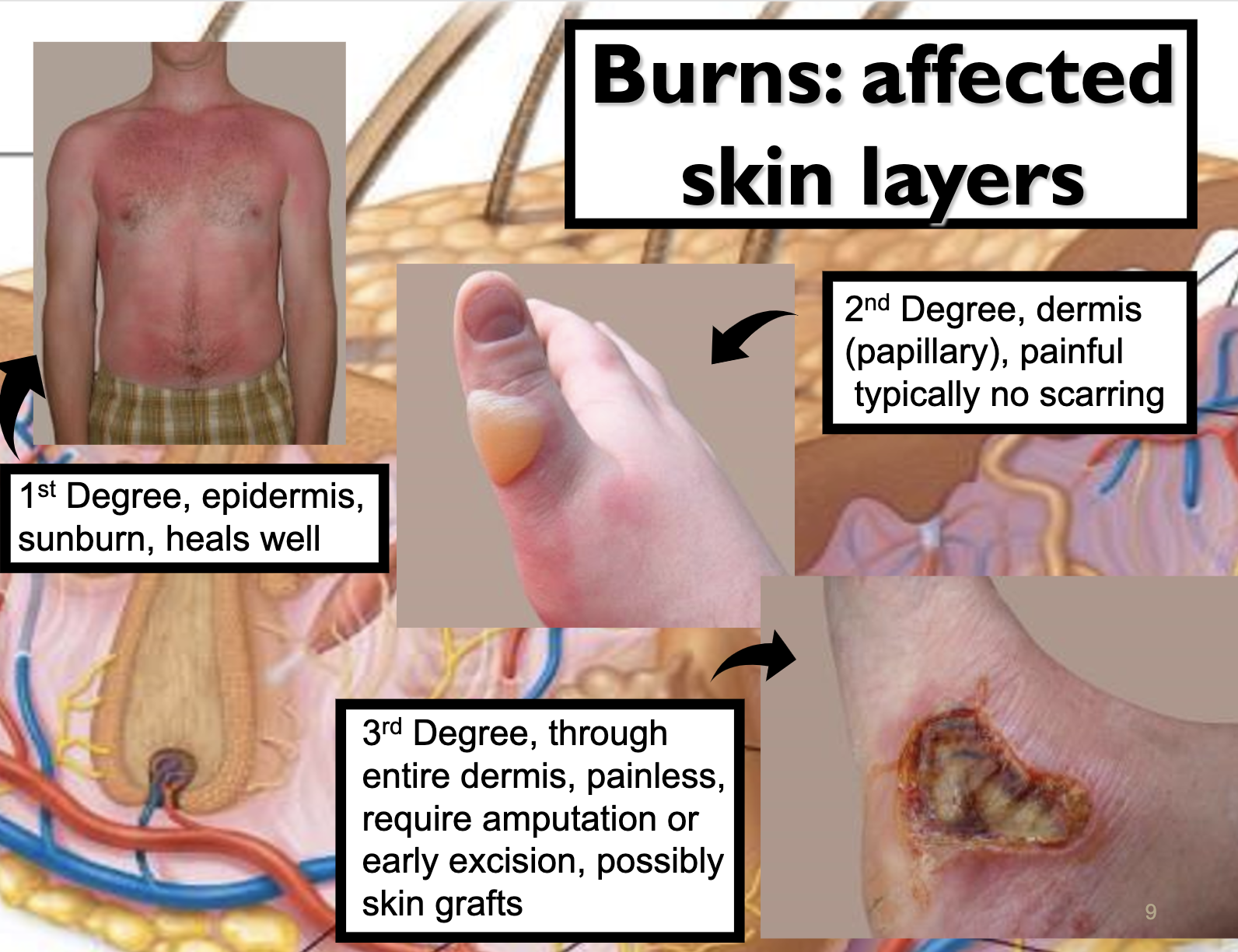

*amputation, excision 절단, 절제..
*skin graft 피부이식
*dermis is more stable than epidermis, tattoo ink is deposited in the dermis.
scar tissue forms around the ink preventing immune cells from ingesting ink.
Laser cause the ink to be broken down into tiny particles that are removed by the lymphatic system.
Appendages of the skin
1. Hair 2. Sweat glands 3.Sebaceous(oil) glands
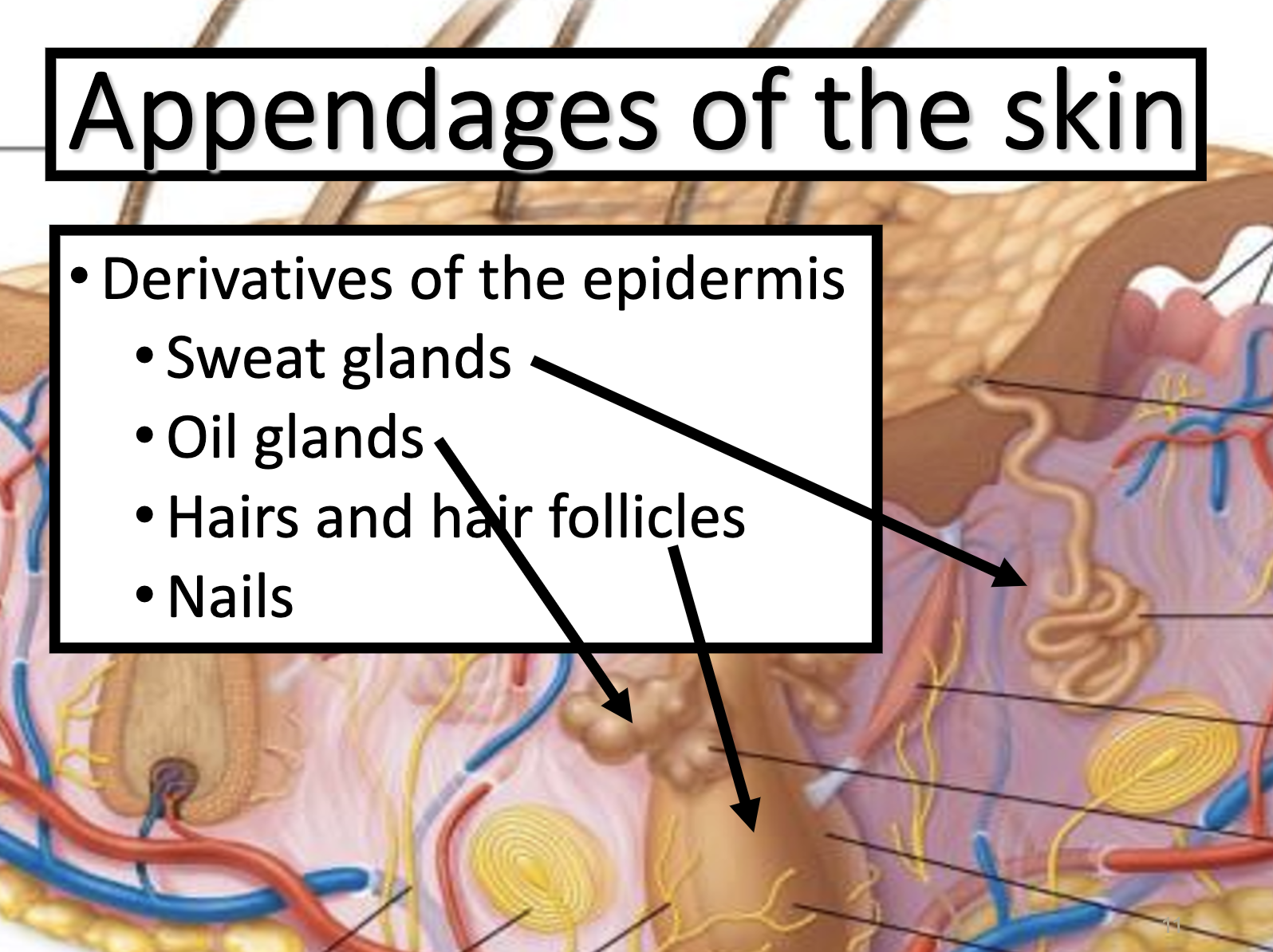
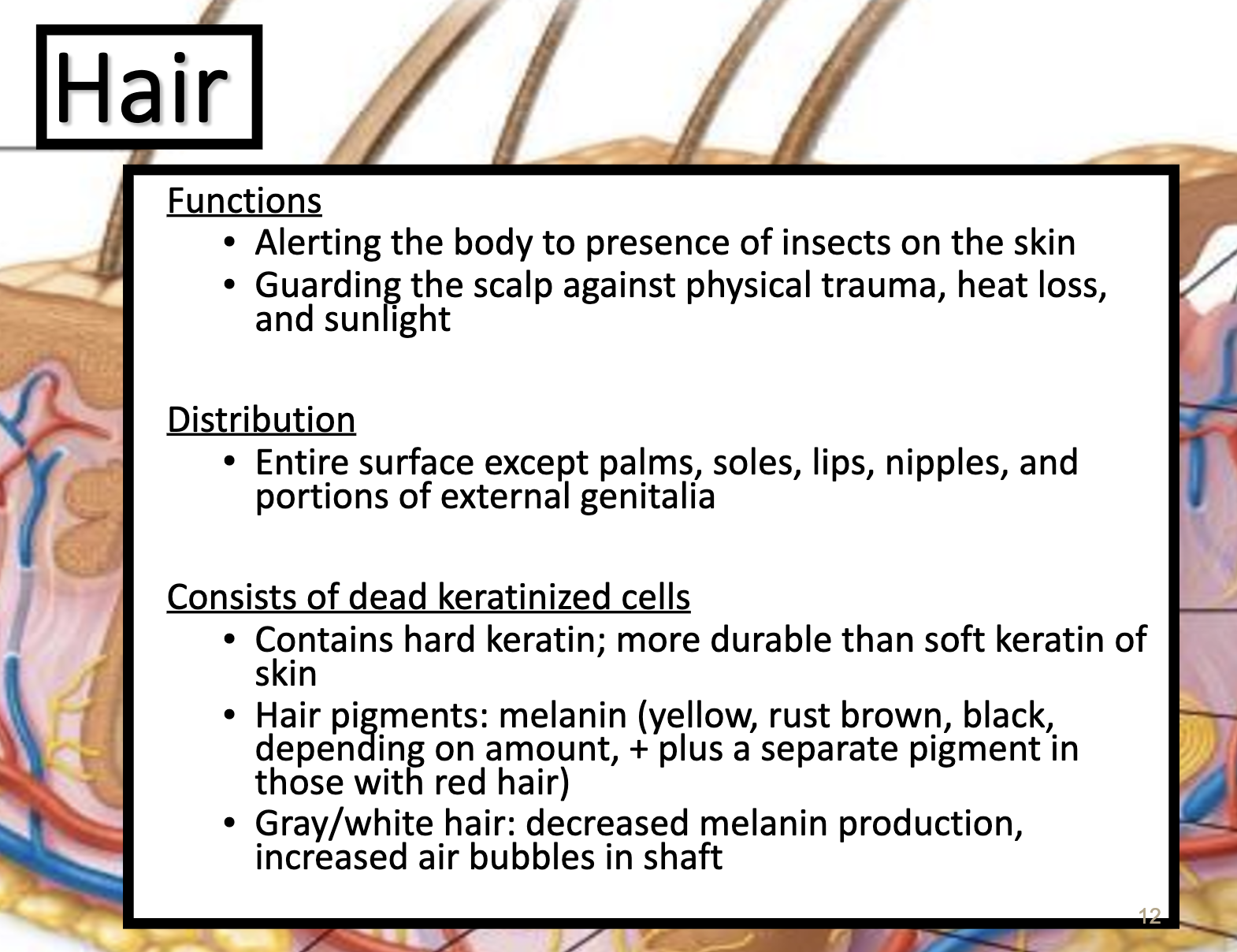


*sudoriferous 땀이나는 / sudoriferous gland 땀샘
*thermoregulation
is a mechanism by which mammals maintain body temperature with tightly controlled self-regulation independent of external temperatures.
As soon as your body's internal temperature starts rising, your hypothalamus (a small region in your brain) tells eccrine sweat glands distributed all over your body that it's time to start cooling you down by producing sweat.
1. Eccrine sweat glands (merocrine) -> sweat glands / pore
2. Apocrine sweat glands -> sebum : sweat + fatty substances and proteins / hair follicles
3. Specialised apocrine glands (cerumionous glands 귀지, mammary glands)
4. Sebaceous (oil) glands -> sebum / hair follicles
1,2 는 sweat glands, 위치에 따라 일분류
3,4 는 내용물이 특별한것, 오일
meocrine, holocrine 은 분비물을 분비하는 방식의 차이를 구분짓는 용어들
1,2은 meocrine
4는 holocrine
GLANDS 정리
Ecrrine is a sweat gland mainly responsible for releasing heat. They are connected to pores by duct. They secrete sweat which are mostly made up of water, salt, and antibodies.
Apocrine is also a sweat gland located in axillary and anogenital area. They secrete sebum , which contains fatty substances and proteins. They are connected to the hair follicles.
There are also specialised apocrine glands such as ceruminous glands and mammary glands.
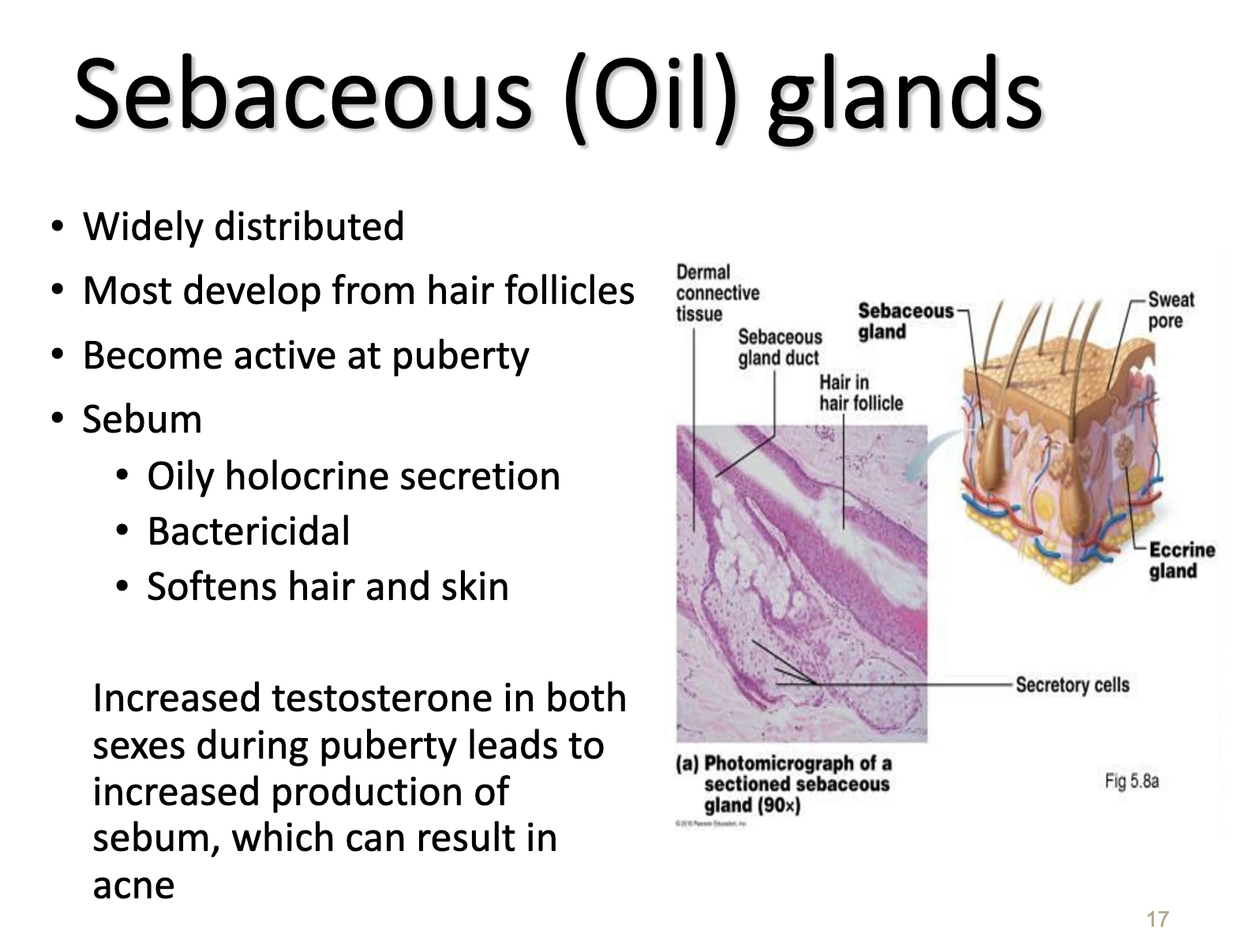
Sebaceous glands which are oil glands are mostly developed in the hair follicles. They become active during puberty. Increased testosterone makes them produce more sebum. They are holocrine which is cells burst when they secrete substances.
ALOPECIA, ANTIPERSPERANTS,DEODORANTS


*antiperspirant는 여름철에 땀이 나지 않도록 겨드랑이에 바르는 것을 말하고, deodorant는 겨드랑이 냄새를 없애기 위해 바르는 것을 말하는데
Antiperspirant : block the sweat gland to reduce the amound of sweating
Deodrant : kill the bacteria to prevent smells being created in the armpits
Self - paced quiz
mechanoreceptors
The four major types of tactile mechanoreceptors include: Merkel’s disks, Meissner’s corpuscles, Ruffini endings, and Pacinian corpuscles.
- Merkel’s disk are slow-adapting, unencapsulated nerve endings that respond to light touch; they are present in the upper layers of skin that has hair or is glabrous.
- Meissner’s corpuscles are rapidly-adapting, encapsulated neurons that responds to low-frequency vibrations and fine touch; they are located in the glabrous skin on fingertips and eyelids.
- Ruffini endings are slow adapting, encapsulated receptors that respond to skin stretch and are present in both the glabrous and hairy skin.
- Pacinian corpuscles are rapidly-adapting, deep receptors that respond to deep pressure and high-frequency vibration.
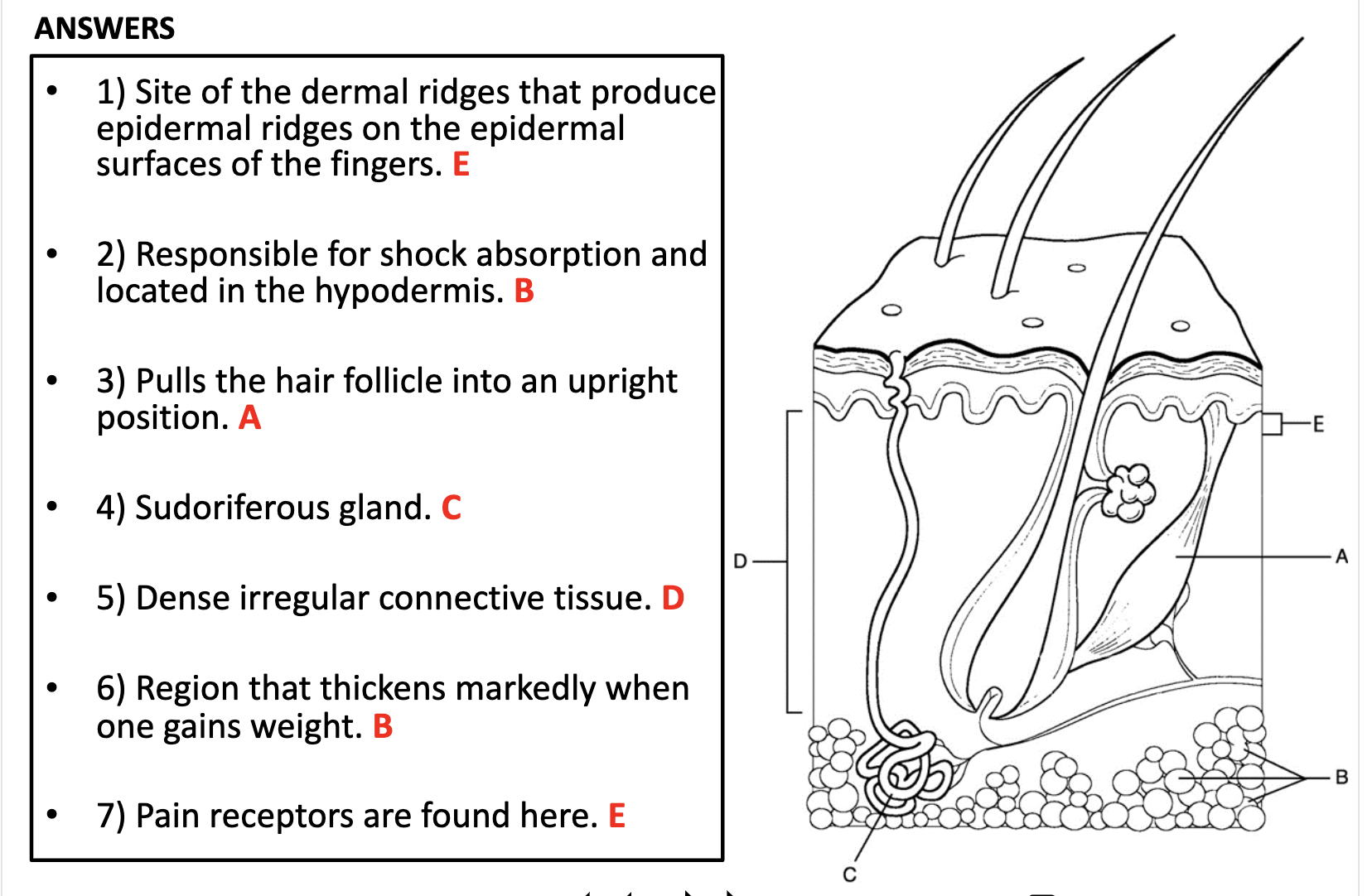







1. Papillary layer of dermis E
2. Adipose tissue absorb shock and they are located in the hypedermis B
3. arrector pilli muscle is A
4. Sudoriferous gland means sweat glands and they are connected to the pores with duct C
5. Reiticular layer of dermis is consist of irregular connective tissue D
6. B
7. Pain receptors are nerve endings and they are found in E (dermis bur close to the epidermis)
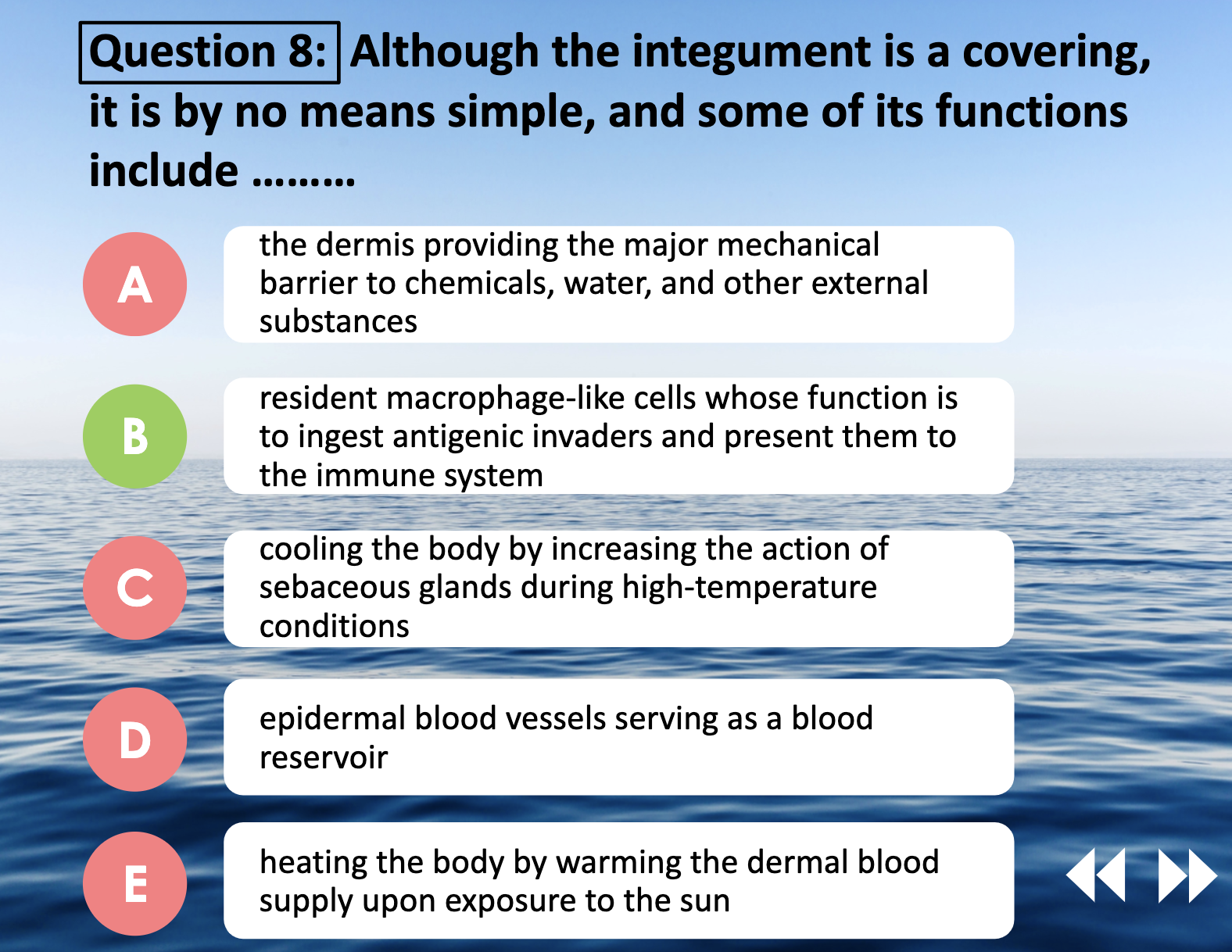
A. epidermis provide the major mechanical barrier
C. Cooling the body by increasing the secretion of sweat is done by eccrine sweat glands, not sebaceous oil glands.
D. Epidermis has no blood vessels.
E. When we exposed to the sun, dermal blood helps our body to cool down , not heating up.
Epidermal corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum,basale
Apocrine sweat glands secrete sebum and via hair follicles. They are mostly located in axillary and anogenital area, where in disadvantage with evaporating sweat efficiently to cool down.
Sweat glands - eccrine, apocrine
Specialised apocrine
Sebaceous oil glands (holocrine)
*Papillary and Reticular layer functions
Papillary layers are made of areolar loose connective tissue. It allows immune cells to move around and ingest antigenic invaders. There are sensation receptors such as Meissner's corpuscles (touch receptors) and free nerve endings (pain receptors). They also provide oxygen and nutrients to epidermis.
Reticular layers are consist of irregular dense connective tissue. Collagen fibers hold water for skin to be hydrated and provide skin strength and resiliency. Elastic fibers in reticular tissue enable skin to recoil
*Body reaction to heat
Dilated Blood stream in the dermis moves toward to the surface of the skin so that they can release more heat to outside. Sweat glands(eccrine) secrete some sweat to cool the body by evaporating them.
*Function of the skin
1. Protection- by chemical, physical, and biological barriers.
(Low pH secretions(acid mantle), Limited penetration by lipid-soluble substances(glycolipid and keratin), and dendritic cells(immune system, macrophages)
2. Sensation
3.Thermoreugulation
4.Blood reservoir
5. Metabolic functions -VitaminD precursor is synthesised with the cholesterol in epidermis by the sun. Vitamin D is vital for calcium metabolism.
6. Excretions - Through sweat glands and oil glands, skin excrete sweat and sebum including urea and other wastes.
Summary




*Compare sublayers of Dermis
Papillary layers include touch receptors (Meissner's corpuscles) and pain receptors (free nerve endings)
They feed and oxygenate the epidermis
They form the underlying foundation for the ridges of the hands and toes
Reticular layer has collagen fibers. collagen binds water to keep skin hydrated. They also provide strength and resiliency. Elastic fibers provide stretch-recoil properties.
ECCRINE, APOCRINE,SEBACEOUS GLAND COMPARE
Eccrine and apocrine are basically the sweat glands however sebaceous glands are oil gland.
eccrine sweat glands secrete sweat which is mainly made up of water and salt. They are responsible for releasing heat by evaporating sweat. Eccrine glands are connected to pores through ducts. Apocrine sweat glands are located in axillary and anogenital area where are at a disvantage in dissipitating heat. They secrete sebum which includes fatty acids and protein also. They are released via hair follicles.
Sebaceous glands are oil glands. They are activated in the puberty. They secretes sebum in hair follicles. They lubricate the hair skin.
SKIN FUNCTIONS
Skin has five major functions. First, they protect our body with physical, chemical, and biological ways.
Second, they are responsible to thermoreuglation with sweat glands. Third, sense receptors in skin help us to sense vibration, pain, pressure and so on. Fourth, with the sunlight, skin produces Vitamin D precursor with the cholesterol in epidermis that is, they do the metabolic function. Lastly apocrine, specialised apocrine and sebaceous glands help us to execrete nitrogen containing waste.
'Griffith college Tri3 2022 > 1014MSC (CTR)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| LAB EXAM - ppt1,2 (0) | 2022.11.23 |
|---|---|
| WEEK5 - module2. Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport (0) | 2022.11.17 |
| WEEK3 - module2. From cells to tissues (0) | 2022.11.06 |
| WEEK2 - module 1. Introduction to Microbiology (0) | 2022.10.29 |
| WEEK1- module 1. Cell structure and function (0) | 2022.10.21 |



